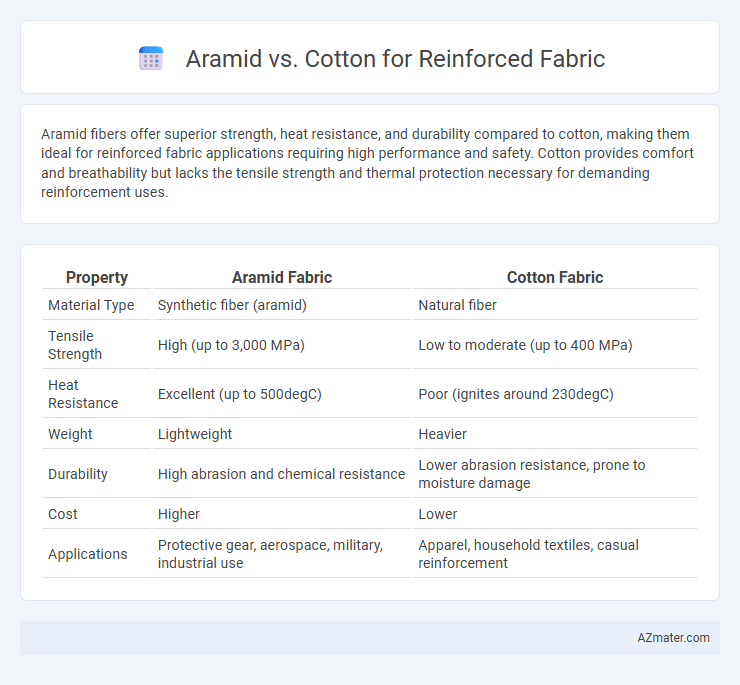
Aramid fibers offer superior strength, heat resistance, and durability compared to cotton, making them ideal for reinforced fabric applications requiring high performance and safety. Cotton provides comfort and breathability but lacks the tensile strength and thermal protection necessary for demanding reinforcement uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fabric | Cotton Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic fiber (aramid) | Natural fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,000 MPa) | Low to moderate (up to 400 MPa) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent (up to 500degC) | Poor (ignites around 230degC) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Durability | High abrasion and chemical resistance | Lower abrasion resistance, prone to moisture damage |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Protective gear, aerospace, military, industrial use | Apparel, household textiles, casual reinforcement |
Introduction to Reinforced Fabrics
Reinforced fabrics combine high-strength fibers with traditional textiles to enhance durability, resistance, and performance in demanding applications. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, outperform cotton in reinforced fabric contexts where durability and safety are critical. Cotton offers breathability and comfort but lacks the robust mechanical properties of aramid, making aramid the preferred choice for high-performance, reinforced textile products.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are synthetic materials known for exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high thermal resistance, making them ideal for reinforced fabrics in demanding applications. Unlike cotton, aramid fibers offer superior durability against abrasion, chemical exposure, and extreme temperatures, which enhances the performance and lifespan of composite materials. These fibers are widely used in aerospace, military, and industrial safety gear due to their lightweight and flame-retardant properties.
Overview of Cotton Fibers
Cotton fibers, derived from the natural cellulose of the cotton plant, offer high breathability and moisture absorption, making them comfortable for wear and use in textiles. Their natural softness and biodegradability contrast with the synthetic strength of aramid fibers, which provide superior tensile strength and heat resistance for reinforced fabrics. While cotton lacks the durability and flame retardant properties of aramid, it remains valued for flexibility and environmental sustainability in fabric reinforcement applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit significantly higher tensile strength and modulus compared to cotton, making them ideal for reinforced fabric applications requiring superior mechanical performance. Their resistance to abrasion, impact, and heat far surpasses that of cotton, which has lower fiber strength and durability under stress. This mechanical advantage positions aramid as the preferred choice in high-performance composites and protective textiles where robust reinforcement is critical.
Thermal Resistance: Aramid vs Cotton
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 500degC, making them ideal for reinforced fabrics used in high-heat environments. In contrast, cotton fibers have a much lower thermal resistance, typically degrading around 150degC and providing limited protection in extreme heat conditions. This significant disparity positions aramid as the superior choice for reinforced fabrics requiring durability and safety under intense thermal stress.
Durability and Longevity
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior durability and longevity compared to cotton in reinforced fabric applications due to their exceptional tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemicals. Cotton, while comfortable and breathable, tends to degrade faster under stress and environmental exposure, making it less suitable for high-performance reinforcement. The inherent molecular structure of aramid fibers ensures long-term structural integrity, maintaining fabric performance over extended use and harsh conditions.
Comfort and Flexibility
Aramid fibers offer superior strength and heat resistance but tend to be stiffer and less breathable compared to cotton, which provides enhanced comfort and flexibility for reinforced fabrics. Cotton's natural softness and moisture-wicking properties improve wearability in applications requiring prolonged use and ease of movement. For optimal balance, blending aramid with cotton can enhance durability while maintaining comfortable flexibility in protective textiles.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior strength and heat resistance compared to cotton, resulting in higher initial costs but longer lifespan and enhanced durability for reinforced fabrics. Cotton is widely available and significantly cheaper, making it suitable for applications with lower performance demands and budget constraints. The cost analysis favors cotton for mass production due to its accessibility, while aramid is preferred in high-stress environments despite limited availability and premium pricing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, used in reinforced fabrics, offer high strength and durability while being less biodegradable than natural cotton, which decomposes more readily but requires extensive water and pesticide use during cultivation. Cotton's environmental impact includes significant land and water consumption, whereas aramid production relies on petrochemicals, contributing to fossil fuel depletion and higher carbon emissions. Sustainable practices in cotton farming, such as organic cotton and water management, reduce its environmental footprint, while innovations in recycling and bio-based aramid aim to enhance the sustainability of synthetic reinforced fabrics.
Best Applications for Aramid and Cotton Reinforced Fabrics
Aramid reinforced fabrics excel in high-performance applications requiring exceptional heat resistance, tensile strength, and durability, such as firefighter gear, ballistic armor, and aerospace components. Cotton reinforced fabrics are best suited for comfort-focused and breathable uses like casual workwear, upholstery, and lightweight protective clothing where flexibility and softness are prioritized. Choosing between aramid and cotton reinforced fabrics depends on the specific demands of thermal protection, mechanical strength, and comfort in the application.
Infographic: Aramid vs Cotton for Reinforced Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com