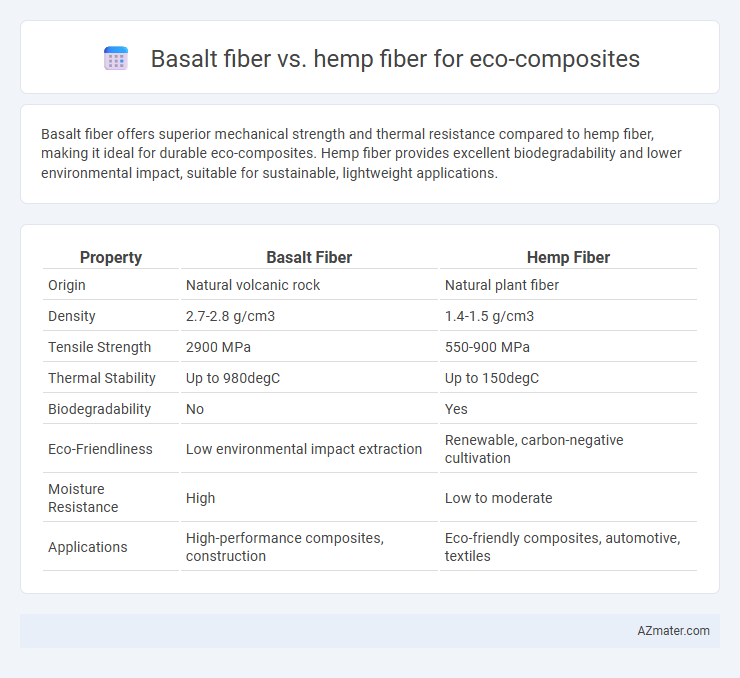
Basalt fiber offers superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for durable eco-composites. Hemp fiber provides excellent biodegradability and lower environmental impact, suitable for sustainable, lightweight applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural volcanic rock | Natural plant fiber |
| Density | 2.7-2.8 g/cm3 | 1.4-1.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2900 MPa | 550-900 MPa |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 980degC | Up to 150degC |
| Biodegradability | No | Yes |
| Eco-Friendliness | Low environmental impact extraction | Renewable, carbon-negative cultivation |
| Moisture Resistance | High | Low to moderate |
| Applications | High-performance composites, construction | Eco-friendly composites, automotive, textiles |
Introduction to Basalt and Hemp Fibers
Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic rock, offers high tensile strength, thermal resistance, and durability, making it an excellent reinforcement in eco-composites. Hemp fiber, obtained from the Cannabis sativa plant, is renewable, biodegradable, and known for its lightweight and good mechanical properties. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives to synthetic materials, with basalt emphasizing strength and heat tolerance while hemp excels in environmental benefits and biodegradability.
Material Origins and Production Processes
Basalt fiber originates from natural volcanic basalt rock, which is melted at high temperatures and extruded into continuous fibers, offering excellent strength and thermal resistance. Hemp fiber is derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, processed through retting, decortication, and mechanical separation to extract long, durable fibers with biodegradability and low environmental impact. Both fibers serve as sustainable reinforcements in eco-composites, with basalt providing mineral-based durability and hemp supplying renewable plant-based flexibility.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Basalt fiber exhibits higher tensile strength, typically ranging from 2,800 to 4,800 MPa, compared to hemp fiber's tensile strength of approximately 500 to 900 MPa, making basalt a superior choice for load-bearing eco-composites. Basalt fiber also offers greater stiffness with a Young's modulus between 85 and 110 GPa, while hemp fiber's modulus ranges from 30 to 70 GPa, contributing to enhanced structural integrity in composites. Despite hemp fiber's lower mechanical properties, its biodegradability and lower density provide advantages in lightweight, sustainable applications where mechanical performance demands are moderate.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt fiber offers significant environmental benefits due to its natural origin from volcanic rock, requiring minimal water and chemical inputs during production, resulting in low carbon emissions. Hemp fiber excels in sustainability by being a rapidly renewable resource with high carbon sequestration capacity and biodegradability, making it ideal for reducing ecological footprint in eco-composites. Both fibers contribute to eco-friendly composite materials, yet basalt fiber provides superior durability while hemp fiber enhances soil health and reduces dependency on synthetic inputs.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Basalt fiber offers higher tensile strength and durability but comes with a cost approximately 20-30% higher than hemp fiber, affecting overall eco-composite production budgets. Hemp fiber is more widely available globally due to extensive agricultural cultivation, leading to lower raw material prices and easier supply chain management. Market analysis shows hemp-based eco-composites dominate due to cost-effectiveness and scalability, while basalt fibers target niche applications requiring enhanced mechanical properties despite limited supplier diversity.
Performance in Composite Applications
Basalt fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and durability compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for high-performance eco-composites in automotive and construction industries. Hemp fiber, while offering excellent biodegradability and lower density, generally provides lower tensile strength and moisture resistance, which can limit its use in load-bearing applications but enhances sustainability and flexibility. The choice between basalt and hemp fibers depends on balancing project requirements for environmental impact with performance demands in composite material engineering.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Basalt fiber exhibits superior durability and weather resistance compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for long-term applications in eco-composites exposed to harsh environments. Its inherent resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations outperforms hemp fiber, which tends to degrade under prolonged exposure to these conditions. The enhanced mechanical strength and longevity of basalt fiber composites contribute to sustainable construction and automotive industries by reducing material replacement frequency.
Applications in Automotive and Construction Industries
Basalt fiber offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for high-performance automotive components such as engine covers and structural panels. Hemp fiber, valued for its biodegradability and lightweight properties, is commonly used in car interior panels and non-structural construction materials like insulation and composite boards. Both fibers enhance sustainability in eco-composites, but basalt fiber's resistance to chemical corrosion and fire makes it preferable in demanding construction applications like reinforcing concrete and load-bearing structures.
Life Cycle Assessment and Recycling Potential
Basalt fiber exhibits a lower environmental impact in Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) compared to hemp fiber due to its high durability and resistance to degradation, reducing the need for frequent replacements in eco-composites. Hemp fiber, while renewable and biodegradable, involves higher agricultural inputs and processing emissions, impacting its overall LCA performance. Recycling potential is significantly higher for basalt fiber because it can be mechanically or chemically recycled without significant loss of properties, whereas hemp fiber composites often face challenges in recycling due to fiber-matrix separation difficulties.
Future Trends in Eco-Composite Materials
Basalt fiber and hemp fiber exhibit distinct advantages in eco-composite applications, with basalt offering superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, while hemp provides renewable, biodegradable benefits. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining basalt and hemp to maximize strength-to-weight ratios and environmental sustainability. Advances in bio-based matrix materials and processing technologies are accelerating the adoption of these fibers in automotive, construction, and aerospace sectors.
Infographic: Basalt fiber vs Hemp fiber for eco-composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com