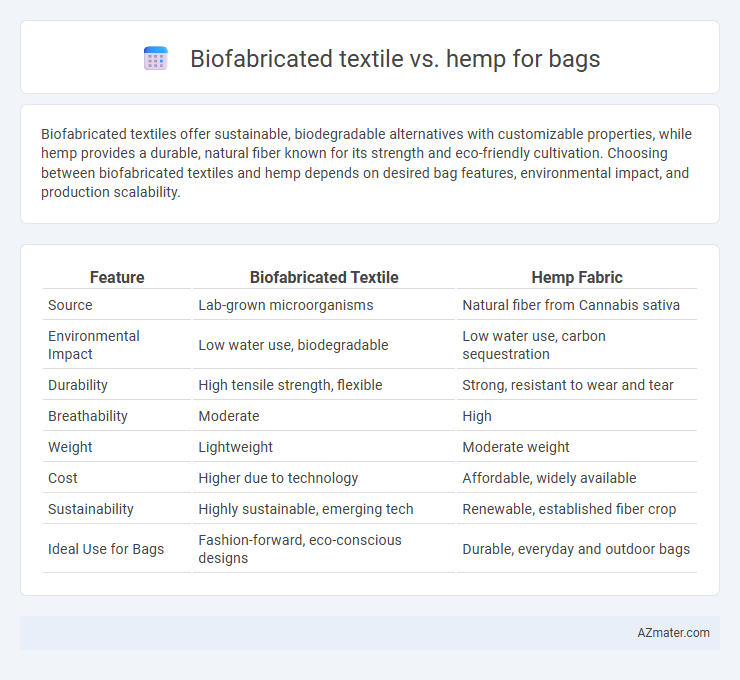
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives with customizable properties, while hemp provides a durable, natural fiber known for its strength and eco-friendly cultivation. Choosing between biofabricated textiles and hemp depends on desired bag features, environmental impact, and production scalability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Hemp Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown microorganisms | Natural fiber from Cannabis sativa |
| Environmental Impact | Low water use, biodegradable | Low water use, carbon sequestration |
| Durability | High tensile strength, flexible | Strong, resistant to wear and tear |
| Breathability | Moderate | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Cost | Higher due to technology | Affordable, widely available |
| Sustainability | Highly sustainable, emerging tech | Renewable, established fiber crop |
| Ideal Use for Bags | Fashion-forward, eco-conscious designs | Durable, everyday and outdoor bags |
Introduction: The Shift Toward Sustainable Bag Materials
Biofabricated textiles represent an innovative leap in sustainable bag materials, offering customizable durability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional fibers. Hemp, a naturally robust and biodegradable plant fiber, remains a popular eco-friendly choice due to its low water usage and soil-regenerative properties. Both materials align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products, but biofabricated textiles provide enhanced potential in reducing resource consumption and waste throughout the supply chain.
Understanding Biofabricated Textiles: Definition and Process
Biofabricated textiles are engineered materials created through biological processes such as microbial fermentation, where cells produce fibers or matrices that can be transformed into fabric, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional plant-based fibers like hemp. Unlike hemp, which requires extensive agricultural cultivation and processing to produce durable fibers for bags, biofabricated textiles are grown in controlled environments, reducing land use, water consumption, and carbon emissions. This innovative method allows for customizable textile properties, improved biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional hemp-based bag materials.
Hemp Fabric: History and Production Methods
Hemp fabric, derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, has been used for centuries due to its durability and sustainability. Traditional processing methods involve retting, drying, and decortication to separate fibers, followed by combing and spinning into yarn. Modern advancements include enzyme retting and mechanical decortication, enhancing fiber quality and reducing environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives like biofabricated textiles.
Environmental Impact: Biofabricated vs Hemp Textiles
Biofabricated textiles reduce resource consumption by using lab-grown fibers that minimize water usage and eliminate pesticides, offering a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional agriculture. Hemp textiles require less water and chemicals than cotton, promoting soil health and carbon sequestration through natural farming practices. Both materials present eco-friendly options, but biofabricated textiles have the potential to further decrease environmental degradation by bypassing traditional farming limitations.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Biofabricated textiles exhibit superior durability due to their engineered molecular structure, offering enhanced resistance to wear, tear, and environmental factors compared to hemp. Hemp fibers provide strong tensile strength and natural breathability, but they tend to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and moisture. Performance-wise, biofabricated materials often deliver consistent texture and water resistance, making them ideal for high-performance bags, whereas hemp bags offer sustainability benefits with moderate durability.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Biofabricated textiles offer superior aesthetic versatility with customizable textures, patterns, and colors that mimic luxury materials, enhancing high-end bag designs. Hemp provides a natural, rustic look with limited color options but excels in durability and eco-friendly appeal, favored for artisanal and earthy bag aesthetics. Designers choose biofabricated textiles for innovative, sleek finishes, while hemp suits minimalist, organic styles emphasizing sustainability.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Biofabricated textiles, created through cellular agriculture, offer superior biodegradability by breaking down efficiently without releasing harmful residues, making them ideal for eco-friendly bag production. Hemp fibers also provide excellent biodegradability and natural durability, composting within months while reducing landfill waste. Considering end-of-life scenarios, biofabricated textiles can be engineered for specific degradation rates, whereas hemp bags benefit from established recycling and composting infrastructure globally.
Market Availability and Scalability
Biofabricated textiles, produced through cellular agriculture, offer sustainable alternatives but face limited market availability and high production costs that hinder large-scale adoption in the bag industry. Hemp, a well-established natural fiber, demonstrates broad market presence with scalable cultivation and processing methods enabling consistent supply for eco-friendly bag manufacturing. The scalability advantage of hemp lies in its rapid growth cycles and existing agricultural infrastructure, contrasting with the nascent, resource-intensive biofabricated textile sector.
Consumer Perception and Adoption
Biofabricated textiles are gaining attention for their sustainability and innovative production methods, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking cutting-edge materials. Hemp is widely recognized for its durability, biodegradability, and natural appeal, attracting buyers who prioritize traditional eco-friendly fibers. Consumer adoption favors hemp for its established reputation and affordability, while biofabricated textiles are emerging within niche markets driven by technological interest and environmental innovation.
Future Prospects: Innovations and Trends in Sustainable Bag Materials
Biofabricated textiles offer groundbreaking potential in sustainable bag manufacturing by utilizing microorganisms to produce biodegradable, customizable materials with minimal environmental impact. Hemp remains a strong contender due to its natural durability, carbon-negative cultivation process, and biodegradability, aligning with eco-conscious consumer demand. Innovations merging biofabrication technologies with hemp fibers promise enhanced strength, reduced resource consumption, and scalable production for the future of sustainable bag materials.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Hemp for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com