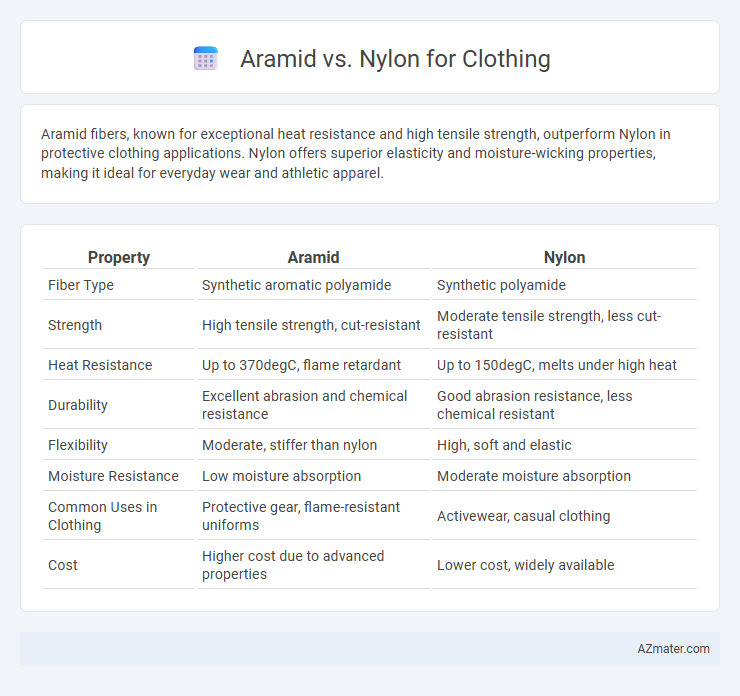
Aramid fibers, known for exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, outperform Nylon in protective clothing applications. Nylon offers superior elasticity and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for everyday wear and athletic apparel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide | Synthetic polyamide |
| Strength | High tensile strength, cut-resistant | Moderate tensile strength, less cut-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 370degC, flame retardant | Up to 150degC, melts under high heat |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion and chemical resistance | Good abrasion resistance, less chemical resistant |
| Flexibility | Moderate, stiffer than nylon | High, soft and elastic |
| Moisture Resistance | Low moisture absorption | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Common Uses in Clothing | Protective gear, flame-resistant uniforms | Activewear, casual clothing |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Aramid and Nylon Fabrics
Aramid fabrics, known for their exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, are widely used in protective clothing and industrial applications. Nylon, a synthetic polymer fiber prized for its elasticity, durability, and lightweight properties, is commonly found in everyday apparel and activewear. Both fibers offer distinct advantages: aramid provides superior flame retardance and abrasion resistance, while nylon excels in flexibility and moisture-wicking capabilities.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Aramid fibers, composed of aromatic polyamides, feature rigid molecular chains with benzene rings linked by amide bonds, providing exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength. Nylon, a synthetic polyamide made from aliphatic chains, has a more flexible molecular structure, enhancing elasticity and moisture absorption. The chemical composition and structural differences directly influence their respective durability, thermal stability, and comfort in clothing applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit exceptional tensile strength and high resistance to abrasion, outperforming Nylon in durability under extreme conditions. Nylon offers good flexibility and moderate strength but tends to degrade faster with prolonged exposure to UV light and chemicals compared to aramid. For clothing requiring superior impact resistance and long-lasting wear, aramid is the preferred material due to its unmatched combination of toughness and thermal stability.
Heat and Flame Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer superior heat and flame resistance compared to nylon, making them ideal for protective clothing in high-temperature environments like firefighting and industrial workwear. Nylon melts and ignites at lower temperatures, posing a higher risk of burns or damage under heat exposure, whereas aramid fabrics maintain structural integrity and resist ignition even at extreme temperatures beyond 400degC (752degF). For garments requiring both durability and enhanced safety against flames, aramid materials provide unmatched performance over conventional nylon textiles.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Aramid fibers provide exceptional heat resistance and durability but tend to be stiffer and less breathable compared to nylon, which offers superior softness and flexibility ideal for everyday clothing comfort. Nylon excels in moisture-wicking and stretchability, enhancing wearability for active use, whereas aramid's rigidity can limit comfort during prolonged wear. When prioritizing comfort and wearability in clothing, nylon is generally preferred, especially for garments requiring lightweight and breathable properties.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Aramid fibers exhibit low moisture absorption, typically less than 5%, making them highly resistant to water and ideal for protective clothing that requires durability and flame resistance without retaining moisture. Nylon absorbs more moisture, around 4-7%, which can impact comfort but provides better breathability and stretch, suitable for activewear and everyday garments. The balance between aramid's moisture resistance and nylon's breathability influences their use in specialized versus casual clothing applications.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to nylon, making them significantly lighter while maintaining high durability for protective clothing applications. Nylon exhibits greater flexibility and elasticity, providing enhanced comfort and ease of movement in everyday apparel but with lower tensile strength relative to aramid. Weight analysis consistently shows aramid fabrics reduce overall garment weight, while flexibility assessments favor nylon for stretch and adaptability in various clothing designs.
Cost and Availability
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional heat and abrasion resistance, typically come at a higher cost compared to nylon, which is more affordable and widely available. Nylon's broad availability in diverse textile markets makes it a cost-effective choice for mass-produced clothing, while aramid is often reserved for specialized, high-performance garments due to limited suppliers and complex manufacturing processes. Consumers seeking budget-friendly options usually favor nylon, whereas professionals requiring durability and safety prioritize aramid despite the premium price.
Typical Applications in Clothing
Aramid fibers are predominantly used in protective clothing such as firefighter suits, military uniforms, and industrial workwear due to their exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength. Nylon is commonly found in everyday apparel including sportswear, hosiery, and outerwear because of its elasticity, durability, and moisture-wicking properties. The choice between aramid and nylon depends largely on the required performance attributes like flame retardancy for aramid or flexibility and comfort for nylon garments.
Choosing Between Aramid and Nylon for Your Needs
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent durability, making them ideal for protective clothing and industrial applications where safety is paramount. Nylon is more flexible, lightweight, and cost-effective, providing comfort and ease of movement for everyday apparel or activewear. Selecting between aramid and nylon depends on whether you prioritize enhanced protection and durability or lightweight comfort and affordability for your specific clothing needs.
Infographic: Aramid vs Nylon for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com