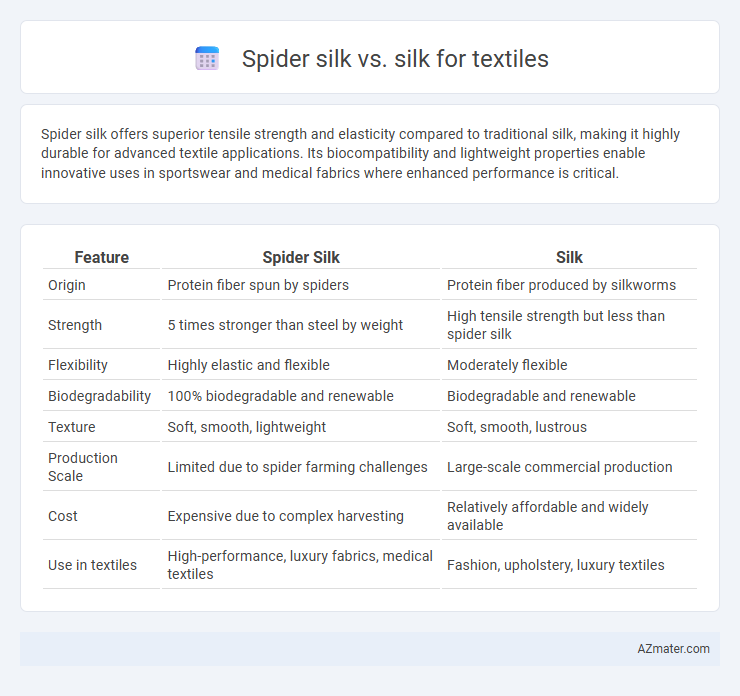
Spider silk offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to traditional silk, making it highly durable for advanced textile applications. Its biocompatibility and lightweight properties enable innovative uses in sportswear and medical fabrics where enhanced performance is critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spider Silk | Silk |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Protein fiber spun by spiders | Protein fiber produced by silkworms |
| Strength | 5 times stronger than steel by weight | High tensile strength but less than spider silk |
| Flexibility | Highly elastic and flexible | Moderately flexible |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable and renewable | Biodegradable and renewable |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, lightweight | Soft, smooth, lustrous |
| Production Scale | Limited due to spider farming challenges | Large-scale commercial production |
| Cost | Expensive due to complex harvesting | Relatively affordable and widely available |
| Use in textiles | High-performance, luxury fabrics, medical textiles | Fashion, upholstery, luxury textiles |
Introduction to Spider Silk and Traditional Silk
Spider silk, renowned for its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and elasticity, is a protein fiber produced by spiders and gaining interest for sustainable textile development. Traditional silk, derived from the cocoons of the Bombyx mori silkworm, is prized for its smooth texture and luster but involves intensive farming practices. Advances in bioengineering aim to replicate spider silk's superior mechanical properties while maintaining the softness characteristic of traditional silk fibers.
Origins: How Spider Silk and Silk Are Produced
Spider silk originates from the protein-based fibers secreted by spiders through specialized spinnerets, while traditional silk is produced by silkworms that spin cocoons composed of fibroin proteins. Spider silk production is a natural process involving multiple silk glands with each producing different types of silk for specific uses like web-building or wrapping prey, whereas silkworm silk production involves harvesting and unwinding cocoons after the larvae spin them. The complexity and diversity of spider silk proteins contribute to its exceptional mechanical properties, whereas silkworm silk's uniform fibroin structure is prized for textile softness and luster.
Physical Properties: Strength, Elasticity, and Durability
Spider silk exhibits exceptional tensile strength, often surpassing that of traditional silk, making it one of the strongest natural fibers known. Its remarkable elasticity allows it to stretch up to five times its original length without breaking, providing superior flexibility compared to conventional silk. Durability in spider silk is enhanced by its resistance to environmental factors like moisture and UV radiation, which contributes to longer-lasting textile applications relative to standard silk fibers.
Biochemical Composition of Spider Silk vs Silk
Spider silk contains fibroin proteins rich in alanine and glycine, forming b-sheet crystals that provide exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, while silkworm silk primarily consists of fibroin with a higher content of glycine and serine, resulting in a more rigid fiber structure. The presence of unique spidroins in spider silk contributes to its remarkable toughness and lightweight properties compared to the more uniform fibroin chains in silkworm silk. These biochemical differences define their distinct mechanical properties and potential applications in advanced textiles and biotechnological materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk exhibits a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional silk, as it requires no large-scale farming or chemical-intensive processes, reducing land use and pollution. Its biodegradability and renewable production from engineered microbes offer a sustainable alternative to conventional silk, which relies heavily on mulberry cultivation and sericulture with intensive water consumption. The potential for spider silk to be produced without harming spiders or the environment positions it as a highly sustainable textile innovation.
Applications in Modern Textile Industry
Spider silk outperforms traditional silk in strength and elasticity, making it ideal for high-performance textiles in sportswear, medical sutures, and ballistic protection. Its biocompatibility and biodegradability facilitate sustainable fashion innovations and advanced biomedical applications. Synthetic spider silk production is scaling, enabling broader integration into eco-friendly and functional textile markets.
Cost and Scalability of Production
Spider silk offers exceptional strength and elasticity but remains costly and challenging to scale due to limited spider farming and complex bioengineering processes. Traditional silk production from silkworms benefits from established large-scale sericulture infrastructure, making it more affordable and widely available for textile manufacturing. However, ongoing advances in synthetic spider silk aim to reduce costs and improve scalability, potentially transforming the textile industry.
Ethical Considerations in Silk Harvesting
Spider silk offers a sustainable alternative to traditional silk by eliminating the need to kill silkworms, addressing significant animal welfare concerns in textile production. Conventional silk harvesting involves boiling silkworm cocoons, resulting in ethical issues related to insect mortality and environmental impact. Innovations in spider silk biosynthesis provide cruelty-free fibers with strong mechanical properties, supporting ethical and eco-friendly textile manufacturing.
Performance in Fashion and Technical Textiles
Spider silk exhibits superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to conventional silk, making it highly desirable for both fashion and technical textiles where durability and flexibility are crucial. Its biocompatibility and lightweight properties enhance comfort and functionality in wearable technology and advanced performance apparel. Unlike traditional silk, spider silk's natural resilience to moisture and environmental stress ensures extended lifecycle and improved performance in harsh conditions.
Future Innovations in Silk-Based Materials
Spider silk exhibits extraordinary tensile strength and elasticity, outperforming traditional silk from silkworms in durability and biocompatibility, making it a promising candidate for advanced textile applications. Future innovations focus on bioengineering synthetic spider silk proteins, enabling scalable production with enhanced mechanical properties and eco-friendly processes. Emerging technologies integrate spider silk into smart textiles, offering self-healing fabrics, moisture-wicking capabilities, and lightweight protective gear for various industries.
Infographic: Spider silk vs Silk for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com