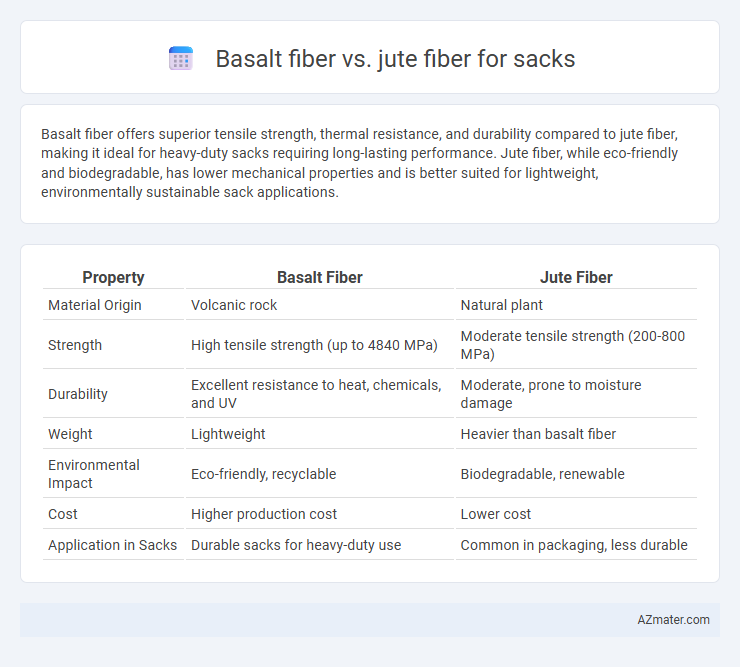
Basalt fiber offers superior tensile strength, thermal resistance, and durability compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty sacks requiring long-lasting performance. Jute fiber, while eco-friendly and biodegradable, has lower mechanical properties and is better suited for lightweight, environmentally sustainable sack applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Volcanic rock | Natural plant |
| Strength | High tensile strength (up to 4840 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (200-800 MPa) |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and UV | Moderate, prone to moisture damage |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than basalt fiber |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, recyclable | Biodegradable, renewable |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost |
| Application in Sacks | Durable sacks for heavy-duty use | Common in packaging, less durable |
Introduction to Basalt and Jute Fibers
Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic basalt rock, offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to chemical and thermal degradation, making it an innovative material for sack production. Jute fiber, a natural bast fiber sourced from the jute plant, is renewable, biodegradable, and widely used for eco-friendly sacks due to its affordability and excellent moisture absorption. Comparing both fibers highlights basalt's enhanced mechanical properties and longevity versus jute's sustainability and cost-effectiveness in sack applications.
Material Properties: Basalt Fiber vs Jute Fiber
Basalt fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for sacks requiring durability in harsh environments. Jute fiber offers biodegradability and cost-effectiveness but has lower moisture resistance and mechanical strength than basalt fiber. The choice between basalt and jute fibers depends on balancing performance needs with environmental impact and budget constraints.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Basalt fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, typically ranging from 2,800 to 4,800 MPa, compared to jute fiber, which averages around 400 to 600 MPa, making basalt fiber sacks significantly more resistant to tearing and heavy loads. In terms of durability, basalt fiber offers excellent resistance to weathering, chemical exposure, and UV radiation, extending the lifespan of sacks beyond that of biodegradable and moisture-sensitive jute fiber. This combination of high mechanical strength and environmental resilience makes basalt fiber an optimal choice for industrial and long-term storage sacks.
Environmental Impact of Basalt and Jute Sacks
Basalt fiber sacks offer superior environmental benefits due to their natural volcanic rock origin, providing high durability and recyclability without toxic chemicals. Jute fiber sacks, derived from renewable plant sources, are biodegradable and compostable, supporting soil health but with lower durability and faster degradation rates. The choice between basalt and jute sacks hinges on balancing longevity and reusability against rapid biodegradability and agricultural sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Basalt Sacks vs Jute Sacks
Basalt fiber sacks generally incur higher initial costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and raw material expenses compared to jute sacks, which are derived from widely available, low-cost natural fibers. However, basalt sacks offer superior durability, resistance to moisture, and extended lifespan, potentially reducing replacement and maintenance costs over time. In contrast, jute sacks, while economically favorable upfront, may require more frequent replacement due to susceptibility to wear and environmental degradation, impacting long-term cost efficiency.
Weight and Load-Bearing Capacity
Basalt fiber sacks offer significantly higher load-bearing capacity compared to jute fiber sacks, making them ideal for transporting heavy materials due to their tensile strength of approximately 4840 MPa versus jute's average 400-800 MPa. Weight-wise, basalt fiber is denser but still provides a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for durable sacks that do not add excessive bulk. Jute fibers are lighter and biodegradable but lack the superior mechanical strength and durability required for heavy load applications in industrial use.
Moisture Resistance and Weather Adaptability
Basalt fiber exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for sacks used in high-humidity or wet environments. Its natural weather adaptability ensures durability against UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure, outperforming traditional jute fibers that tend to degrade when exposed to prolonged moisture and harsh weather. This enhanced resistance and adaptability make basalt fiber sacks a more reliable solution for long-term outdoor storage and transport applications.
Ease of Manufacturing and Processing
Basalt fiber offers superior ease of manufacturing and processing for sacks due to its consistent fiber diameter and compatibility with standard textile machines, resulting in uniform fabric quality and reduced production downtime. Jute fiber, while biodegradable and eco-friendly, presents challenges such as variability in fiber strength and moisture sensitivity, which complicate spinning and weaving processes. The thermal stability of basalt fiber also enables higher temperature tolerance during processing, making it more versatile for industrial sack production.
Common Applications in Sack Production
Basalt fiber is commonly used in sacks designed for heavy-duty industrial applications due to its high tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability, making it ideal for transporting construction materials and chemicals. Jute fiber sacks are widely favored in agricultural and food packaging sectors because of their natural biodegradability, breathability, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for storing grains, potatoes, and coffee beans. Both fibers serve crucial roles with basalt fibers excelling in protective, long-term storage conditions, while jute fibers support sustainable and eco-friendly packaging needs.
Final Verdict: Which Fiber is Better for Sacks?
Basalt fiber offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty sack applications requiring long-term performance. Jute fiber provides biodegradability and cost-effectiveness, suitable for lightweight, eco-friendly sacks but lacks the robustness and weather resistance of basalt fiber. For sacks demanding high durability and environmental resilience, basalt fiber is the better choice, while jute fiber is preferred for sustainable, low-cost alternatives.
Infographic: Basalt fiber vs Jute fiber for Sack
 azmater.com
azmater.com