Viscose sweaters offer breathable, soft, and biodegradable fabric that mimics silk, enhancing comfort and sustainability. Acrylic sweaters provide durable, lightweight, and colorfast fibers with excellent insulation, ideal for affordable, easy-care winter wear.
Table of Comparison
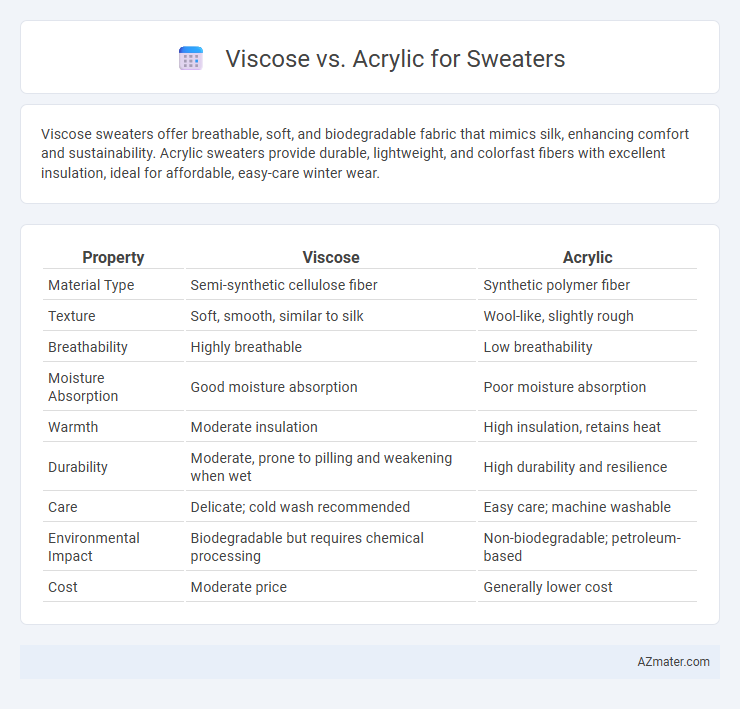
| Property | Viscose | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Semi-synthetic cellulose fiber | Synthetic polymer fiber |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, similar to silk | Wool-like, slightly rough |
| Breathability | Highly breathable | Low breathability |
| Moisture Absorption | Good moisture absorption | Poor moisture absorption |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation | High insulation, retains heat |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to pilling and weakening when wet | High durability and resilience |
| Care | Delicate; cold wash recommended | Easy care; machine washable |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable but requires chemical processing | Non-biodegradable; petroleum-based |
| Cost | Moderate price | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Viscose and Acrylic Fibers
Viscose fibers are semi-synthetic, derived from cellulose in wood pulp, offering a soft, breathable texture ideal for sweaters. Acrylic fibers are synthetic, made from polymer-based chemicals, known for their warmth, durability, and resistance to wrinkles and shrinkage. Both materials provide distinct advantages in sweaters, balancing comfort and performance.
Key Differences Between Viscose and Acrylic
Viscose and acrylic differ significantly in fiber origin and fabric properties, with viscose being a semi-synthetic fiber derived from natural cellulose and acrylic being a fully synthetic polymer. Viscose offers a soft, breathable texture ideal for sweaters, mimicking natural fibers like cotton or silk, while acrylic is often warmer, more durable, and resistant to moths and chemicals. The moisture-wicking ability of viscose makes it comfortable in various climates, whereas acrylic excels in maintaining shape and color over time, especially in machine-washable sweaters.
Fiber Origins: Natural vs Synthetic
Viscose fiber is derived from natural cellulose found in wood pulp, making it a semi-synthetic material that combines natural origins with chemical processing. Acrylic fiber, on the other hand, is fully synthetic, produced from polymerized acrylonitrile through a chemical process unrelated to natural sources. Sweaters made from viscose tend to offer a softer, more breathable texture due to their natural cellulose base, while acrylic sweaters are valued for their durability, color retention, and resistance to moths and mildew.
Texture and Feel: Comfort Comparison
Viscose sweaters offer a smooth, silky texture that feels breathable and lightweight against the skin, making them ideal for comfort in mild weather. Acrylic sweaters provide a soft and warm feel but can sometimes feel slightly synthetic or less breathable compared to viscose. The choice between viscose and acrylic depends on desired comfort levels, with viscose excelling in softness and breathability while acrylic delivers superior warmth and resilience.
Durability and Longevity of Sweaters
Viscose sweaters offer moderate durability but tend to weaken and pill with frequent washing, reducing their longevity over time. Acrylic sweaters provide superior durability, resisting wear, shrinkage, and fading, which ensures a longer lifespan and consistent appearance. Choosing acrylic enhances sweater longevity and maintains fabric integrity through repeated use and washing cycles.
Breathability and Warmth Performance
Viscose offers excellent breathability due to its natural cellulosic fibers, making it ideal for lightweight sweaters that regulate temperature effectively. Acrylic provides superior warmth by mimicking wool's insulating properties, making it suitable for colder climates but with less moisture-wicking ability. Choosing between viscose and acrylic depends on the desired balance between ventilation and heat retention in sweater performance.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Viscose sweaters require gentle hand washing or dry cleaning to prevent fiber weakening and maintain softness, as harsh detergents and high heat can cause shrinkage and distortion. Acrylic sweaters are more durable and machine washable, with resistance to wrinkles and shrinkage, making them easier to maintain and suitable for frequent use. Proper drying methods, such as laying flat for viscose and tumble drying on low for acrylic, further extend the lifespan of each fabric.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Concerns
Viscose production involves significant deforestation and chemical-intensive processes that contribute to environmental degradation and water pollution. Acrylic fibers are synthetic, derived from petrochemicals, resulting in high carbon emissions and non-biodegradable waste that exacerbate landfill issues. Both materials raise sustainability concerns, with viscose impacting ecosystems and acrylic contributing to microplastic pollution in oceans.
Price Comparison: Viscose vs Acrylic Sweaters
Viscose sweaters generally have a higher price point due to the semi-synthetic fiber derived from natural cellulose and often involve more complex manufacturing processes. Acrylic sweaters are typically more affordable, offering a budget-friendly alternative since acrylic fibers are fully synthetic and cheaper to produce. Consumers seeking a balance between cost and quality often consider acrylic for its price advantage while opting for viscose when prioritizing fabric softness and breathability.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Viscose sweaters offer excellent breathability and softness, making them ideal for lightweight, comfortable garments suited for mild weather or layering. Acrylic sweaters provide superior durability and warmth, making them a prime choice for cold climates and frequent wear. Choose viscose for elegant, breathable sweaters and acrylic for affordable, long-lasting winter wear.
Infographic: Viscose vs Acrylic for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com