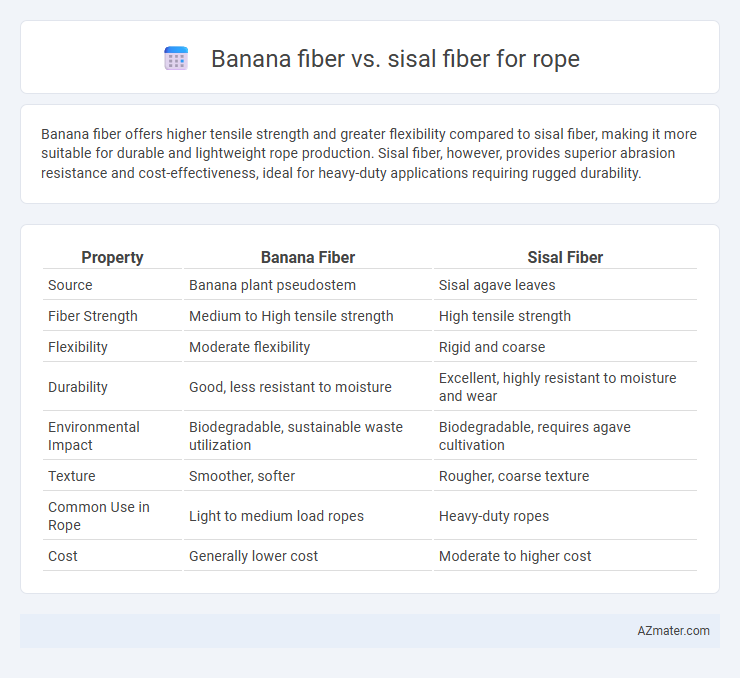
Banana fiber offers higher tensile strength and greater flexibility compared to sisal fiber, making it more suitable for durable and lightweight rope production. Sisal fiber, however, provides superior abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring rugged durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Banana Fiber | Sisal Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Banana plant pseudostem | Sisal agave leaves |
| Fiber Strength | Medium to High tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Rigid and coarse |
| Durability | Good, less resistant to moisture | Excellent, highly resistant to moisture and wear |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable waste utilization | Biodegradable, requires agave cultivation |
| Texture | Smoother, softer | Rougher, coarse texture |
| Common Use in Rope | Light to medium load ropes | Heavy-duty ropes |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate to higher cost |
Introduction to Natural Fiber Ropes
Natural fiber ropes like banana fiber and sisal fiber are widely valued for their eco-friendly properties and strength. Banana fiber offers high tensile strength and flexibility, making it suitable for lightweight ropes, while sisal fiber is known for its rough texture and durability in heavy-duty applications. Both fibers provide excellent biodegradability, making them sustainable choices compared to synthetic alternatives.
Overview of Banana Fiber
Banana fiber, derived from the pseudostem of the banana plant, is a sustainable and eco-friendly material widely used in rope manufacturing due to its high tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to moisture. Compared to sisal fiber, banana fiber offers superior softness and biodegradability, making it an excellent choice for environmentally conscious applications. Its natural durability and ability to withstand heavy loads make banana fiber a competitive alternative to traditional sisal fiber ropes.
Overview of Sisal Fiber
Sisal fiber, derived from the Agave sisalana plant, offers exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it a preferred choice for rope manufacturing. Compared to banana fiber, sisal fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance, providing enhanced performance in marine, agricultural, and industrial applications. Its coarse texture and natural rigidity contribute to superior knot-holding capacity and longevity in harsh environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Banana fiber exhibits tensile strength ranging between 458 to 914 MPa, making it highly effective for rope applications requiring flexibility and durability. Sisal fiber, with tensile strength typically around 400 to 700 MPa, offers excellent abrasion resistance but generally lower strength compared to banana fiber. The higher mechanical strength of banana fiber enhances rope performance in heavy-duty uses, while sisal fiber provides a balance of strength and resilience suitable for medium-load ropes.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Banana fiber exhibits moderate durability but lower weather resistance compared to sisal fiber when used for rope, often showing faster degradation in humid or wet conditions. Sisal fiber is highly durable and possesses superior weather resistance, maintaining strength and flexibility under exposure to sunlight, moisture, and varying temperatures. For long-lasting outdoor rope applications, sisal fiber is generally preferred due to its enhanced resilience against environmental stressors.
Flexibility and Handling
Banana fiber offers superior flexibility compared to sisal fiber, making it ideal for ropes that require easy bending and smooth handling. Sisal fiber is stiffer and rougher, providing higher strength but less pliability, which can affect knotting and maneuverability. For applications demanding greater ease in tying and flexibility, banana fiber ropes are preferred, while sisal fibers excel in durability and abrasion resistance.
Environmental Sustainability
Banana fiber and sisal fiber both offer environmentally sustainable options for rope production due to their natural, biodegradable properties and low-impact harvesting processes. Banana fiber is derived from the pseudostem of banana plants, a byproduct of fruit cultivation, which promotes waste reduction and resource efficiency. Sisal fiber, sourced from Agave sisalana leaves, is highly durable and requires minimal chemical processing, making it a renewable resource with a smaller ecological footprint compared to synthetic alternatives.
Cost and Availability
Banana fiber rope is generally more affordable due to the abundant availability of banana plants in tropical regions, making raw material sourcing cost-effective. Sisal fiber, extracted from the Agave sisalana plant, tends to be pricier because of limited cultivation areas and more intensive processing requirements. Both fibers offer durability, but banana fiber's lower cost and wider availability make it a preferred choice for budget-conscious rope production.
Common Applications of Banana and Sisal Ropes
Banana fiber ropes are commonly used in marine applications, agriculture, and packaging industries due to their high tensile strength and resistance to saltwater. Sisal fiber ropes find extensive use in construction, landscaping, and animal husbandry because of their durability, abrasion resistance, and eco-friendly nature. Both fibers are favored for making biodegradable ropes that support sustainable and environmentally conscious practices.
Which Fiber is Best for Your Needs?
Banana fiber offers superior flexibility and softness, making it ideal for ropes used in delicate applications or crafts requiring a gentle touch. Sisal fiber provides excellent strength and durability, suitable for heavy-duty ropes exposed to rough handling and outdoor conditions. Choosing the best fiber depends on whether you prioritize tensile strength and abrasion resistance (sisal) or softness and eco-friendly sustainability (banana fiber).
Infographic: Banana fiber vs Sisal fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com