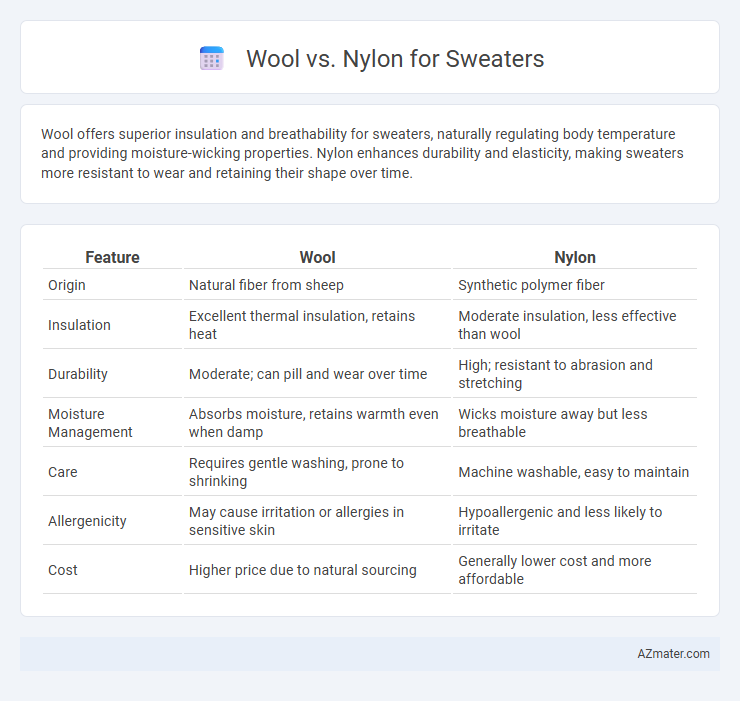
Wool offers superior insulation and breathability for sweaters, naturally regulating body temperature and providing moisture-wicking properties. Nylon enhances durability and elasticity, making sweaters more resistant to wear and retaining their shape over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wool | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural fiber from sheep | Synthetic polymer fiber |
| Insulation | Excellent thermal insulation, retains heat | Moderate insulation, less effective than wool |
| Durability | Moderate; can pill and wear over time | High; resistant to abrasion and stretching |
| Moisture Management | Absorbs moisture, retains warmth even when damp | Wicks moisture away but less breathable |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, prone to shrinking | Machine washable, easy to maintain |
| Allergenicity | May cause irritation or allergies in sensitive skin | Hypoallergenic and less likely to irritate |
| Cost | Higher price due to natural sourcing | Generally lower cost and more affordable |
Introduction: Wool vs Nylon Sweaters
Wool sweaters offer natural warmth, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for cold weather. Nylon sweaters provide increased durability, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion, contributing to long-lasting wear. Comparing wool and nylon highlights key benefits for selecting the right material based on comfort and performance needs.
Material Origins: Natural Wool vs Synthetic Nylon
Wool comes from the fleece of sheep, making it a natural, renewable fiber cherished for its breathability and moisture-wicking properties. Nylon, a synthetic polymer derived from petrochemicals, offers durability and elasticity but lacks the natural insulation and biodegradability found in wool. Choosing wool provides eco-friendly benefits and superior temperature regulation, while nylon emphasizes strength and resistance to abrasion in sweater fabrics.
Comfort and Feel: Texture Differences
Wool sweaters offer a naturally soft, breathable texture that provides warmth without overheating, while maintaining moisture-wicking properties ideal for cold weather. Nylon sweaters tend to feel smoother and lighter but can lack the natural breathability and moisture regulation found in wool, sometimes resulting in a less comfortable feel during prolonged wear. Wool fibers create a plush, slightly coarse surface that enhances insulation, whereas nylon's synthetic texture provides durability and stretch but may feel less cozy against the skin.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Wool fibers contain natural crimps that trap heat and provide superior insulation, making wool sweaters exceptionally warm even in damp conditions. Nylon, a synthetic material, offers durability and moisture-wicking properties but has lower insulation capacity compared to wool. Choosing wool ensures better temperature regulation and comfort in cold weather, while nylon sweaters excel in lightweight performance and abrasion resistance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Wool fibers naturally resist wear and tear, offering high durability and excellent longevity in sweaters due to their elasticity and resilience to stretching. Nylon, a synthetic fiber, provides superior abrasion resistance and strength but may degrade faster when exposed to heat or UV light over time. Sweaters combining wool and nylon blends often benefit from enhanced durability and longer lifespan by balancing natural fiber comfort with synthetic fiber toughness.
Moisture-Wicking and Breathability
Wool excels in moisture-wicking and breathability due to its natural lanolin content, which repels water while allowing sweat vapor to escape, keeping the skin dry and comfortable. Nylon, a synthetic fiber, tends to trap moisture and heat, reducing breathability and potentially causing discomfort during prolonged wear. Therefore, wool is often preferred for sweaters meant for active or outdoor use where moisture management is critical.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Wool sweaters require gentle hand washing or dry cleaning to maintain fiber integrity and prevent shrinkage, while nylon sweaters are more durable and machine washable, offering easier maintenance. Wool fibers are prone to felting and pilling if exposed to heat or agitation, necessitating careful drying flat to retain shape. Nylon's synthetic composition resists wrinkles and abrasion, making it a low-maintenance option that dries quickly and holds color longer.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wool is a renewable, biodegradable fiber derived from sheep, offering a lower environmental footprint due to its natural degradation and ability to be sustainably harvested with proper grazing practices. Nylon, a synthetic polymer made from petrochemicals, relies heavily on non-renewable fossil fuels and generates significant greenhouse gas emissions during production, contributing to microplastic pollution. Choosing wool supports circular economy principles and soil health, while nylon's environmental impact includes long-lasting waste accumulation and higher carbon emissions.
Price and Overall Value
Wool sweaters typically cost more upfront due to the natural fiber's quality, warmth, and durability, often ranging from $50 to $200, while nylon sweaters are generally cheaper, priced between $20 and $60. Wool offers superior insulation, moisture-wicking, and breathability, making it a better long-term investment despite the higher price. Nylon provides affordability and durability but lacks the same comfort and temperature regulation, which can affect overall value for colder climates.
Best Uses: Choosing the Right Sweater Fabric
Wool sweaters excel in insulation and moisture-wicking, making them ideal for cold, damp conditions and outdoor activities like hiking or skiing. Nylon sweaters offer durability and lightweight comfort, suited for everyday wear and layering during mild weather. Selecting between wool and nylon depends on the climate, activity level, and desired warmth, with wool favored for thermal protection and nylon for flexibility and ease of care.
Infographic: Wool vs Nylon for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com