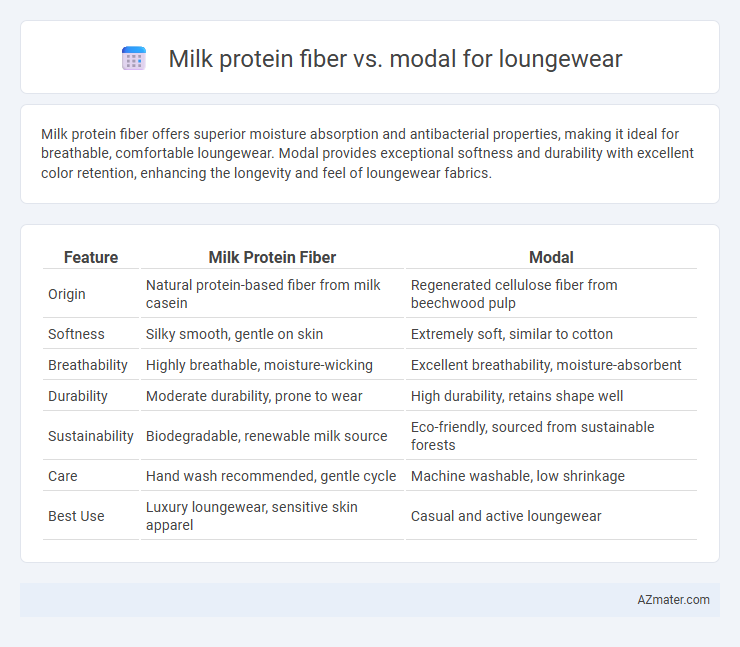
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture absorption and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for breathable, comfortable loungewear. Modal provides exceptional softness and durability with excellent color retention, enhancing the longevity and feel of loungewear fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Modal |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural protein-based fiber from milk casein | Regenerated cellulose fiber from beechwood pulp |
| Softness | Silky smooth, gentle on skin | Extremely soft, similar to cotton |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Excellent breathability, moisture-absorbent |
| Durability | Moderate durability, prone to wear | High durability, retains shape well |
| Sustainability | Biodegradable, renewable milk source | Eco-friendly, sourced from sustainable forests |
| Care | Hand wash recommended, gentle cycle | Machine washable, low shrinkage |
| Best Use | Luxury loungewear, sensitive skin apparel | Casual and active loungewear |
Introduction to Milk Protein Fiber and Modal
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein in milk, offers unique moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties ideal for comfortable loungewear. Modal, a semi-synthetic fiber made from beech tree pulp, is known for its exceptional softness, breathability, and durability, making it a popular choice in casual and loungewear fabrics. Both fibers enhance comfort but differ in sustainability and texture, with milk protein fiber emphasizing natural bioactive benefits and modal focusing on eco-friendly smoothness.
Historical Development of Loungewear Fabrics
Milk protein fiber emerged in the early 21st century as an innovative, sustainable textile derived from casein in milk, offering softness and moisture-wicking properties ideal for modern loungewear. Modal, developed in the mid-20th century as a type of rayon from beech tree cellulose, gained popularity for its durability, smooth texture, and breathability, becoming a staple in comfortable, casual apparel. The historical development of loungewear fabrics reflects a shift from traditional cotton and wool to advanced fibers like milk protein and modal, emphasizing comfort, sustainability, and performance.
Production Process: Milk Protein Fiber vs Modal
Milk protein fiber is produced by extracting casein from milk, which is then processed into a biodegradable fiber through a non-toxic spinning method, making it eco-friendly and sustainable. Modal is derived from beech tree pulp, utilizing a chemical-intensive process called viscose spinning that involves solvents like sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide, which can have environmental impacts if not managed properly. While milk protein fiber emphasizes renewable resources from dairy byproducts with lower chemical use, Modal relies on wood-based cellulose and chemical treatments that require stricter environmental controls during production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Milk protein fiber is a biodegradable, renewable material derived from milk casein, requiring less water and energy during production compared to Modal, which is made from beech tree pulp through a chemical-intensive process. Modal, despite being sourced from sustainable forestry, involves high water consumption and chemical treatments that can impact ecosystems if not properly managed. The biodegradability and lower resource footprint of milk protein fiber often make it a more environmentally friendly choice for sustainable loungewear.
Comfort and Softness Comparison
Milk protein fiber offers exceptional softness and moisture-wicking properties, making it highly breathable and gentle on the skin, ideal for loungewear comfort. Modal, derived from beech tree pulp, provides a silky smooth texture with excellent drape and durability, maintaining softness even after multiple washes. Both fibers excel in comfort, but milk protein fiber stands out for its enhanced skin hydration and anti-bacterial traits, while modal is prized for resilience and vibrant color retention.
Moisture Wicking and Breathability
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties by drawing sweat away from the skin, keeping loungewear dry and comfortable during extended wear. Modal, derived from beechwood, excels in breathability with its fine, soft fibers that allow air to circulate freely, preventing overheating. Both fibers enhance loungewear comfort, but milk protein fiber is preferred for active moisture management, while Modal prioritizes lightweight breathability.
Durability and Longevity in Loungewear
Milk protein fiber offers enhanced durability due to its strong molecular structure, providing long-lasting wear and resistance to pilling in loungewear. Modal, derived from beechwood, is known for its softness but tends to have slightly less tensile strength, which may result in faster fabric wear over time. Choosing milk protein fiber loungewear ensures greater longevity and maintained fabric integrity through multiple washes and extended use.
Skin Sensitivity and Hypoallergenic Properties
Milk protein fiber offers superior hypoallergenic properties due to its natural antibacterial and moisture-wicking abilities, making it ideal for sensitive skin often affected by common irritants. Modal, derived from beech tree pulp, is known for its smooth texture and breathability but may cause mild irritation in extremely sensitive individuals due to its chemical processing. For loungewear focusing on skin sensitivity, milk protein fiber provides a gentler, more skin-friendly option that reduces the risk of allergic reactions and enhances overall comfort.
Style, Appearance, and Dye Affinity
Milk protein fiber offers a smooth, silky texture with a natural sheen that enhances the style and luxurious appearance of loungewear, while modal boasts an exceptionally soft, drapey fabric with a matte finish that lends a casual yet refined look. In terms of dye affinity, modal excels due to its high moisture absorption, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting colors and excellent color retention after repeated washing. Milk protein fibers provide decent dye receptivity but typically yield more muted tones, making modal a superior choice for richly colored loungewear collections.
Price Point and Market Availability
Milk protein fiber offers a sustainable alternative to traditional fabrics with moderate price points typically ranging from $15 to $30 per yard, making it accessible for mid-range loungewear brands. Modal, derived from beech tree pulp, is generally more affordable, priced around $8 to $20 per yard, and benefits from wide market availability due to established supply chains. Both fibers provide softness and breathability ideal for loungewear, but Modal's lower cost and greater availability often make it the preferred choice for mass-market production.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Modal for Loungewear
 azmater.com
azmater.com