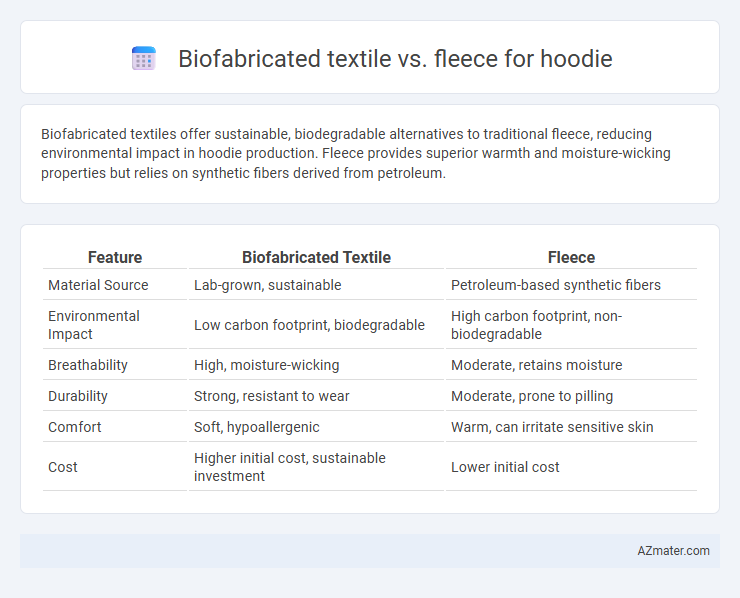
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives to traditional fleece, reducing environmental impact in hoodie production. Fleece provides superior warmth and moisture-wicking properties but relies on synthetic fibers derived from petroleum.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Fleece |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown, sustainable | Petroleum-based synthetic fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Breathability | High, moisture-wicking | Moderate, retains moisture |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to wear | Moderate, prone to pilling |
| Comfort | Soft, hypoallergenic | Warm, can irritate sensitive skin |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, sustainable investment | Lower initial cost |
Introduction: The Future of Hoodie Fabrics
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable alternatives to traditional fleece, using lab-grown fibers that reduce environmental impact while maintaining warmth and comfort. These innovative materials are engineered for durability and breathability, addressing common drawbacks of fleece such as pilling and synthetic waste. Embracing biofabricated fabrics revolutionizes hoodie production with eco-friendly solutions that align with modern demands for performance and sustainability.
What Is Biofabricated Textile?
Biofabricated textile is created through sustainable biological processes, utilizing living cells to grow materials that mimic traditional fabrics without the environmental impact of conventional manufacturing. Unlike fleece, typically made from synthetic polyester derived from petroleum, biofabricated textiles offer biodegradable and renewable alternatives with reduced carbon footprints. This cutting-edge approach to fabric production supports eco-friendly hoodie designs by enhancing durability, breathability, and softness while minimizing pollution.
Understanding Fleece: Composition and Uses
Fleece, traditionally made from polyester fibers derived from petroleum, offers exceptional insulation and moisture-wicking properties ideal for hoodies in cold weather. Its lightweight, breathable fabric traps heat efficiently while remaining soft and comfortable against the skin, making it a popular choice for outdoor and athletic apparel. Compared to biofabricated textiles, fleece's mass production and durability provide widespread availability but raise concerns regarding sustainability and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biofabricated textiles significantly reduce environmental impact compared to traditional fleece by minimizing resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during production. Unlike conventional fleece made from petroleum-based polyester, biofabricated materials rely on renewable bio-based sources, leading to lower carbon footprints and reduced microplastic pollution. The biodegradability of biofabricated textiles also enhances end-of-life sustainability, whereas fleece often contributes to persistent environmental waste in landfills and oceans.
Comfort and Wearability: How Do They Feel?
Biofabricated textiles offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional fleece, enhancing comfort during extended wear. Their lightweight, soft texture adapts well to body movements, reducing chafing and maintaining temperature regulation. Fleece, known for its warmth and plush feel, excels in insulation but may retain moisture, which can affect long-term comfort and wearability in varying conditions.
Durability and Maintenance Differences
Biofabricated textiles exhibit enhanced durability compared to traditional fleece, resisting pilling and wear over extended use. Maintenance of biofabricated textiles typically requires less frequent washing and retains structural integrity after multiple cycles, unlike fleece which may soften but degrade faster. These advanced materials often offer sustainable, long-lasting alternatives with reduced environmental impact during upkeep.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Biofabricated textiles offer superior breathability compared to traditional fleece, allowing enhanced air circulation that helps regulate body temperature during physical activity. Their advanced moisture management properties rapidly wick sweat away from the skin, promoting quicker drying times and reducing discomfort from dampness. Fleece, while warm and soft, tends to retain moisture longer and breathes less effectively, making biofabricated textiles a more efficient choice for performance hoodies.
Cost Analysis: Biofabricated Textile vs Fleece
Biofabricated textiles for hoodies typically incur higher production costs due to advanced biotechnology processes and limited manufacturing scale, often resulting in prices 2 to 3 times greater than traditional fleece materials. Fleece benefits from established mass production methods and inexpensive synthetic fibers like polyester, making it a cost-effective option for budget-conscious consumers. The investment in biofabricated textile not only raises initial costs but also offers potential long-term savings by reducing environmental impact and waste in the apparel lifecycle.
Market Availability and Consumer Trends
Biofabricated textiles are emerging in the hoodie market with limited availability but growing consumer interest due to their sustainability and innovative production methods. Fleece remains widely available, favored for its affordability, warmth, and established supply chains. Market trends indicate increasing demand for eco-friendly materials, positioning biofabricated textiles as a potential future alternative to traditional fleece in hoodies.
The Future of Hoodies: Which Fabric Wins?
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives to traditional fleece, reducing environmental impact while maintaining comfort and durability in hoodies. Advanced bio-based fibers provide superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to conventional synthetic fleece, enhancing wearability in diverse climates. With growing consumer demand for eco-friendly fashion, biofabricated textiles position themselves as the future-winning fabric choice for hoodies.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Fleece for Hoodie
 azmater.com
azmater.com