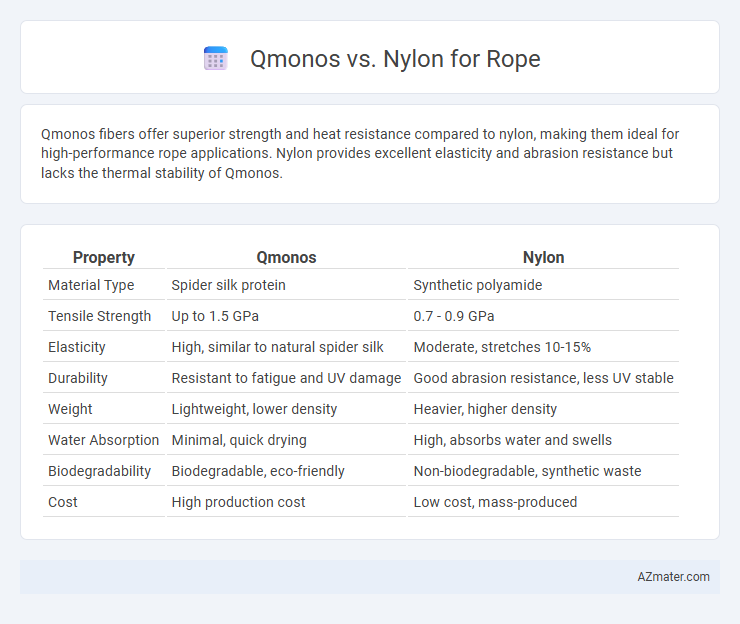
Qmonos fibers offer superior strength and heat resistance compared to nylon, making them ideal for high-performance rope applications. Nylon provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but lacks the thermal stability of Qmonos.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Qmonos | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Spider silk protein | Synthetic polyamide |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1.5 GPa | 0.7 - 0.9 GPa |
| Elasticity | High, similar to natural spider silk | Moderate, stretches 10-15% |
| Durability | Resistant to fatigue and UV damage | Good abrasion resistance, less UV stable |
| Weight | Lightweight, lower density | Heavier, higher density |
| Water Absorption | Minimal, quick drying | High, absorbs water and swells |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, synthetic waste |
| Cost | High production cost | Low cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Qmonos and Nylon Ropes
Qmonos rope, made from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers, offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior abrasion resistance compared to traditional nylon ropes. Nylon ropes are known for their elasticity, shock absorption, and durability, making them suitable for dynamic loads but typically heavier and more prone to UV degradation. Selecting between Qmonos and nylon depends on application demands such as load capacity, wear resistance, and environmental conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Qmonos is a synthetic rope fiber composed primarily of poly(p-phenylene-2,6-benzobisoxazole) (PBO), characterized by a rigid, rod-like molecular structure that provides exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability. Nylon, a polyamide polymer, features a flexible aliphatic chain with amide linkages that confer elasticity and abrasion resistance but offer lower strength and heat resistance compared to Qmonos. The crystalline and highly oriented molecular alignment in Qmonos contributes to its superior performance in high-performance rope applications, outperforming the semi-crystalline, less rigid structure of nylon.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Qmonos fiber exhibits superior tensile strength compared to traditional nylon, making it more resistant to breakage under heavy loads. Its enhanced durability stems from improved resistance to abrasion and UV degradation, resulting in longer lifespan ropes for demanding applications. Nylon ropes, while strong and versatile, tend to absorb moisture and weaken over time, whereas Qmonos maintains structural integrity in harsher environmental conditions.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Qmonos rope offers exceptional flexibility due to its ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers, allowing easy maneuverability and reduced stiffness compared to traditional nylon ropes. Nylon ropes, while strong and durable, tend to be less flexible and can feel stiffer, which may impact handling comfort during extended use. The superior flexibility of Qmonos enhances knot tying and grip, making it ideal for applications requiring precise control and smooth handling.
Weight and Density Differences
Qmonos fibers have a significantly lower density of approximately 1.26 g/cm3 compared to Nylon's density of around 1.15 g/cm3, which directly impacts the overall weight of ropes made from these materials. Ropes manufactured from Nylon tend to be lighter due to its lower density, making them preferable for applications requiring minimal weight without sacrificing strength. However, Qmonos ropes offer superior tensile strength and heat resistance, often justifying the slightly heavier weight in specialized high-performance environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Qmonos, a spider silk protein-based fiber, offers significant environmental advantages over traditional nylon due to its biodegradable nature and lower carbon footprint during production. Nylon, derived from petrochemicals, contributes to plastic pollution and requires energy-intensive manufacturing processes that emit substantial greenhouse gases. Choosing Qmonos for rope materials promotes sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing microplastic waste in marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
Resistance to Moisture and Chemicals
Qmonos rope exhibits superior resistance to moisture and chemicals compared to Nylon, maintaining strength and flexibility even in wet or corrosive environments. Nylon tends to absorb water, which can weaken its fibers and degrade performance over time when exposed to chemicals. Qmonos, derived from Kevlar aramid fibers, offers enhanced durability and longevity in applications requiring high resistance to harsh substances and moisture.
Cost and Availability
Qmonos rope typically costs more than nylon due to its superior heat resistance and strength, making it ideal for specialized applications like firefighting and rescue. Nylon rope is vastly more available worldwide, found in hardware stores and online retailers at competitive prices, often preferred for general-purpose use. The cost-effectiveness of nylon versus Qmonos depends largely on application requirements and budget constraints.
Common Applications in Industry
Qmonos fibers exhibit exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for aerospace and electrical industries where durability under extreme conditions is critical. Nylon ropes are widely used in marine, construction, and safety applications due to their elasticity, abrasion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Industrial sectors prefer Qmonos for specialized high-performance needs, while nylon remains popular for general-purpose and load-bearing tasks.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Qmonos fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to traditional nylon, positioning them as a revolutionary material for next-generation rope manufacturing. Innovations in Qmonos production promise enhanced durability and environmental sustainability through bio-based synthesis methods, outperforming conventional petroleum-derived nylon. Future prospects include integration into high-performance industrial and safety applications, driven by ongoing research in molecular engineering and fiber optimization.
Infographic: Qmonos vs Nylon for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com