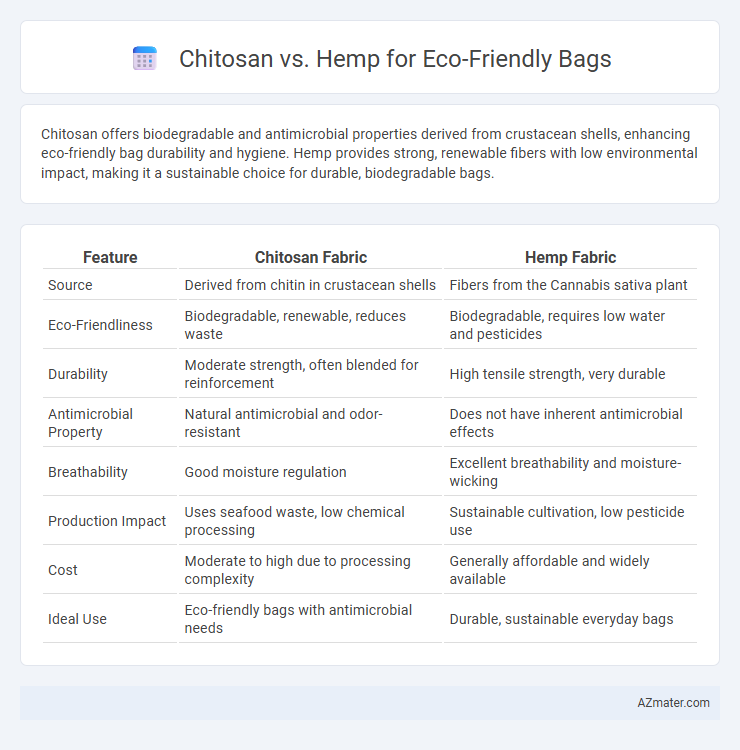
Chitosan offers biodegradable and antimicrobial properties derived from crustacean shells, enhancing eco-friendly bag durability and hygiene. Hemp provides strong, renewable fibers with low environmental impact, making it a sustainable choice for durable, biodegradable bags.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chitosan Fabric | Hemp Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from chitin in crustacean shells | Fibers from the Cannabis sativa plant |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable, reduces waste | Biodegradable, requires low water and pesticides |
| Durability | Moderate strength, often blended for reinforcement | High tensile strength, very durable |
| Antimicrobial Property | Natural antimicrobial and odor-resistant | Does not have inherent antimicrobial effects |
| Breathability | Good moisture regulation | Excellent breathability and moisture-wicking |
| Production Impact | Uses seafood waste, low chemical processing | Sustainable cultivation, low pesticide use |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to processing complexity | Generally affordable and widely available |
| Ideal Use | Eco-friendly bags with antimicrobial needs | Durable, sustainable everyday bags |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Bag Materials
Chitosan and hemp represent two sustainable materials gaining traction in eco-friendly bags due to their biodegradable and renewable properties. Chitosan, derived from chitin found in crustacean shells, offers antimicrobial benefits and strong film-forming capabilities, making it a valuable alternative to synthetic fibers. Hemp stands out for its durability, fast growth cycle, and minimal need for pesticides, positioning it as an environmentally responsible option in sustainable bag production.
What is Chitosan?
Chitosan is a natural biopolymer derived from chitin, primarily found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans like shrimp and crabs, known for its biodegradability and antimicrobial properties. Unlike hemp, which is a plant-based fiber, chitosan offers unique advantages in eco-friendly bag production due to its ability to enhance durability and moisture resistance. Its sustainable extraction process and compatibility with various biodegradable materials make chitosan a valuable alternative in developing innovative, eco-friendly packaging solutions.
What is Hemp?
Hemp is a sustainable plant-based fiber known for its durability, biodegradability, and minimal environmental impact, making it ideal for eco-friendly bag production. Cultivated with low water requirements and no need for pesticides, hemp reduces soil depletion and supports regenerative agriculture. Its strong, lightweight fibers provide excellent longevity and resistance, offering a practical alternative to synthetic materials in green packaging.
Environmental Impact: Chitosan vs Hemp
Hemp bags offer a lower environmental footprint due to their rapid growth, minimal water requirements, and ability to regenerate soil quality, making them highly sustainable. Chitosan, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, is biodegradable and utilizes seafood industry waste but involves energy-intensive extraction processes that can impact its overall eco-friendliness. Comparing the two, hemp's renewable cultivation and carbon sequestration advantages generally surpass chitosan's benefits related to waste valorization, positioning hemp as the more environmentally favorable material for eco-friendly bags.
Biodegradability and Sustainability
Chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, offers excellent biodegradability and antimicrobial properties that enhance the longevity and eco-friendliness of bags. Hemp fibers provide high durability with rapid biodegradation rates, requiring less water and pesticides during cultivation, which significantly reduces environmental impact. Both materials support sustainable manufacturing, but hemp's renewable growth cycle and chitosan's ability to utilize waste byproducts make them top choices in eco-friendly bag production.
Production Process and Resource Use
Chitosan, derived from crustacean shells through deacetylation, offers a biodegradable alternative using seafood industry waste, minimizing resource input and chemical use during extraction. Hemp cultivation requires minimal pesticides and water, thriving on low-nutrient soil, which reduces environmental impact while producing durable fibers through mechanical or retting processes. Both materials prioritize sustainability, with chitosan leveraging waste valorization and hemp emphasizing regenerative agriculture and efficient fiber yield.
Durability and Practicality
Chitosan-based bags offer excellent antimicrobial properties and water resistance, enhancing durability for everyday use. Hemp fibers provide superior tensile strength and breathability, making bags highly practical for carrying heavy loads and long-term use. Both materials contribute to sustainable fashion, with hemp excelling in strength and chitosan delivering enhanced biodegradability and functional benefits.
Cost Comparison
Chitosan-based bags generally have a higher production cost due to complex extraction processes from crustacean shells and limited large-scale manufacturing infrastructure. Hemp bags offer a more cost-effective alternative as hemp cultivation is widespread and processing hemp fibers is well-established, leading to lower material and production expenses. While chitosan provides antimicrobial properties, hemp's affordability and scalability make it a preferred choice for budget-conscious, eco-friendly bag production.
Consumer Trends and Market Demand
Consumer trends indicate a rising preference for eco-friendly bags made from sustainable materials, with chitosan and hemp emerging as prominent options due to their biodegradability and minimal environmental footprint. Market demand favors hemp for its durability, natural resistance to pests, and ability to be cultivated with low water usage, while chitosan attracts interest for its antimicrobial properties and biodegradability derived from crustacean shells. The increasing consumer awareness of environmental impact drives growth in both materials, with hemp dominating in volume and chitosan gaining traction in niche, high-performance eco-friendly bag segments.
Future Outlook: Chitosan vs Hemp in Eco-Bags
Chitosan and hemp both show promising potential for eco-friendly bag production, with chitosan offering biodegradable antimicrobial properties ideal for sustainable packaging innovations. Hemp's durability, rapid growth cycle, and carbon-negative footprint position it as a leading natural fiber for large-scale, eco-conscious bag manufacturing. Future advancements in chitosan extraction and hemp fiber processing are expected to enhance performance, cost-efficiency, and market adoption in sustainable fashion and packaging industries.
Infographic: Chitosan vs Hemp for Eco-Friendly Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com