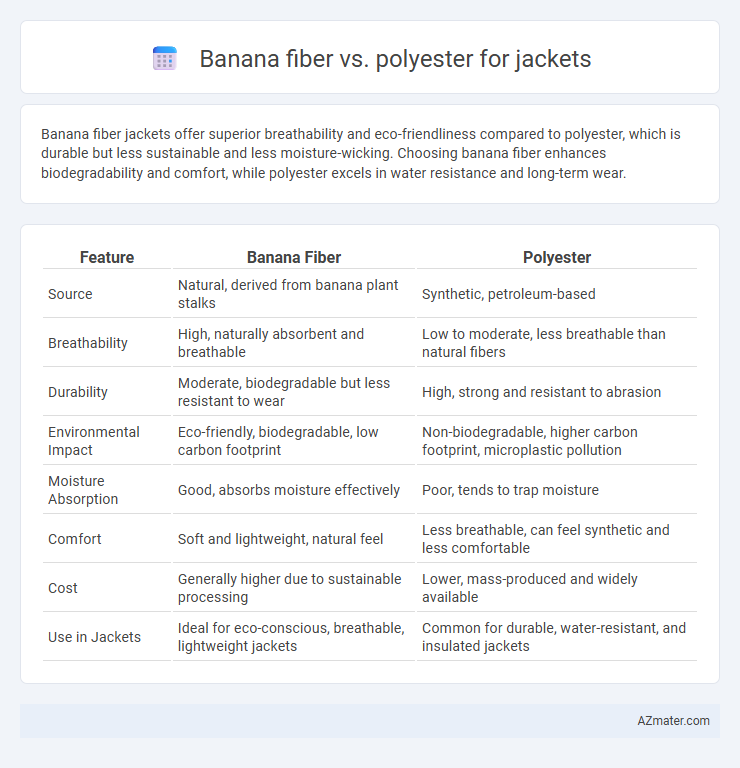
Banana fiber jackets offer superior breathability and eco-friendliness compared to polyester, which is durable but less sustainable and less moisture-wicking. Choosing banana fiber enhances biodegradability and comfort, while polyester excels in water resistance and long-term wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Banana Fiber | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from banana plant stalks | Synthetic, petroleum-based |
| Breathability | High, naturally absorbent and breathable | Low to moderate, less breathable than natural fibers |
| Durability | Moderate, biodegradable but less resistant to wear | High, strong and resistant to abrasion |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint, microplastic pollution |
| Moisture Absorption | Good, absorbs moisture effectively | Poor, tends to trap moisture |
| Comfort | Soft and lightweight, natural feel | Less breathable, can feel synthetic and less comfortable |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable processing | Lower, mass-produced and widely available |
| Use in Jackets | Ideal for eco-conscious, breathable, lightweight jackets | Common for durable, water-resistant, and insulated jackets |
Introduction: Banana Fiber and Polyester in Jacket Manufacturing
Banana fiber, a natural, biodegradable material derived from banana plant stems, is gaining traction in sustainable jacket manufacturing due to its breathability, strength, and eco-friendliness. Polyester, a widely used synthetic fiber made from petroleum-based products, offers durability, wrinkle resistance, and water repellency, making it a popular choice in jacket production. The comparison between banana fiber and polyester revolves around environmental impact, comfort, and performance characteristics essential to consumers and manufacturers.
Material Origins: Natural vs Synthetic Sources
Banana fiber jackets derive fabric from the natural cellulose extracted from banana plant stems, offering biodegradability and eco-friendliness. Polyester jackets are made from petrochemical-based synthetic polymers, primarily polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which provide durability and water resistance but contribute to microplastic pollution. Choosing banana fiber supports sustainable agriculture and reduces reliance on fossil fuels, whereas polyester emphasizes longevity and cost-effectiveness at the expense of environmental impact.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Banana fiber jackets offer superior sustainability due to their biodegradability and low-resource cultivation, requiring minimal water and pesticides compared to polyester production, which relies heavily on fossil fuels and releases significant greenhouse gases. Polyester, a synthetic material derived from petroleum, contributes to microplastic pollution when washed, whereas banana fiber decomposes naturally without harming ecosystems. Choosing banana fiber over polyester supports eco-friendly fashion by reducing carbon footprint and promoting renewable agricultural waste utilization.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Banana fiber jackets offer superior breathability and environmental sustainability compared to polyester, with natural moisture-wicking and biodegradability properties enhancing overall comfort and eco-friendliness. Polyester jackets excel in durability, featuring high resistance to abrasion, stretching, and UV damage, making them ideal for long-term wear and active performance. Performance-wise, polyester provides better water resistance and quicker drying times, while banana fiber's strength and natural texture deliver a unique balance of durability and lightweight comfort.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Banana fiber jackets offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for comfortable all-day wear compared to polyester. While polyester provides durability and water resistance, it often traps heat and moisture, leading to reduced comfort during prolonged use. Natural banana fiber's lightweight and biodegradable nature enhances wearability with less skin irritation and better temperature regulation.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Banana fiber offers superior breathability compared to polyester, allowing better air circulation and temperature regulation in jackets. Its natural moisture-wicking properties efficiently absorb and release sweat, keeping the wearer dry and comfortable during physical activities. Polyester, while durable and water-resistant, tends to trap heat and moisture, often leading to reduced comfort in humid or high-intensity conditions.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Banana fiber offers a unique, natural texture and subtle sheen that enhances the aesthetic qualities of jackets with an eco-friendly appeal, while polyester provides consistent color vibrancy and smooth finishes suited for diverse styles. The design flexibility of banana fiber is limited by its brittle nature and less uniformity, making intricate patterns challenging, whereas polyester allows extensive manipulation through knitting, weaving, and digital printing for complex designs. Choosing banana fiber contributes to sustainable fashion with a rustic charm, whereas polyester excels in durability and versatility for high-performance, fashion-forward outerwear.
Cost Analysis: Banana Fiber vs Polyester Jackets
Banana fiber jackets typically have higher production costs due to labor-intensive extraction and limited industrial processing compared to mass-produced polyester jackets, which benefit from economies of scale. Polyester materials are cheaper and widely available, leading to lower retail prices and more affordable synthetic jacket options. However, banana fiber offers eco-friendly advantages that may justify its premium cost for sustainable fashion consumers.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Banana fiber jackets appeal to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable, biodegradable alternatives to synthetic materials like polyester, which dominates the market due to its durability and affordability. Rising consumer demand for natural fibers drives innovation and increased availability of banana fiber outerwear, aligning with trends toward green fashion and reduced environmental impact. Despite polyester's widespread use for moisture resistance and longevity, the growing preference for organic textiles is shifting market dynamics toward banana fiber in niche, premium segments.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Sustainable Jacket Materials
Banana fiber is emerging as a promising sustainable alternative to polyester in jacket manufacturing due to its biodegradability and low environmental impact. Innovations in processing technologies are improving banana fiber's softness and durability, making it more competitive with synthetic fibers like polyester. As consumer demand shifts toward eco-friendly apparel, future developments will likely integrate banana fiber blends to enhance performance while reducing carbon footprints.
Infographic: Banana fiber vs Polyester for Jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com