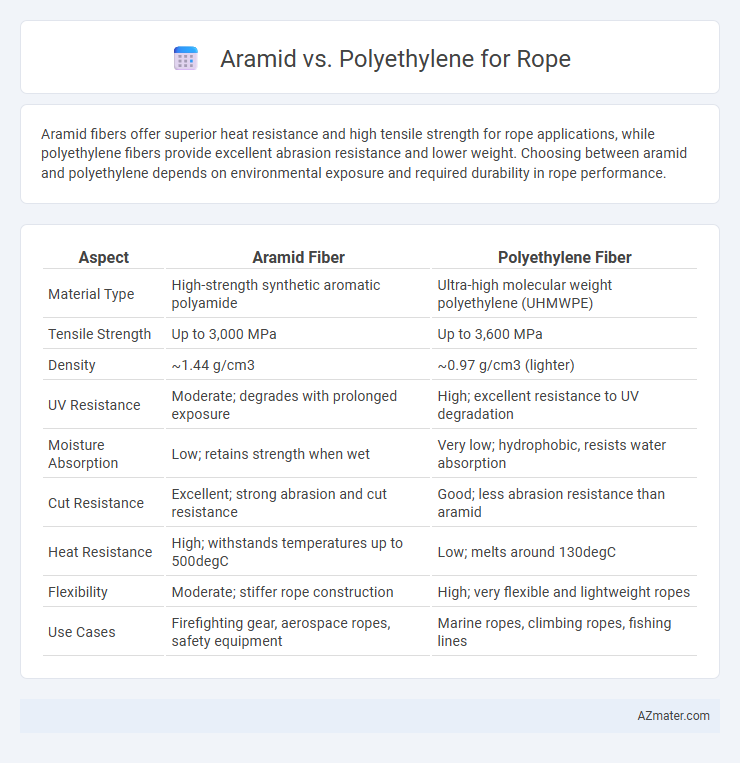
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and high tensile strength for rope applications, while polyethylene fibers provide excellent abrasion resistance and lower weight. Choosing between aramid and polyethylene depends on environmental exposure and required durability in rope performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Aramid Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-strength synthetic aromatic polyamide | Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3,000 MPa | Up to 3,600 MPa |
| Density | ~1.44 g/cm3 | ~0.97 g/cm3 (lighter) |
| UV Resistance | Moderate; degrades with prolonged exposure | High; excellent resistance to UV degradation |
| Moisture Absorption | Low; retains strength when wet | Very low; hydrophobic, resists water absorption |
| Cut Resistance | Excellent; strong abrasion and cut resistance | Good; less abrasion resistance than aramid |
| Heat Resistance | High; withstands temperatures up to 500degC | Low; melts around 130degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate; stiffer rope construction | High; very flexible and lightweight ropes |
| Use Cases | Firefighting gear, aerospace ropes, safety equipment | Marine ropes, climbing ropes, fishing lines |
Introduction to Aramid and Polyethylene Ropes
Aramid ropes are made from synthetic fibers known for exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, commonly used in aerospace and military applications. Polyethylene ropes, particularly ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer lightweight, high tensile strength, and excellent resistance to chemicals and abrasion, making them ideal for marine and industrial use. Both materials provide superior performance but differ in weight, flexibility, and environmental resistance suited to specific rope applications.
Material Composition and Structure
Aramid fibers, like Kevlar, consist of aromatic polyamides with rigid molecular chains that provide exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance for rope applications. Polyethylene ropes are made from ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers, characterized by long, linear polymer chains that offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and excellent abrasion resistance. The molecular arrangement in aramid fibers yields higher thermal stability, while polyethylene's crystalline structure ensures buoyancy and chemical resistance in marine environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit exceptional tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for high-performance ropes in demanding conditions. Polyethylene ropes, particularly Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and outstanding durability against UV exposure and chemical degradation. While aramid ropes provide greater heat resistance and stiffness, polyethylene ropes excel in flexibility and long-term durability in marine environments.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are significantly heavier than polyethylene fibers like Dyneema, impacting the overall weight of rope applications where lightweight performance is crucial. Polyethylene ropes offer superior flexibility due to their low modulus and high elongation at break, enabling easier handling and knotting compared to the stiffer, less stretchy aramid ropes. Weight-sensitive industries often prefer polyethylene ropes for their balance of strength and lightness, while applications requiring heat resistance may favor the heavier, more rigid aramid options.
UV and Chemical Resistance
Aramid fibers, known for their superior UV resistance, maintain tensile strength when exposed to prolonged sunlight, making them ideal for outdoor rope applications. Polyethylene ropes exhibit excellent chemical resistance, particularly against acids and alkalis, which enhances their durability in harsh chemical environments. Combining aramid's UV stability with polyethylene's chemical resilience offers tailored rope solutions for demanding industrial and marine uses.
Water Absorption and Performance
Aramid ropes exhibit low water absorption, maintaining strength and performance even in wet conditions, making them ideal for marine and safety applications. Polyethylene ropes have virtually zero water absorption, offering exceptional buoyancy and resistance to rot, which enhances durability in aquatic environments. While both materials resist moisture, polyethylene generally outperforms aramid in long-term water exposure scenarios due to its superior hydrophobic properties.
Abrasion and Cut Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior cut resistance and maintain strength under abrasion, making them ideal for high-performance ropes exposed to harsh environments. Polyethylene ropes, especially UHMWPE variants like Dyneema, provide exceptional abrasion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratios but are more susceptible to cuts compared to aramid fibers. For applications demanding maximum durability against cuts and abrasion, aramid-based ropes typically outperform polyethylene counterparts.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Aramid ropes, such as Kevlar, typically cost more than polyethylene ropes due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-performance applications but less cost-efficient for general use. Polyethylene ropes, including UHMWPE varieties like Dyneema, offer excellent strength at a lower price and are widely available, providing better cost efficiency for everyday marine, industrial, and recreational uses. Availability of polyethylene ropes is broader globally, ensuring easier procurement and replacement compared to the specialized supply chain of aramid fibers.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are commonly used in ropes requiring high tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for military, aerospace, and climbing applications. Polyethylene ropes, particularly ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer exceptional chemical resistance, low stretch, and lightweight properties, which suit marine, fishing, and industrial lifting uses. The choice between aramid and polyethylene ropes depends on factors like environmental exposure, load requirements, and flexibility needed for specific operational demands.
Choosing the Right Rope: Aramid vs Polyethylene
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and stability under extreme conditions. Polyethylene ropes, especially Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), provide superior abrasion resistance, low density, and excellent resistance to chemicals and moisture, making them lightweight and suitable for marine or outdoor use. Choosing between aramid and polyethylene ropes depends on the specific performance requirements, including strength-to-weight ratio, environmental exposure, and resistance to heat or abrasion.
Infographic: Aramid vs Polyethylene for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com