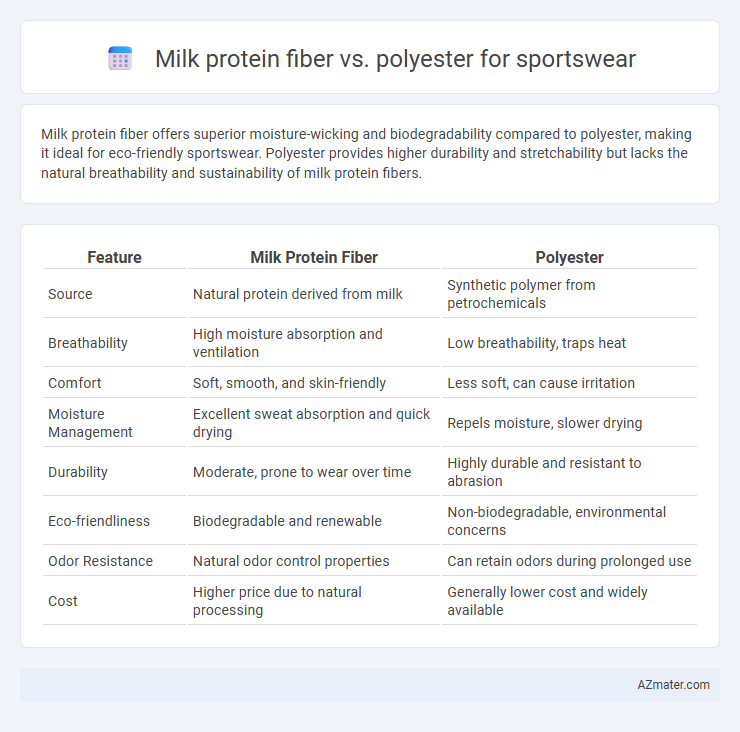
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and biodegradability compared to polyester, making it ideal for eco-friendly sportswear. Polyester provides higher durability and stretchability but lacks the natural breathability and sustainability of milk protein fibers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural protein derived from milk | Synthetic polymer from petrochemicals |
| Breathability | High moisture absorption and ventilation | Low breathability, traps heat |
| Comfort | Soft, smooth, and skin-friendly | Less soft, can cause irritation |
| Moisture Management | Excellent sweat absorption and quick drying | Repels moisture, slower drying |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear over time | Highly durable and resistant to abrasion |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable and renewable | Non-biodegradable, environmental concerns |
| Odor Resistance | Natural odor control properties | Can retain odors during prolonged use |
| Cost | Higher price due to natural processing | Generally lower cost and widely available |
Introduction to Milk Protein Fiber and Polyester
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein protein in milk through a biodegradable process, offers natural moisture-wicking, odor resistance, and softness ideal for sportswear comfort. Polyester, a synthetic polymer made from petrochemicals, provides durability, quick-drying properties, and excellent stretch recovery, making it a common choice for performance apparel. Both fibers serve distinct roles in sportswear, with milk protein fiber emphasizing eco-friendly, skin-friendly benefits and polyester focusing on high strength and technical performance.
Composition and Structure of Milk Protein Fiber
Milk protein fiber is derived from casein, a natural protein found in milk, processed into biodegradable fibers with excellent moisture absorption and softness. Its unique amino acid composition gives it breathability and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for sportswear to enhance comfort and hygiene. Polyester consists of synthetic polymers with a smooth, hydrophobic structure that delivers durability and quick-drying performance but lacks the natural softness and biodegradability of milk protein fiber.
Polyester Fiber: Properties and Manufacturing
Polyester fiber, widely used in sportswear, is synthesized from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), known for its strong, durable, and moisture-wicking properties that enhance athletic performance and comfort. Its manufacturing process involves polymerization, extrusion, spinning, and drawing, resulting in fibers that resist shrinking, stretching, and UV damage. Compared to milk protein fiber, polyester offers superior quick-drying ability, high tensile strength, and excellent color retention, making it a preferred choice for activewear and high-performance garments.
Moisture Management and Breathability Comparison
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture management by naturally absorbing sweat and releasing it quickly, keeping athletes dry and comfortable during intense workouts. Polyester, while durable and lightweight, tends to retain moisture longer, which can lead to a clammy feeling and reduced breathability. The natural properties of milk protein fiber enhance airflow and evaporation, making it a more breathable option for high-performance sportswear compared to synthetic polyester.
Comfort and Softness: User Experience
Milk protein fiber in sportswear offers superior comfort and softness due to its natural moisture-wicking properties and smooth texture, enhancing breathability and reducing skin irritation during intense workouts. Polyester, while durable and quick-drying, often lacks the same level of softness and can sometimes cause discomfort from trapped moisture or friction. Athletes seeking a gentle, breathable fabric for prolonged wear typically prefer milk protein fiber over synthetic polyester for improved overall user experience.
Durability and Longevity in Activewear
Milk protein fiber in sportswear offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort during intense workouts, while polyester excels in durability and resistance to wear and tear. Polyester fibers maintain strength through repeated washing and high-intensity use, making them a popular choice for long-lasting activewear designed to endure rigorous physical activity. However, milk protein fiber, although less durable than polyester, provides biodegradability and a softer feel, offering a sustainable alternative with moderate longevity in sportswear.
Odor Control and Antibacterial Properties
Milk protein fiber naturally contains casein, which exhibits strong antibacterial properties that inhibit bacterial growth and reduce odor buildup during physical activity. Polyester sportswear, while durable and moisture-wicking, typically relies on chemical treatments to achieve odor control and lacks inherent antibacterial qualities. Milk protein fiber fabrics offer sustainable and breathable alternatives that maintain freshness longer without synthetic additives.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Milk protein fiber offers a sustainable alternative to polyester by being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, significantly reducing landfill waste and microplastic pollution. Polyester, while durable and moisture-wicking, is petroleum-based and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions throughout production and degradation. Choosing milk protein fiber for sportswear minimizes environmental footprint by utilizing renewable inputs and ensuring natural decomposition without releasing harmful residues.
Suitability for Different Sports Activities
Milk protein fiber exhibits excellent moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for low to moderate impact sports like yoga, Pilates, and casual gym workouts where comfort and odor control are essential. Polyester, known for its durability, quick-drying capability, and high tensile strength, suits high-intensity activities such as running, cycling, and team sports that demand robust fabric performance and stretch recovery. Choosing between milk protein fiber and polyester depends on the specific sport's intensity and the need for breathability versus durability in sportswear.
Cost and Market Availability
Milk protein fiber offers a sustainable alternative to polyester with a generally higher production cost due to limited raw material sourcing and manufacturing scale. Polyester dominates the sportswear market because of its low cost, mass production, and widespread availability, making it the preferred choice for budget-conscious brands. Despite higher costs, milk protein fiber is gaining interest for its biodegradability and comfort, but market availability remains limited compared to polyester's extensive supply chain.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Polyester for Sportswear
 azmater.com
azmater.com