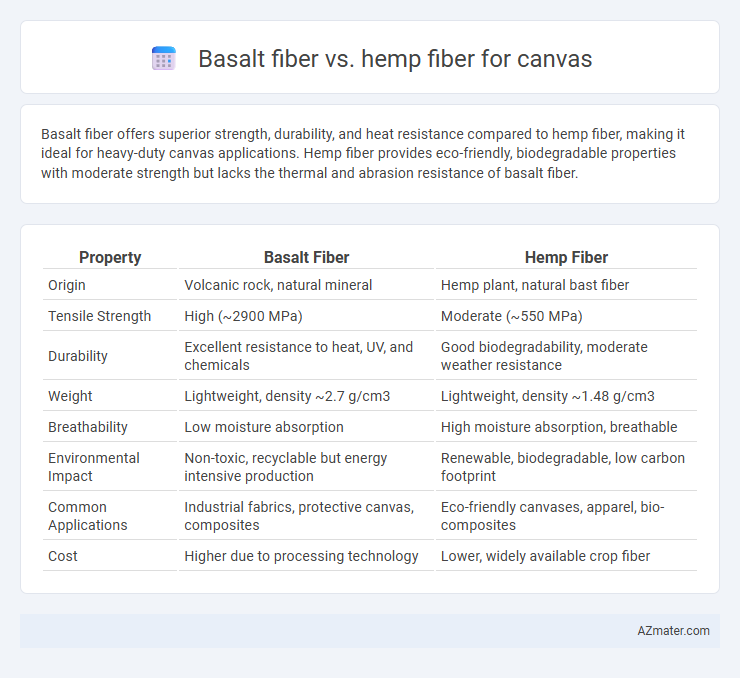
Basalt fiber offers superior strength, durability, and heat resistance compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty canvas applications. Hemp fiber provides eco-friendly, biodegradable properties with moderate strength but lacks the thermal and abrasion resistance of basalt fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Volcanic rock, natural mineral | Hemp plant, natural bast fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (~2900 MPa) | Moderate (~550 MPa) |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to heat, UV, and chemicals | Good biodegradability, moderate weather resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight, density ~2.7 g/cm3 | Lightweight, density ~1.48 g/cm3 |
| Breathability | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption, breathable |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, recyclable but energy intensive production | Renewable, biodegradable, low carbon footprint |
| Common Applications | Industrial fabrics, protective canvas, composites | Eco-friendly canvases, apparel, bio-composites |
| Cost | Higher due to processing technology | Lower, widely available crop fiber |
Introduction to Basalt Fiber and Hemp Fiber
Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic basalt rock, offers superior strength, heat resistance, and durability compared to hemp fiber, which is a natural fiber obtained from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant known for its eco-friendliness and biodegradability. Basalt fiber's high tensile strength and resistance to chemical damage make it ideal for industrial canvas applications requiring longevity and resilience. Hemp fiber, prized for its lightweight texture and moisture-wicking properties, is commonly used in sustainable, breathable canvas products that emphasize environmental benefits.
Composition and Raw Materials
Basalt fiber is derived from volcanic basalt rocks, composed primarily of silica, alumina, and iron oxides, offering high tensile strength and resistance to heat and chemicals. Hemp fiber is sourced from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, rich in cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose, providing natural biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties. While basalt fiber's inorganic mineral composition ensures superior durability and environmental resistance, hemp fiber's organic plant-based composition offers sustainability and flexibility for canvas applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Basalt fiber for canvas manufacturing involves melting volcanic rock at temperatures around 1400degC, followed by extrusion into continuous filaments, which are then woven into durable fabrics with high tensile strength and resistance to chemicals and UV rays. Hemp fiber production includes harvesting mature plants, retting to separate fibers, mechanical decortication, and spinning into yarns, valued for its biodegradability and breathability but requiring more energy-intensive processing to remove lignin and achieve fine textures. Basalt fiber manufacturing is more industrial and energy-intensive but results in a stronger, synthetic-like canvas material, whereas hemp fiber relies on natural, agricultural methods with a focus on sustainability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Basalt fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and improved elasticity compared to hemp fiber, making it more suitable for heavy-duty canvas applications requiring durability and resistance to mechanical stress. Hemp fiber offers moderate strength with superior flexibility and biodegradability, providing a sustainable option with adequate tensile modulus for lighter canvas uses. The mechanical performance of basalt fiber surpasses hemp in abrasion resistance and impact strength, enhancing longevity in industrial fabric products.
Durability and Longevity
Basalt fiber offers superior durability for canvas applications due to its high tensile strength and resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and chemicals, making it ideal for long-term outdoor use. Hemp fiber provides notable longevity with natural resistance to mold and mildew, but it is more prone to degradation under prolonged exposure to harsh environmental conditions compared to basalt fiber. Choosing basalt fiber enhances canvas durability and lifespan, particularly in demanding settings requiring robust performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt fiber offers superior sustainability compared to traditional materials, deriving from abundant volcanic rock without requiring pesticides or extensive water use, which significantly reduces its environmental footprint. Hemp fiber is highly renewable, growing rapidly with minimal chemical input and naturally enriching the soil, making it an eco-friendly choice for canvas production. Both fibers contribute to sustainable manufacturing, but basalt fiber excels in durability and recyclability, while hemp fiber supports biodiversity and organic farming practices.
Cost Analysis: Basalt vs Hemp Fiber
Basalt fiber offers higher durability and resistance to environmental factors but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to hemp fiber, making it less economically viable for large-scale canvas production. Hemp fiber, known for its affordability and sustainable cultivation, provides a cost-effective alternative with moderately strong tensile properties suitable for canvas applications. Cost analysis reveals hemp fiber can reduce material expenses by up to 40% while maintaining acceptable performance levels, benefiting budget-conscious manufacturers.
Performance in Canvas Applications
Basalt fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to hemp fiber, making it highly durable for canvas applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Hemp fiber offers excellent breathability and natural UV resistance but tends to absorb moisture more readily, potentially weakening the canvas over time. For performance-critical canvas, basalt fiber's enhanced mechanical properties and lower moisture absorption result in longer-lasting, more resilient materials.
Market Availability and Adoption
Basalt fiber and hemp fiber for canvas show distinct market availability; hemp fiber enjoys widespread adoption due to its long-established agricultural infrastructure and renewable appeal, making it a widely accessible option for eco-friendly textile production. Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic rock, is less common in canvas applications but is gaining traction in niche markets focused on durability and fire resistance, though its higher production costs limit mass adoption. Market demand for hemp fibers continues to grow driven by sustainability trends, while basalt fiber's adoption remains concentrated in specialized industrial and technical textile sectors.
Future Trends and Innovations
Basalt fiber exhibits superior durability and thermal resistance compared to hemp fiber, making it increasingly favored for advanced canvas applications in industries like automotive and aerospace. Innovations in basalt fiber production are improving sustainability by reducing energy consumption and enhancing recyclability, aligning with future eco-friendly material trends. Hemp fiber continues to gain traction due to its biodegradability and carbon sequestration benefits, with ongoing research focused on improving its strength and water resistance to expand its viability for high-performance canvas products.
Infographic: Basalt fiber vs Hemp fiber for Canvas
 azmater.com
azmater.com