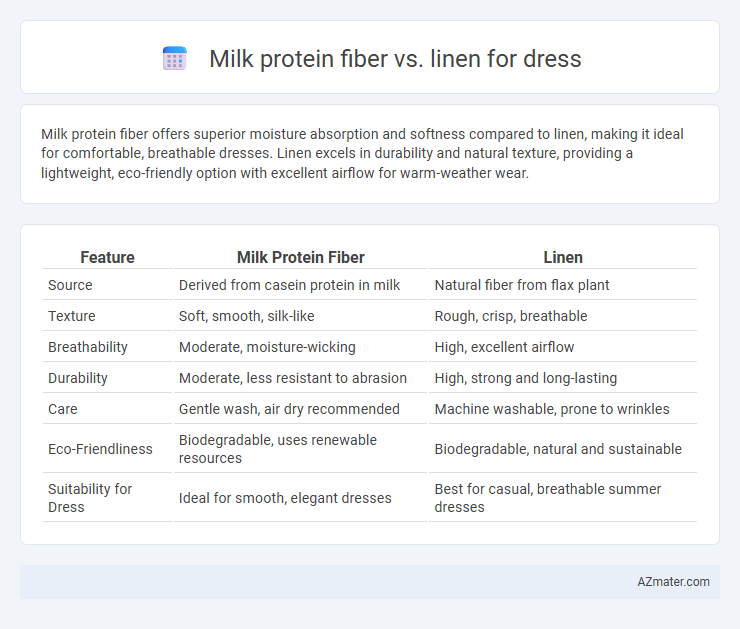
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture absorption and softness compared to linen, making it ideal for comfortable, breathable dresses. Linen excels in durability and natural texture, providing a lightweight, eco-friendly option with excellent airflow for warm-weather wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from casein protein in milk | Natural fiber from flax plant |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like | Rough, crisp, breathable |
| Breathability | Moderate, moisture-wicking | High, excellent airflow |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to abrasion | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Care | Gentle wash, air dry recommended | Machine washable, prone to wrinkles |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, uses renewable resources | Biodegradable, natural and sustainable |
| Suitability for Dress | Ideal for smooth, elegant dresses | Best for casual, breathable summer dresses |
Introduction to Sustainable Dress Fabrics
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein in milk, offers a biodegradable, eco-friendly alternative to traditional textiles, boasting softness and moisture-wicking properties that enhance comfort in sustainable dress fabrics. Linen, cultivated from the flax plant, is renowned for its durability, breathability, and low environmental impact due to minimal water and pesticide use during cultivation. Both fibers contribute to sustainable fashion by reducing reliance on synthetic materials and promoting natural, renewable resources in dress production.
What is Milk Protein Fiber?
Milk protein fiber is a sustainable textile made from casein, the protein found in milk, offering softness and breathability comparable to natural fibers like linen. Unlike linen, which is derived from flax plants and known for its durability and moisture-wicking properties, milk protein fiber provides a silky texture with excellent moisture absorption and antibacterial qualities. Both fibers are eco-friendly, but milk protein fiber stands out for its unique bioactive properties that enhance skin health and comfort in dress materials.
Understanding Linen Fabric
Linen fabric, derived from the flax plant, boasts exceptional breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for warm-weather dresses. Milk protein fiber, created from casein in milk, provides a softer texture and enhanced elasticity but lacks linen's natural durability and cooling effect. Understanding linen's strength and eco-friendly cultivation highlights its superiority in lightweight, breathable dress materials compared to milk protein fiber.
Production Process: Milk Protein Fiber vs Linen
Milk protein fiber is produced through a biotechnological process that extracts casein proteins from milk, which are then spun into fibers using wet-spinning techniques, resulting in a soft and biodegradable material. Linen is derived from the flax plant, where fibers are extracted through retting, followed by mechanical processing such as scutching and hackling to separate and align the fibers before spinning. The production of milk protein fiber involves more controlled, synthetic steps, whereas linen production relies heavily on agricultural and mechanical processes, affecting the texture and environmental impact of the final dress fabric.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Milk protein fiber, derived from biodegradable casein protein, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional linen, reducing reliance on water-intensive crops like flax used in linen production. The processing of milk protein fiber typically consumes less water and energy compared to linen manufacturing, which involves labor-intensive retting and water usage. While linen is known for its durability and natural biodegradability, milk protein fiber's closed-loop production and lower environmental footprint position it as a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable fashion.
Comfort and Feel: Which is Softer?
Milk protein fiber offers a silky, smooth texture that feels exceptionally soft and breathable on the skin, making it highly comfortable for dress materials. Linen, while breathable and moisture-wicking, has a coarser texture with a slightly rougher feel that softens over time but initially offers less immediate softness compared to milk protein fiber. For those prioritizing a gentle, plush touch and superior softness in dresses, milk protein fiber is generally the preferred choice over linen.
Durability and Longevity in Dresses
Milk protein fiber offers excellent durability due to its strong molecular structure, making dresses resistant to wear and tear while maintaining softness. Linen, known for its natural strength and breathability, also provides long-lasting durability but tends to wrinkle easily, which can affect the garment's appearance over time. Dresses made from milk protein fiber generally exhibit enhanced longevity with less maintenance compared to linen, making them ideal for frequent use.
Style and Aesthetic Differences
Milk protein fiber offers a smooth, silky texture with a subtle sheen that enhances dress elegance, creating a modern and luxurious aesthetic. Linen features a natural, breathable weave with a matte finish that emphasizes a rustic, casual style marked by visible texture and slight wrinkling. Dresses made from milk protein fiber present a polished, refined look, while linen dresses convey an effortless, relaxed charm ideal for warm-weather and bohemian-inspired fashion.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Milk protein fiber requires gentle washing with mild detergent and air drying to preserve its softness and prevent shrinkage, as it is sensitive to high temperatures and harsh chemicals. Linen, known for its durability and breathability, can tolerate machine washing but benefits from prompt removal to avoid wrinkles and occasional ironing to maintain its crisp texture. Both fabrics demand careful handling, but milk protein fiber's delicate nature calls for more meticulous maintenance compared to the robust, easy-care properties of linen.
Which Fabric is Best for Dresses?
Milk protein fiber offers exceptional softness, moisture-wicking properties, and natural antibacterial benefits, making it ideal for comfortable and breathable dresses. Linen, known for its durability, breathability, and distinctive texture, provides a cool and lightweight option perfect for warm climates. Choosing between milk protein fiber and linen depends on the desired combination of luxury feel versus classic rustic elegance in dress fabrics.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Linen for Dress
 azmater.com
azmater.com