Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to aramid fiber, making it ideal for high-performance reinforcement applications. Aramid fiber excels in impact resistance and flexibility, providing enhanced durability in dynamic loading environments.
Table of Comparison
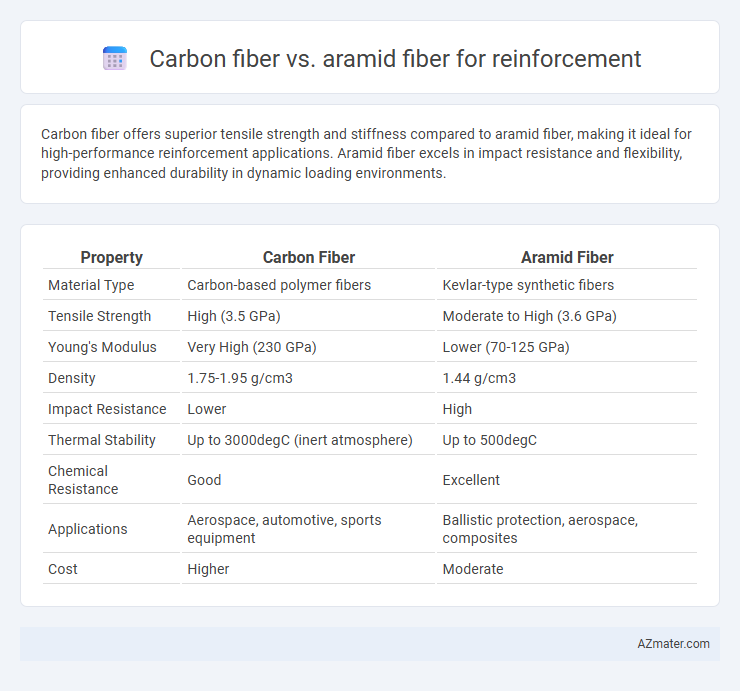
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based polymer fibers | Kevlar-type synthetic fibers |
| Tensile Strength | High (3.5 GPa) | Moderate to High (3.6 GPa) |
| Young's Modulus | Very High (230 GPa) | Lower (70-125 GPa) |
| Density | 1.75-1.95 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Lower | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 3000degC (inert atmosphere) | Up to 500degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, sports equipment | Ballistic protection, aerospace, composites |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforcement Materials
Carbon fiber and aramid fiber are prominent choices for reinforcement due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and durability. Carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and tensile strength, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace and automotive industries. Aramid fiber provides excellent impact resistance and flexibility, commonly used in ballistic protection and sports equipment, highlighting their complementary properties in fiber reinforcement.
Overview of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a lightweight, high-strength material known for its exceptional stiffness and tensile strength, making it ideal for reinforcement in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. Its low density and resistance to corrosion provide durability and performance under extreme environmental conditions. Carbon fiber composites offer superior fatigue resistance compared to aramid fiber, enabling longer service life in structural applications.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional toughness and resistance to impact and abrasion, serves as a reliable reinforcement material in composite applications. Its high tensile strength and superior energy absorption make it ideal for protective gear, aerospace components, and ballistic reinforcement. Compared to carbon fiber, aramid fiber offers enhanced flexibility and better performance under dynamic loading conditions, though it typically has lower stiffness and compressive strength.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carbon fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to aramid fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring high rigidity and load-bearing capacity. Aramid fiber offers excellent impact resistance and toughness, with a lower density that contributes to lightweight reinforcement while maintaining good elongation before failure. Both fibers perform well in mechanical reinforcement, but carbon fiber's higher modulus contrasts with aramid's greater energy absorption and flexibility under stress.
Weight and Density Considerations
Carbon fiber offers a superior strength-to-weight ratio with a density around 1.6 g/cm3, making it ideal for lightweight reinforcement applications requiring high stiffness and tensile strength. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, has a lower density of approximately 1.44 g/cm3 but provides excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it preferable for applications where energy absorption and toughness are critical. Weight-sensitive designs favor carbon fiber for its lighter, stiffer properties, while aramid fiber is selected for balancing moderate weight with enhanced durability and resistance to fatigue.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Carbon fiber offers superior durability with high tensile strength and excellent stiffness, making it ideal for long-term structural reinforcement where rigidity is critical. Aramid fiber excels in environmental resistance, providing exceptional impact resistance and maintaining performance under moisture, heat, and chemical exposure. Both fibers enhance composite materials, but carbon fiber's resistance to fatigue and corrosion contrasts with aramid's ability to resist abrasion and UV degradation.
Cost and Availability
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness but comes at a higher cost and limited availability compared to aramid fiber. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, is more affordable and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale reinforcement projects. Budget-conscious applications often favor aramid fiber despite its lower modulus and durability relative to carbon fiber.
Applications in Various Industries
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries where lightweight and high performance are critical. Aramid fiber, known for its excellent impact resistance and toughness, is widely used in military armor, ballistic protection, and aerospace components requiring energy absorption and durability. Both fibers enhance composite materials, with carbon fiber emphasizing structural rigidity and aramid fiber prioritizing safety and flexibility across diverse industrial applications.
Performance in Composites
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance composite reinforcements requiring lightweight and rigid materials. Aramid fiber provides excellent impact resistance and toughness, enhancing composite durability against abrasion and fatigue. In terms of performance, carbon fiber excels in structural rigidity while aramid fiber improves energy absorption and damage tolerance in composite applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Key Factors
Selecting the right fiber for reinforcement involves evaluating tensile strength, weight, and impact resistance, where carbon fiber excels in high stiffness and lightweight applications, while aramid fiber offers superior toughness and energy absorption. Key factors include environmental exposure, with aramid fiber showing better resistance to abrasion and impact, whereas carbon fiber is more sensitive to fatigue and moisture. Cost and application-specific requirements also influence the decision, making carbon fiber ideal for aerospace and automotive industries, and aramid fiber preferred in ballistic protection and sports equipment.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Aramid fiber for Reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com