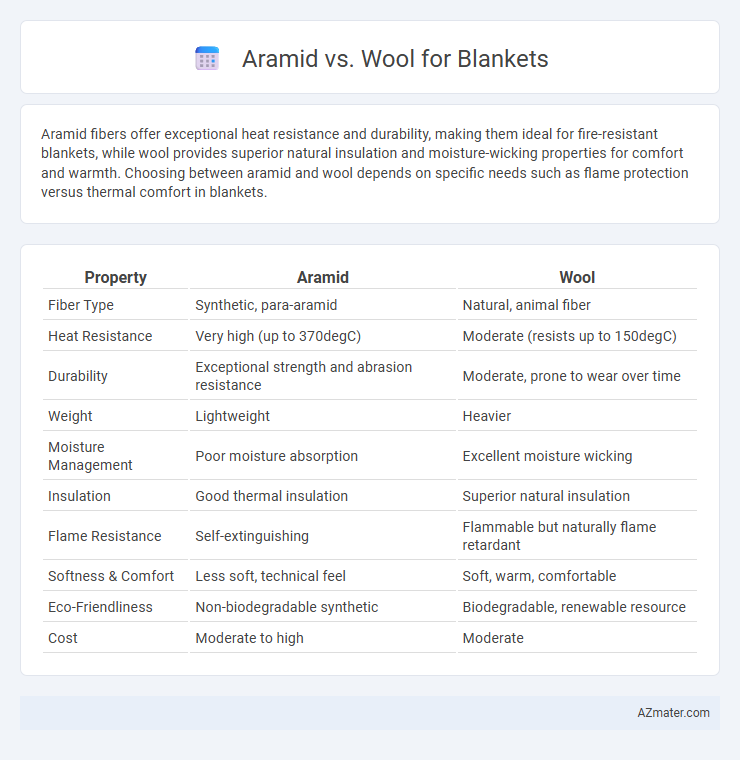
Aramid fibers offer exceptional heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for fire-resistant blankets, while wool provides superior natural insulation and moisture-wicking properties for comfort and warmth. Choosing between aramid and wool depends on specific needs such as flame protection versus thermal comfort in blankets.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Synthetic, para-aramid | Natural, animal fiber |
| Heat Resistance | Very high (up to 370degC) | Moderate (resists up to 150degC) |
| Durability | Exceptional strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate, prone to wear over time |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Moisture Management | Poor moisture absorption | Excellent moisture wicking |
| Insulation | Good thermal insulation | Superior natural insulation |
| Flame Resistance | Self-extinguishing | Flammable but naturally flame retardant |
| Softness & Comfort | Less soft, technical feel | Soft, warm, comfortable |
| Eco-Friendliness | Non-biodegradable synthetic | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Aramid and Wool Blankets
Aramid blankets are made from synthetic fibers known for exceptional heat resistance and durability, commonly used in industrial and firefighting applications. Wool blankets are crafted from natural animal fibers, renowned for their warmth, moisture-wicking abilities, and sustainability. Each type offers distinct advantages, with aramid blankets excelling in safety and durability, while wool blankets provide natural insulation and comfort.
Material Composition: Aramid vs Wool
Aramid fibers are synthetic polymers known for their exceptional heat resistance, strength, and durability, commonly used in protective clothing and industrial applications. Wool, a natural protein fiber from sheep, offers excellent insulation, moisture-wicking properties, and softness, making it ideal for comfort in blankets. The material composition difference between aramid and wool directly influences blanket performance, with aramid emphasizing thermal resistance and durability, while wool provides natural warmth and breathability.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Aramid fibers exhibit superior thermal insulation properties compared to wool, offering exceptional heat resistance and flame retardancy ideal for high-performance blankets. Wool provides natural insulation through its moisture-wicking ability and crimped fiber structure, retaining warmth even when damp. Aramid blankets excel in environments requiring enhanced thermal protection, while wool blankets remain preferred for comfort and breathability in everyday use.
Fire Resistance Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, demonstrate superior fire resistance compared to wool, withstanding higher temperatures without melting or igniting. Wool naturally resists flames due to its high nitrogen and water content, which helps self-extinguish, but it chars and degrades faster under extreme heat. In high-risk fire environments, aramid blankets provide enhanced protection through thermal stability and non-flammability, outperforming wool in durability and safety.
Durability and Longevity
Aramid blankets exhibit exceptional durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making them highly suitable for heavy-duty and industrial use. Wool blankets, while naturally resilient and capable of maintaining warmth over time, tend to show wear faster under harsh conditions compared to aramid fibers. The superior longevity of aramid materials ensures blankets retain structural integrity and protective qualities significantly longer than traditional wool in demanding environments.
Comfort and Softness
Wool blankets offer exceptional softness and natural warmth, making them highly comfortable for everyday use and gentle against the skin. Aramid fibers prioritize durability and heat resistance, often resulting in a coarser texture that can feel less soft compared to wool. Wool's breathable and moisture-wicking properties enhance comfort, whereas aramid blankets are better suited for protective purposes rather than softness or coziness.
Weight and Portability
Aramid blankets weigh significantly less than wool blankets, making them ideal for portability and outdoor use. Wool, while heavier, offers superior insulation but can be bulky and less convenient for carrying during travel. Choosing aramid enhances ease of transport without sacrificing durability in compact blanket options.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Aramid blankets require minimal maintenance due to their high resistance to stains, moisture, and abrasion, often needing only spot cleaning with mild detergents. Wool blankets demand more careful care, including regular airing to prevent odors and hand washing or dry cleaning to maintain fiber integrity and avoid shrinkage. Proper storage in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight is essential for both materials to prolong their lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, synthetic and petroleum-based, have a higher environmental footprint due to energy-intensive production and non-biodegradability, contributing to long-term waste issues. Wool, a natural and renewable fiber, offers greater sustainability through biodegradability and minimal chemical processing, though sheep farming impacts land use and methane emissions. Selecting blankets made from responsibly sourced wool or recycled aramid can mitigate environmental concerns and support sustainable textile choices.
Choosing the Right Blanket: Aramid or Wool
When selecting a blanket, consider the superior heat resistance and durability of aramid fibers, making them ideal for high-performance and protective uses. Wool offers excellent natural insulation, moisture-wicking, and softness, providing warmth and comfort for everyday use. Assess your needs for either enhanced flame resistance or cozy thermal regulation to choose between aramid and wool blankets.
Infographic: Aramid vs Wool for Blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com