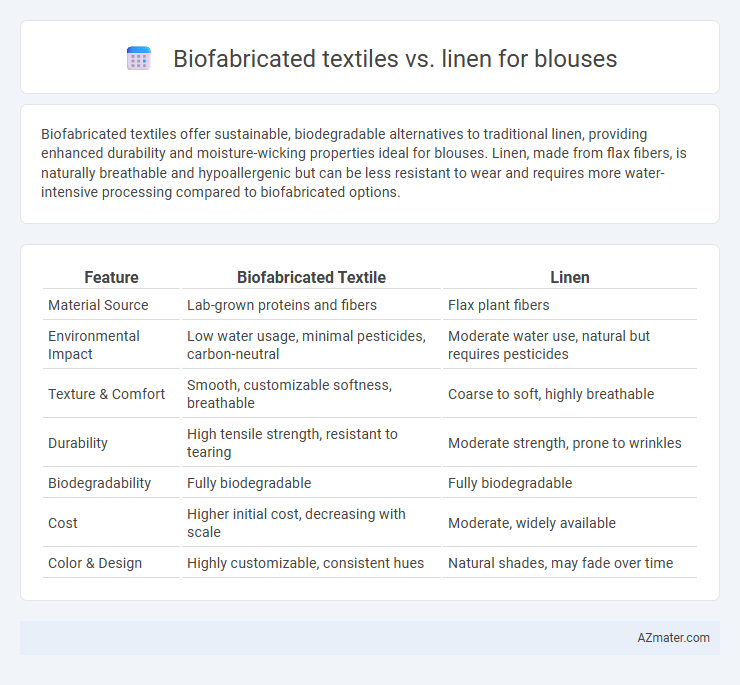
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives to traditional linen, providing enhanced durability and moisture-wicking properties ideal for blouses. Linen, made from flax fibers, is naturally breathable and hypoallergenic but can be less resistant to wear and requires more water-intensive processing compared to biofabricated options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown proteins and fibers | Flax plant fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Low water usage, minimal pesticides, carbon-neutral | Moderate water use, natural but requires pesticides |
| Texture & Comfort | Smooth, customizable softness, breathable | Coarse to soft, highly breathable |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to tearing | Moderate strength, prone to wrinkles |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable | Fully biodegradable |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, decreasing with scale | Moderate, widely available |
| Color & Design | Highly customizable, consistent hues | Natural shades, may fade over time |
Introduction to Biofabricated Textiles and Linen
Biofabricated textiles are innovative materials created through biological processes involving microorganisms or cells, offering sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional fabrics. Linen, derived from the flax plant, boasts natural breathability, durability, and moisture-wicking properties, making it a long-standing choice for blouses. Comparing biofabricated textile to linen highlights advancements in eco-friendly fashion alongside the timeless benefits of natural plant-based fibers.
Defining Biofabricated Textiles: An Overview
Biofabricated textiles are innovative materials produced through biological processes, such as microbial fermentation or cell culture, usually resulting in sustainable and biodegradable fabrics. Unlike conventional linen derived from flax plants through traditional harvesting and weaving methods, biofabricated textiles offer customizable properties and reduced environmental impact by minimizing water usage and chemical processing. These textiles represent a cutting-edge shift in the fashion industry, aiming to combine functionality with ecological responsibility for apparel like blouses.
The History and Origin of Linen Fabrics
Linen fabric, derived from the flax plant, is one of the oldest textiles known to humanity, with origins tracing back over 6,000 years to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. Historically prized for its durability, breathability, and cool texture, linen was used for garments such as blouses, symbolizing purity and high social status. In contrast, biofabricated textiles are a modern innovation using cultured cells or microbial synthesis to create sustainable fabrics, representing the future of eco-friendly fashion beyond traditional linen's natural origins.
Sustainability: Biofabricated Textiles vs Linen
Biofabricated textiles offer a revolutionary approach to sustainability by utilizing lab-grown fibers that minimize resource consumption and reduce environmental impact compared to traditional linen cultivation. Linen production requires significant water and land use alongside pesticide applications, while biofabricated alternatives rely on controlled bioreactors that drastically lower carbon emissions and waste. Choosing biofabricated textiles for blouses supports circular economy principles and promotes innovation in renewable, biodegradable materials beyond the agricultural constraints of flax-based linen.
Production Process Comparison: Biofabricated vs Linen
Biofabricated textiles are produced using microbial fermentation and cell culture techniques, which significantly reduce water consumption and chemical use compared to traditional linen production derived from flax fibers. Linen manufacturing involves labor-intensive harvesting, retting, and scutching processes, requiring large amounts of water and energy, whereas biofabrication emphasizes sustainability through closed-loop bioreactors and biodegradable inputs. Both materials offer distinct environmental impacts, but biofabricated textiles provide a cutting-edge, scalable alternative with lower carbon footprint and resource efficiency.
Comfort and Breathability in Blouse Applications
Biofabricated textiles offer superior moisture-wicking properties and enhanced breathability compared to traditional linen, making them ideal for blouse applications in warm climates. These innovative materials provide excellent softness and lightweight comfort while maintaining durability and resistance to wrinkles. Linen, although naturally breathable and hypoallergenic, tends to be heavier and may wrinkle more easily, potentially affecting the blouse's overall comfort and crisp appearance in daily wear.
Durability and Longevity in Everyday Wear
Biofabricated textiles, engineered from sustainable materials and advanced biotechnologies, offer superior durability and resistance to wear in everyday blouses compared to traditional linen, which tends to weaken and fray over time due to its natural fibers. The molecular structure of biofabricated fabrics enhances tensile strength and reduces pilling, extending the garment's lifespan significantly. Linen's breathability is offset by its susceptibility to shrinkage and fiber degradation with frequent washing, making biofabricated options more reliable for long-term, everyday wear.
Style, Texture, and Aesthetics: Visual Differences
Biofabricated textiles offer a futuristic aesthetic with smooth surfaces and customizable patterns that differ from the natural irregularities found in linen, which presents a more organic and breathable texture. Linen's slightly coarse yet soft weave gives blouses a classic, rustic charm, while biofabricated fabrics often showcase uniformity and sleek finishes that highlight innovative design. Visually, biofabricated textiles tend to reflect light evenly, creating a polished look, whereas linen's matte appearance and visible fiber structure evoke timeless elegance and casual sophistication.
Cost Implications and Market Trends
Biofabricated textiles for blouses present higher initial costs compared to traditional linen due to advanced production technologies and limited scalability, but they offer potential long-term savings through durability and sustainability benefits. Linen remains a cost-effective choice favored for its natural fibers and established supply chains, maintaining steady demand in eco-conscious fashion markets. Market trends indicate increasing investment in biofabricated textiles driven by growing consumer preference for sustainable and innovative materials, forecasting gradual price reductions and expanded adoption.
Choosing the Ideal Fabric for Modern Blouses
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable and innovative alternatives to traditional fabrics like linen, providing enhanced durability and moisture-wicking properties ideal for modern blouses. Linen remains popular for its breathability and natural texture, making it suitable for lightweight, comfortable summer wear. Selecting between biofabricated textile and linen depends on priorities such as eco-friendliness, fabric performance, and desired aesthetic in blouse design.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Linen for Blouse
 azmater.com
azmater.com