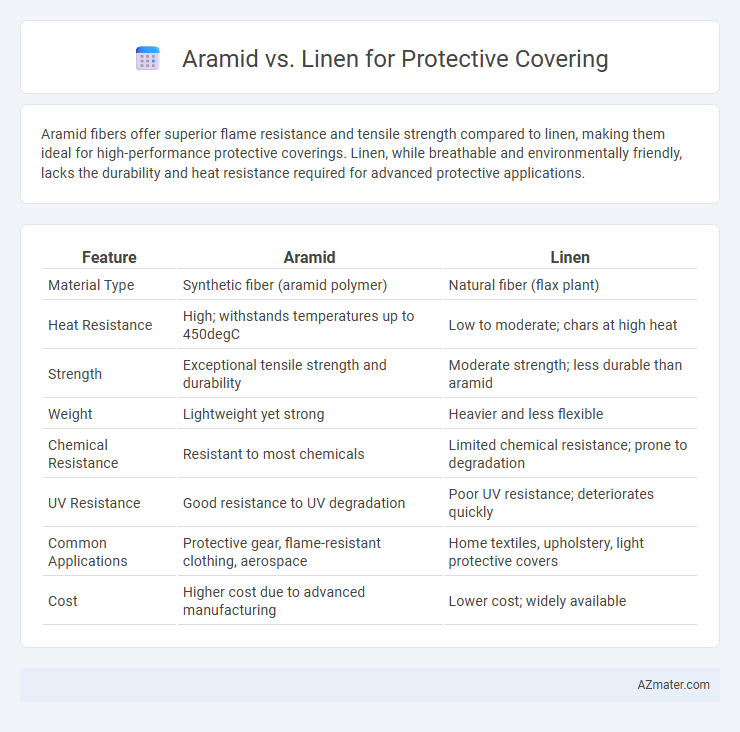
Aramid fibers offer superior flame resistance and tensile strength compared to linen, making them ideal for high-performance protective coverings. Linen, while breathable and environmentally friendly, lacks the durability and heat resistance required for advanced protective applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid | Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic fiber (aramid polymer) | Natural fiber (flax plant) |
| Heat Resistance | High; withstands temperatures up to 450degC | Low to moderate; chars at high heat |
| Strength | Exceptional tensile strength and durability | Moderate strength; less durable than aramid |
| Weight | Lightweight yet strong | Heavier and less flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most chemicals | Limited chemical resistance; prone to degradation |
| UV Resistance | Good resistance to UV degradation | Poor UV resistance; deteriorates quickly |
| Common Applications | Protective gear, flame-resistant clothing, aerospace | Home textiles, upholstery, light protective covers |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced manufacturing | Lower cost; widely available |
Introduction to Protective Covering Materials
Aramid fibers, known for exceptional strength and heat resistance, are widely used in protective coverings for high-performance applications such as firefighting gear and ballistic vests. Linen, derived from flax fibers, offers natural breathability and moderate durability, making it suitable for lightweight protective textiles and environmental shielding. Comparing aramid and linen highlights the balance between synthetic high-strength protection and natural fiber comfort in protective covering materials.
What is Aramid?
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Twaron, are synthetic materials known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for protective coverings in high-risk environments. They offer superior impact resistance and flame retardancy compared to natural fibers like linen, which is made from flax plant fibers and lacks comparable thermal protection. Aramid's molecular structure enables it to maintain integrity under extreme stress, providing reliable defense against cuts, abrasions, and heat in industrial and military applications.
What is Linen?
Linen is a natural fiber derived from the flax plant, valued for its strength, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties in protective coverings. Unlike synthetic materials such as aramid, linen provides a sustainable and biodegradable option while offering moderate durability against wear and tear. Its lightweight nature and resistance to static make linen suitable for applications requiring comfort and environmental consideration in protective fabrics.
Key Properties of Aramid
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength, high resistance to heat, and excellent durability, making them ideal for protective coverings in extreme environments. Their inherent flame resistance and low thermal conductivity provide superior protection against fire hazards and high temperatures compared to natural fibers like linen. Aramid's lightweight nature combined with chemical resistance ensures prolonged performance and safety in industrial and military applications.
Key Properties of Linen
Linen offers exceptional breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for protective coverings in humid environments where comfort and dryness are crucial. Its natural strength and resistance to abrasion contribute to long-lasting durability while maintaining flexibility and softness. Unlike synthetic fibers, linen is biodegradable and environmentally friendly, appealing to sustainability-conscious applications.
Durability Comparison: Aramid vs Linen
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior durability compared to linen due to their high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure. Linen, derived from flax fibers, provides moderate durability but is more prone to wear, tear, and degradation under harsh environmental conditions. For protective coverings requiring long-lasting performance and enhanced durability, aramid materials outperform linen, making them the preferred choice in industrial and safety applications.
Heat and Fire Resistance Differences
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior heat and fire resistance compared to linen, withstanding temperatures up to 500degC without degrading, whereas linen typically chars at around 200degC. Aramid's inherent flame-retardant properties prevent ignition and self-extinguish when exposed to high heat, making it ideal for protective coverings in industrial and firefighting applications. Linen, being a natural fiber, ignites more easily and offers limited thermal protection, thus is less suitable for environments requiring stringent fire resistance.
Comfort and Breathability
Aramid fibers, known for their high tensile strength and heat resistance, offer limited breathability compared to linen, making them less comfortable for prolonged wear in hot environments. Linen, derived from flax plants, excels in moisture-wicking and airflow, enhancing comfort by regulating temperature and reducing sweat buildup. Protective coverings incorporating linen fibers provide superior breathability, ideal for applications where comfort under heat stress is critical, whereas aramid is favored primarily for its durability and resistance to flames and abrasions.
Environmental Impact of Aramid and Linen
Aramid fibers, widely used in protective coverings, are derived from synthetic polymers, leading to higher energy consumption and non-biodegradability issues, which contribute to environmental concerns such as microplastic pollution and landfill waste. Linen, made from flax plants, offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative, with lower water and chemical usage during cultivation and processing, thereby reducing its overall environmental footprint. Choosing linen over aramid not only supports sustainability through natural fiber sourcing but also promotes easier end-of-life disposal via composting or recycling.
Choosing the Right Material for Protective Covering
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior heat resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for protective coverings exposed to extreme conditions or requiring puncture resistance. Linen, a natural fiber, provides breathability and comfort but lacks the durability and thermal protection of aramid materials. Selecting the right protective covering depends on balancing the need for thermal performance, durability, and flexibility based on the specific application environment.
Infographic: Aramid vs Linen for Protective Covering
 azmater.com
azmater.com