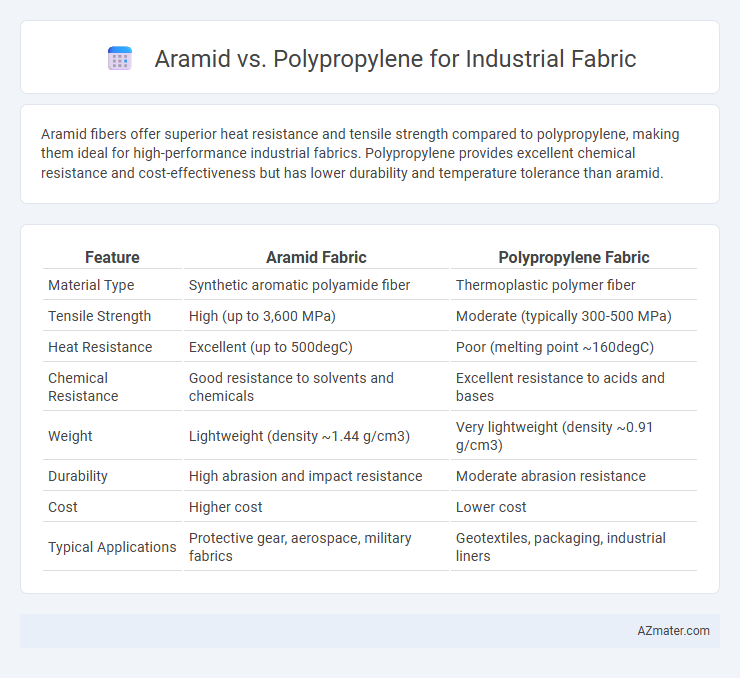
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and tensile strength compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for high-performance industrial fabrics. Polypropylene provides excellent chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness but has lower durability and temperature tolerance than aramid.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid Fabric | Polypropylene Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fiber | Thermoplastic polymer fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,600 MPa) | Moderate (typically 300-500 MPa) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent (up to 500degC) | Poor (melting point ~160degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and chemicals | Excellent resistance to acids and bases |
| Weight | Lightweight (density ~1.44 g/cm3) | Very lightweight (density ~0.91 g/cm3) |
| Durability | High abrasion and impact resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Typical Applications | Protective gear, aerospace, military fabrics | Geotextiles, packaging, industrial liners |
Introduction to Aramid and Polypropylene Fabrics
Aramid fabrics, known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, are widely used in industrial applications requiring durability and protection against high temperatures. Polypropylene fabrics offer lightweight, chemical resistance, and moisture-wicking properties, making them suitable for diverse industrial environments where cost-efficiency and resistance to corrosion are critical. Both materials cater to specific performance needs, with aramid excelling in protective gear and polypropylene favored for filtration and packaging solutions.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional chemical resistance to solvents, oils, and heat, maintaining strength up to 500degC, while polypropylene offers moderate chemical resistance and melts at around 160degC. Aramid has high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, surpassing polypropylene, which is lighter but less durable under mechanical stress. Industrial fabrics made from aramid are preferred for high-performance applications requiring flame retardance and durability, whereas polypropylene is chosen for cost-effective, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant uses.
Strength and Durability Differences
Aramid fibers exhibit significantly higher tensile strength and superior heat resistance compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for demanding industrial fabric applications where durability is critical. Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance and lightweight properties but falls short in abrasion resistance and long-term mechanical strength under high stress conditions. Industrial fabrics utilizing aramid provide enhanced durability in extreme environments, whereas polypropylene suits applications requiring cost-effective and corrosion-resistant materials.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Performance
Aramid fibers exhibit superior thermal resistance, maintaining integrity at temperatures up to 500degC, making them ideal for industrial fabrics exposed to extreme heat and flame. Polypropylene, with a lower melting point around 160degC, offers limited heat performance but excels in chemical resistance and cost-efficiency for moderate temperature applications. Aramid's inherent flame retardancy and dimensional stability under high thermal stress outperform polypropylene, positioning it as the preferred choice in high-temperature industrial environments.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Aramid fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance, particularly against solvents, oils, and acids, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments requiring durable fabric performance. Polypropylene offers excellent resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including alkalis and acids, while showcasing low moisture absorption, which enhances its suitability for wet or corrosive conditions. Environmental suitability favors polypropylene due to its resistance to UV degradation and its lightweight nature, whereas aramid's strength and thermal stability provide robustness in high-temperature and chemically aggressive settings.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Aramid fibers exhibit higher strength-to-weight ratios compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet durable industrial fabrics. Polypropylene offers superior flexibility and is less prone to stiffness, enhancing ease of handling in dynamic environments. The weight advantage of aramid combined with the flexible nature of polypropylene informs material selection based on specific industrial load and movement requirements.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, typically come at a higher initial cost compared to polypropylene, which is more affordable and widely used in industrial fabrics. Polypropylene offers superior cost efficiency for applications that do not demand extreme durability or thermal stability, making it an economical choice for bulk production and disposable products. Considering lifecycle costs, aramid fabrics provide long-term economic advantages in high-performance environments by reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses.
Typical Industrial Applications
Aramid fibers are widely used in industrial fabrics for high heat resistance and cut protection, making them ideal for applications like protective clothing, conveyor belts, and fire-resistant materials. Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and lightweight durability, which suits applications such as packaging, geotextiles, and agricultural fabrics. The selection between aramid and polypropylene depends on the specific industrial requirement for thermal stability versus chemical and moisture resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, have a higher environmental footprint due to energy-intensive production and limited recyclability compared to polypropylene, which is lighter and easier to recycle. Polypropylene fabrics offer better sustainability through lower carbon emissions during manufacturing and greater biodegradability in controlled conditions. However, aramid's durability can extend product lifespan, which partially offsets its environmental costs in industrial fabric applications.
Choosing the Right Fabric for Your Industrial Needs
Aramid fibers offer exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and durability, making them ideal for extreme industrial applications such as protective clothing and reinforcement composites. Polypropylene fabrics provide excellent chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and moisture-wicking capabilities, suitable for filtration, packaging, and geotextiles. Selecting the right fabric depends on specific industrial requirements including temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Infographic: Aramid vs Polypropylene for Industrial Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com