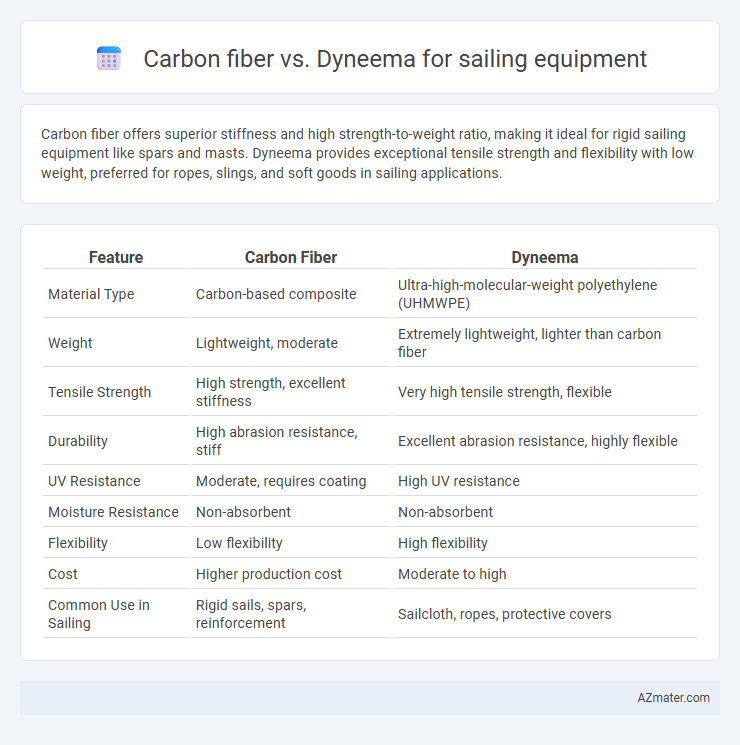
Carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for rigid sailing equipment like spars and masts. Dyneema provides exceptional tensile strength and flexibility with low weight, preferred for ropes, slings, and soft goods in sailing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Fiber | Dyneema |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based composite | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
| Weight | Lightweight, moderate | Extremely lightweight, lighter than carbon fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High strength, excellent stiffness | Very high tensile strength, flexible |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, stiff | Excellent abrasion resistance, highly flexible |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, requires coating | High UV resistance |
| Moisture Resistance | Non-absorbent | Non-absorbent |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility | High flexibility |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Moderate to high |
| Common Use in Sailing | Rigid sails, spars, reinforcement | Sailcloth, ropes, protective covers |
Introduction to Carbon Fiber and Dyneema in Sailing
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity, making it ideal for high-performance sailing equipment such as masts, booms, and hull reinforcements. Dyneema, an ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber, excels in tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and UV exposure, commonly used for sails, rigging lines, and protective covers. Both materials enhance sailing performance through advanced durability and weight savings, yet serve distinct roles based on their mechanical properties and application requirements.
Material Properties: Strength, Weight, and Flexibility
Carbon fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and rigidity, making it ideal for load-bearing sailing equipment, while maintaining a lightweight profile that enhances vessel performance. Dyneema, a high-modulus polyethylene fiber, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding flexibility, allowing for dynamic load absorption and resistance to abrasion in rigging applications. Both materials provide critical advantages, but carbon fiber excels in stiffness and structural components, whereas Dyneema dominates in flexible, impact-resistant uses such as lines and sails.
Durability and Fatigue Resistance Comparison
Carbon fiber exhibits exceptional fatigue resistance and high tensile strength, making it ideal for sailing equipment subjected to repetitive loading and harsh marine environments. Dyneema, a high-performance polyethylene fiber, offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, contributing to excellent durability against abrasion and dynamic stresses in sails and rigging. While carbon fiber provides greater stiffness and long-term structural integrity, Dyneema excels in resilience and resistance to continuous flexing, both critical factors in extending the lifespan of sailing components.
UV and Weather Resistance
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength and stiffness but is vulnerable to UV degradation unless properly coated, requiring specialized UV-resistant resins to maintain its integrity in sailing equipment. Dyneema excels in UV and weather resistance due to its high molecular weight polyethylene composition, providing outstanding durability and minimal moisture absorption under harsh marine conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the balance between mechanical performance and long-term environmental resilience necessary for specific sailing applications.
Performance Impacts on Sailing Equipment
Carbon fiber offers exceptional stiffness and tensile strength, significantly enhancing sail rigging responsiveness and durability under high loads. Dyneema, known for its ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers, provides superior abrasion resistance and lightweight flexibility, improving handling and reducing fatigue on lines and sheets. The performance impact of carbon fiber results in increased precision and load-bearing capacity, while Dyneema excels in resilience and ease of maneuverability, critical for dynamic sailing conditions.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Fiber vs Dyneema
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio but comes with a significantly higher price compared to Dyneema, making upfront costs for sailing equipment considerably steeper. Dyneema provides high tensile strength and durability at a fraction of carbon fiber's cost, offering better value for budget-conscious sailors. When factoring in lifecycle expenses, Dyneema's resistance to abrasion and UV damage often results in lower long-term maintenance and replacement costs than carbon fiber.
Common Sailing Applications for Each Material
Carbon fiber excels in sailing equipment requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as mast sections, booms, and high-performance spars, where stiffness and durability are critical. Dyneema is commonly used in running rigging, sheets, and control lines due to its exceptional tensile strength, low stretch, and resistance to UV and moisture. Both materials optimize performance by balancing weight, strength, and flexibility in their respective applications on racing and cruising sailboats.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Carbon fiber sailing equipment offers high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent stiffness but requires careful maintenance to prevent UV damage and moisture infiltration, which can compromise its structural integrity over time. Dyneema, a high-modulus polyethylene fiber, boasts superior resistance to abrasion and UV exposure, making it highly durable with minimal maintenance in marine environments. For longevity, Dyneema typically outperforms carbon fiber in harsh saltwater conditions due to its inherent flexibility and resistance to environmental degradation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber manufacturing involves high energy consumption and emits significant greenhouse gases, raising concerns about its environmental footprint. Dyneema, made from ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers better recyclability and lower energy use during production, contributing to improved sustainability in sailing gear. Both materials provide durability, but Dyneema's reduced carbon emissions and potential for recycling make it a more eco-friendly choice for environmentally conscious sailors.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Sailing Needs
Carbon fiber offers exceptional stiffness and lightweight properties, ideal for performance sailing components such as masts and booms requiring high strength-to-weight ratios. Dyneema excels in tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it the preferred choice for lines, sheets, and rigging that demand flexibility and durability under dynamic loads. Selecting the right material depends on specific sailing applications: carbon fiber suits rigid structural parts, while Dyneema provides superior performance in load-bearing, flexible gear.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Dyneema for Sailing equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com