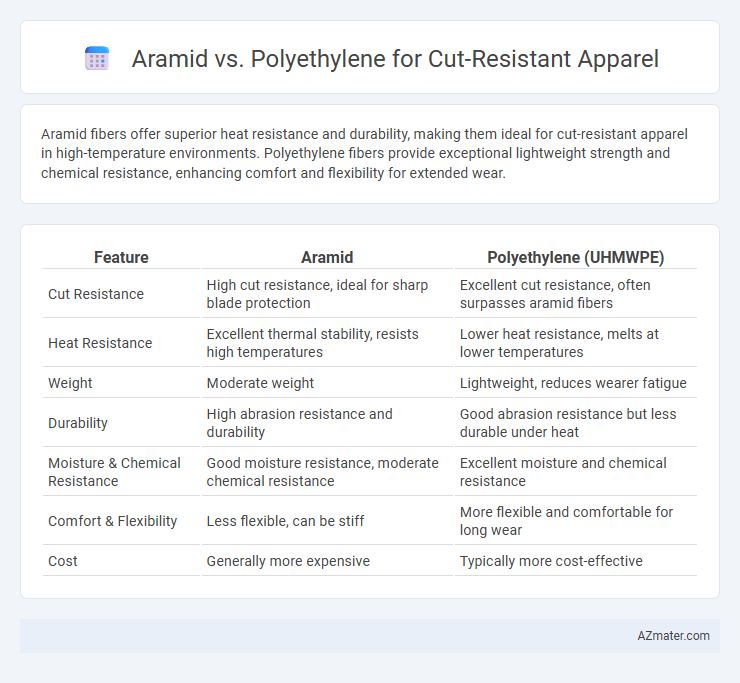
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for cut-resistant apparel in high-temperature environments. Polyethylene fibers provide exceptional lightweight strength and chemical resistance, enhancing comfort and flexibility for extended wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid | Polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Cut Resistance | High cut resistance, ideal for sharp blade protection | Excellent cut resistance, often surpasses aramid fibers |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent thermal stability, resists high temperatures | Lower heat resistance, melts at lower temperatures |
| Weight | Moderate weight | Lightweight, reduces wearer fatigue |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance and durability | Good abrasion resistance but less durable under heat |
| Moisture & Chemical Resistance | Good moisture resistance, moderate chemical resistance | Excellent moisture and chemical resistance |
| Comfort & Flexibility | Less flexible, can be stiff | More flexible and comfortable for long wear |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically more cost-effective |
Introduction to Cut-resistant Apparel Materials
Cut-resistant apparel primarily utilizes materials such as aramid fibers and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) for enhanced protection against sharp objects. Aramid fibers, like Kevlar, offer high heat resistance and excellent tensile strength, making them ideal for industrial safety gear. UHMWPE provides superior cut resistance with lightweight durability and chemical resistance, favored in scenarios requiring flexibility and comfort.
What is Aramid? Key Properties and Uses
Aramid fibers, including renowned variants like Kevlar and Nomex, are synthetic fibers known for exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high heat resistance, and superior cut resistance, making them ideal for protective apparel. Their molecular structure provides outstanding durability, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy, essential for industries such as firefighting, law enforcement, and industrial safety. Aramid-based fabrics excel in environments demanding high-performance cut-resistant clothing, outperforming materials like polyethylene in thermal stability and impact protection.
Polyethylene Explained: Structure and Advantages
Polyethylene used in cut-resistant apparel is typically in the form of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), characterized by its long polymer chains that provide exceptional tensile strength and durability. Its lightweight and high abrasion resistance make it ideal for protective clothing, offering superior comfort without compromising safety. This synthetic fiber outperforms traditional materials by delivering enhanced cut resistance with flexibility and moisture resistance, making it a preferred choice in industrial safety gear.
Cut Resistance: Aramid vs Polyethylene Performance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior cut resistance due to their strong molecular bonds and high tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring durable protection against sharp objects. Polyethylene fibers, especially ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer excellent cut resistance with a lighter weight and higher abrasion resistance but may have lower heat resistance compared to aramids. In terms of cut performance, aramid materials generally provide better durability under extreme conditions, while polyethylene excels in flexibility and comfort for cut-resistant apparel.
Comfort and Wearability Comparison
Aramid fibers, known for their heat resistance and durability, often provide superior cut protection but tend to be heavier and less flexible, impacting overall comfort and wearability. Polyethylene fibers offer a lightweight, breathable alternative with high tensile strength, enhancing wearer comfort during extended use without significantly compromising cut resistance. Choosing between aramid and polyethylene depends on the specific balance needed between protection, flexibility, and heat resistance in cut-resistant apparel.
Heat and Chemical Resistance Differences
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior heat resistance withstanding temperatures up to 500degC, making them ideal for applications involving exposure to extreme heat or flames. Polyethylene fibers, like Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), excel in chemical resistance, resisting acids, bases, and solvents while maintaining high tensile strength. Choosing between aramid and polyethylene for cut-resistant apparel involves balancing the need for thermal protection versus chemical exposure resistance based on specific workplace hazards.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional durability with high resistance to heat, abrasion, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for long-lasting cut-resistant apparel. Polyethylene fibers, including ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), provide excellent cut resistance and lightweight comfort but can degrade faster under UV exposure and abrasion compared to aramid. Overall, aramid-based materials generally exhibit superior longevity and sustained performance in harsh working conditions.
Cost Analysis: Affordability of Aramid vs Polyethylene
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, generally have a higher cost per yard compared to ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers like Dyneema, impacting the overall expense of cut-resistant apparel. The superior tensile strength and heat resistance of aramid materials justify their premium price in high-risk environments, whereas polyethylene offers a more affordable alternative with excellent cut resistance but lower heat tolerance. Companies balance these factors by selecting polyethylene for budget-conscious applications and aramid for scenarios demanding enhanced durability and thermal protection.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers such as Kevlar offer excellent cut resistance but are derived from petroleum-based sources with limited biodegradability, leading to environmental concerns in production and disposal. Polyethylene fibers, especially Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), provide strong cut protection while being more energy-efficient to produce and having a lower carbon footprint compared to aramid. Both materials challenge sustainability efforts, but ongoing innovations in recycling and biodegradable alternatives aim to reduce the environmental impact of cut-resistant apparel.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Application
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar(r), offer exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring durability against high temperatures and sharp objects. Polyethylene fibers, like Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), provide superior cut resistance with lighter weight and excellent impact absorption, suitable for situations demanding mobility and comfort. Selecting between aramid and polyethylene depends on specific use-case factors such as thermal exposure, required flexibility, and the environment in which the cut-resistant apparel will be used.
Infographic: Aramid vs Polyethylene for Cut-resistant Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com