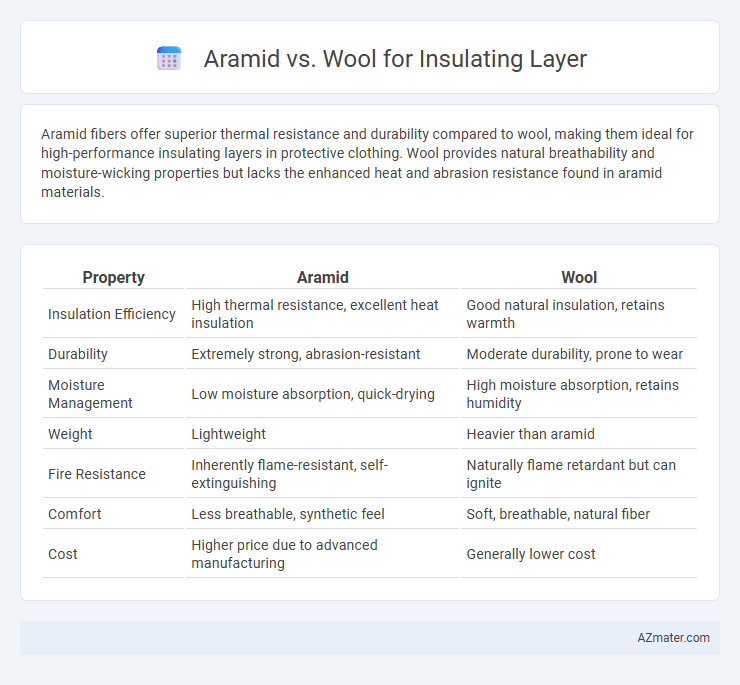
Aramid fibers offer superior thermal resistance and durability compared to wool, making them ideal for high-performance insulating layers in protective clothing. Wool provides natural breathability and moisture-wicking properties but lacks the enhanced heat and abrasion resistance found in aramid materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Efficiency | High thermal resistance, excellent heat insulation | Good natural insulation, retains warmth |
| Durability | Extremely strong, abrasion-resistant | Moderate durability, prone to wear |
| Moisture Management | Low moisture absorption, quick-drying | High moisture absorption, retains humidity |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than aramid |
| Fire Resistance | Inherently flame-resistant, self-extinguishing | Naturally flame retardant but can ignite |
| Comfort | Less breathable, synthetic feel | Soft, breathable, natural fiber |
| Cost | Higher price due to advanced manufacturing | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Insulating Layers
Aramid fibers and wool represent two distinct materials commonly used as insulating layers in protective and thermal garments. Aramid offers exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and durability, making it ideal for environments requiring flame retardancy and mechanical protection. Wool provides natural insulation, moisture-wicking properties, and breathability, ensuring comfort and thermal regulation in variable conditions.
Key Properties of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional thermal resistance, maintaining strength and stability at temperatures exceeding 400degC, making them ideal for high-performance insulating layers. Their inherent high tensile strength, superior abrasion resistance, and low flammability provide enhanced durability compared to wool, which tends to degrade under extreme heat. Unlike wool, aramid fibers also resist chemical exposure and moisture, ensuring sustained insulation efficiency in demanding industrial and protective applications.
Key Properties of Wool Fibers
Wool fibers provide excellent thermal insulation due to their natural crimp, which traps air and retains heat effectively, making wool ideal for cold weather clothing layers. Unlike aramid fibers, wool is moisture-wicking and breathable, maintaining warmth even when damp without losing insulating properties. Its biodegradable and renewable nature also offers an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic aramid fibers in insulation applications.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Aramid fibers offer superior thermal insulation performance compared to wool due to their high heat resistance and low thermal conductivity, making them ideal for extreme temperature environments. Wool provides natural insulation by trapping air in its fibers, maintaining warmth effectively but with lower heat resistance and durability under high-heat conditions. The choice between aramid and wool insulation layers depends on application-specific thermal requirements, with aramid favored in industrial and high-heat settings, while wool suits moderate temperature and moisture-regulating needs.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Aramid fibers offer exceptional moisture-wicking properties that rapidly disperse sweat, maintaining dryness and enhancing comfort in insulating layers. Wool naturally regulates moisture through its hygroscopic structure, absorbing and releasing water vapor without feeling wet, which promotes breathability and temperature balance. Combining aramid's quick-drying capabilities with wool's moisture retention creates an insulating layer optimized for both moisture management and sustained breathability in diverse conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional durability and longevity compared to wool, maintaining structural integrity under extreme conditions such as high heat and abrasion. Wool, while naturally insulating and resistant to moisture, tends to degrade faster due to exposure to environmental factors like UV rays and repeated compression. The superior tensile strength and resilience of aramid make it the preferred choice for long-lasting insulating layers in demanding applications.
Comfort and Wearability
Aramid fibers offer exceptional heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for high-performance insulation but tend to be less breathable and softer compared to wool. Wool provides superior moisture-wicking properties and natural temperature regulation, enhancing overall comfort during varied activities. Choosing between aramid and wool depends on balancing wearability, where wool excels in softness and comfort, while aramid prioritizes protection and longevity.
Fire and Heat Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior fire and heat resistance compared to wool due to their high thermal stability and ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 400degC without melting. Wool, while naturally flame-retardant and self-extinguishing, begins to degrade at temperatures around 570degC but offers lower thermal insulation performance. For applications requiring enhanced protection against extreme heat and direct flame exposure, aramid-based insulating layers deliver more reliable and durable fire-resistant properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, known for their high strength and durability, have a significant environmental impact due to their petroleum-based production and non-biodegradability. Wool, a natural and renewable fiber, offers superior sustainability with its biodegradability and minimal chemical processing, making it an eco-friendly insulating layer choice. Wool's carbon sequestration ability during sheep grazing also contributes positively to reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Best Uses: Aramid vs Wool in Real-World Applications
Aramid fibers excel in high-performance insulation applications requiring exceptional heat resistance, flame retardancy, and durability, making them ideal for protective clothing, firefighting gear, and aerospace components. Wool provides natural insulation with moisture-wicking properties and breathability, suited for everyday wear, outdoor clothing, and sustainable building insulation. In real-world use, aramid suits harsh industrial environments while wool thrives in comfort-focused, eco-friendly settings.
Infographic: Aramid vs Wool for Insulating Layer
 azmater.com
azmater.com