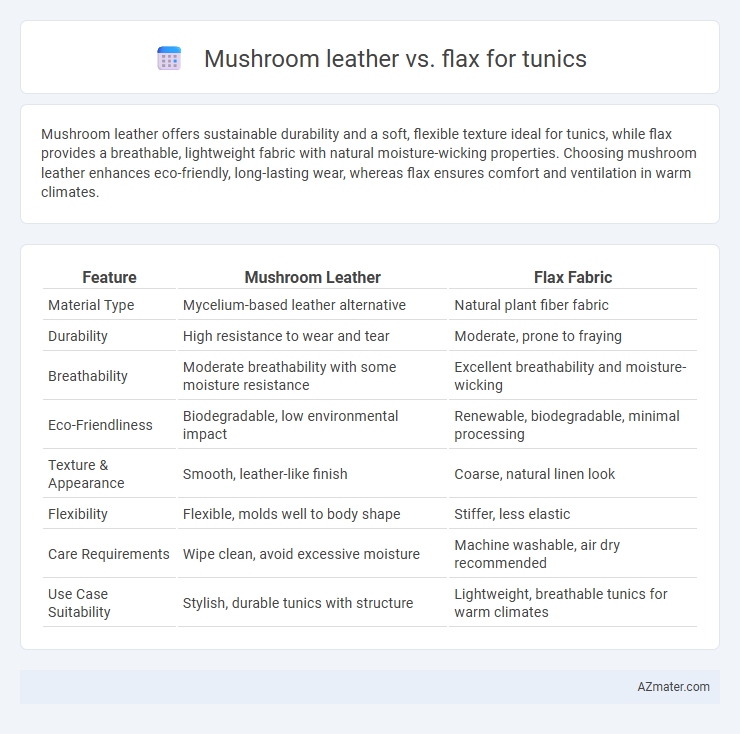
Mushroom leather offers sustainable durability and a soft, flexible texture ideal for tunics, while flax provides a breathable, lightweight fabric with natural moisture-wicking properties. Choosing mushroom leather enhances eco-friendly, long-lasting wear, whereas flax ensures comfort and ventilation in warm climates.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mushroom Leather | Flax Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Mycelium-based leather alternative | Natural plant fiber fabric |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Moderate, prone to fraying |
| Breathability | Moderate breathability with some moisture resistance | Excellent breathability and moisture-wicking |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, low environmental impact | Renewable, biodegradable, minimal processing |
| Texture & Appearance | Smooth, leather-like finish | Coarse, natural linen look |
| Flexibility | Flexible, molds well to body shape | Stiffer, less elastic |
| Care Requirements | Wipe clean, avoid excessive moisture | Machine washable, air dry recommended |
| Use Case Suitability | Stylish, durable tunics with structure | Lightweight, breathable tunics for warm climates |
Introduction to Sustainable Textiles: Mushroom Leather and Flax
Mushroom leather, derived from mycelium, offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to traditional animal leather, making it an innovative choice for sustainable tunics. Flax, the natural fiber used to produce linen, provides breathability, durability, and low environmental impact due to its minimal water and pesticide requirements. Both materials exemplify eco-friendly textiles that reduce reliance on synthetic fabrics and promote circular fashion in tunic production.
Material Origins: How Mushroom Leather and Flax are Produced
Mushroom leather is derived from the mycelium of fungi, cultivated through a controlled fermentation process that transforms organic substrates into a durable, leather-like material. Flax, on the other hand, originates from the fibers of the flax plant's stalks, which are harvested, retted, and processed into linen fabric used for tunics. While mushroom leather production emphasizes sustainable fungal growth with minimal water and chemical use, flax relies on agricultural practices and mechanical processing for fiber extraction.
Environmental Impact: Comparing Sustainability Metrics
Mushroom leather, derived from mycelium, offers a biodegradable alternative with low water usage and minimal chemical input, significantly reducing environmental pollution compared to traditional leather. Flax fabric, sourced from flax plants, boasts a low carbon footprint due to its ability to grow with limited pesticides and fast renewability, enhancing soil health through crop rotation. Both materials promote sustainability in tunics by minimizing resource consumption, but mushroom leather's rapid biodegradability and lower water requirement provide a distinct ecological advantage over flax.
Durability and Longevity: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Mushroom leather, made from mycelium, offers enhanced durability and water resistance compared to flax fabric, making it more suitable for prolonged wear in tunics. Flax, derived from flax fibers, is breathable and biodegradable but tends to degrade faster with frequent use and exposure to moisture. The longevity of mushroom leather outperforms flax due to its resilient structure and resistance to environmental stressors, offering a more durable option for tunics.
Comfort and Breathability in Tunics
Mushroom leather offers a soft, supple texture that molds comfortably to the body, providing excellent breathability through its natural fungal fibers, which helps regulate temperature and reduce moisture buildup in tunics. Flax fabric, derived from flax fibers, is lightweight and highly breathable, allowing for efficient air circulation that keeps the skin cool and dry during wear. Both materials enhance comfort in tunics, but mushroom leather combines durability with moisture-wicking properties, while flax excels in lightweight breathability and natural softness.
Aesthetic Qualities: Texture, Color, and Style Potential
Mushroom leather offers a smooth, supple texture with natural variations that create a rich, organic look, ideal for contemporary or avant-garde tunics. Flax fabric presents a matte, slightly coarse texture with earthy tones ranging from beige to green, lending a rustic, timeless aesthetic suited for casual or bohemian styles. Both materials provide unique color palettes and tactile experiences, allowing designers to explore diverse style potentials from sleek modernity to natural elegance.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Scenarios
Mushroom leather, derived from mycelium, offers superior biodegradability compared to flax-based tunics, decomposing naturally within months without releasing harmful residues. Flax, while biodegradable, often undergoes processing treatments that slow degradation and may introduce synthetic substances, complicating its end-of-life scenario. The sustainable disposal of mushroom leather aligns with circular economy principles by enabling composting or soil integration, whereas flax tunics may require industrial composting or recycling to minimize environmental impact.
Ethical Considerations and Production Practices
Mushroom leather, derived from mycelium, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials by utilizing biodegradable, renewable fungi sources with minimal water and chemical use. Flax fabric, produced from flax plants, is celebrated for its natural cultivation requiring fewer pesticides and promoting soil health through crop rotation. Both materials emphasize sustainable agricultural practices, but mushroom leather's rapid growth cycle and waste reduction provide notable advantages in ethical production and environmental impact for tunic manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Market Availability
Mushroom leather typically costs more than flax fabric due to its innovative production processes and limited-scale manufacturing, making it less affordable for mass-market tunics. Flax, derived from flax fibers, is widely available and cheaper to produce, offering a cost-effective option for tunic fabric with established supply chains. Market availability of mushroom leather remains niche with premium pricing, while flax enjoys broad accessibility and competitive pricing in textile markets.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Eco-Friendly Tunic Material
Mushroom leather offers durability, water resistance, and a unique texture ideal for sustainable tunics, while flax provides exceptional breathability, softness, and natural moisture-wicking properties. Both materials contribute significantly to reducing environmental impact by using renewable resources and minimizing chemical processing. Choosing between mushroom leather and flax depends on the desired balance of durability versus comfort, with mushroom leather suited for rugged wear and flax excelling in lightweight, breathable garments.
Infographic: Mushroom leather vs Flax for Tunic
 azmater.com
azmater.com