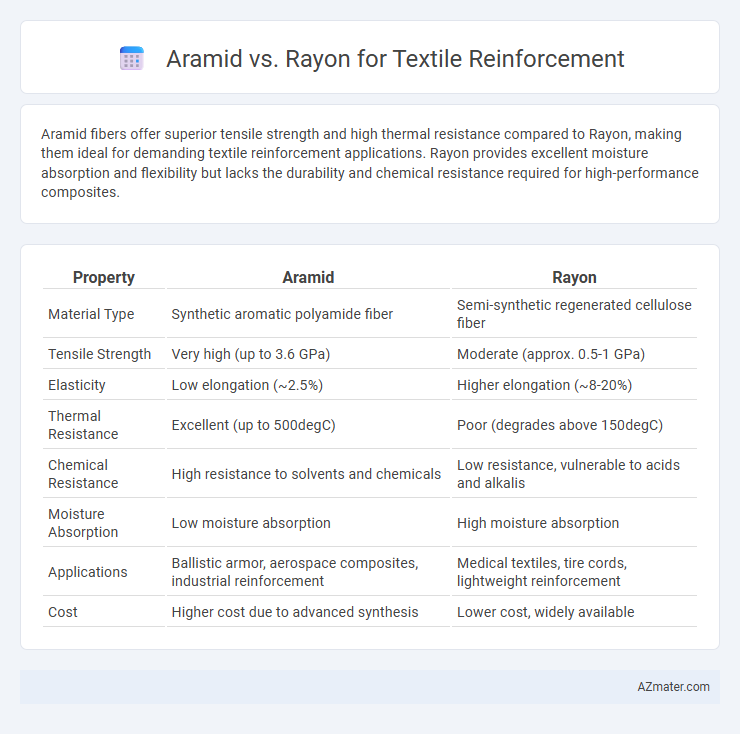
Aramid fibers offer superior tensile strength and high thermal resistance compared to Rayon, making them ideal for demanding textile reinforcement applications. Rayon provides excellent moisture absorption and flexibility but lacks the durability and chemical resistance required for high-performance composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fiber | Semi-synthetic regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Very high (up to 3.6 GPa) | Moderate (approx. 0.5-1 GPa) |
| Elasticity | Low elongation (~2.5%) | Higher elongation (~8-20%) |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent (up to 500degC) | Poor (degrades above 150degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to solvents and chemicals | Low resistance, vulnerable to acids and alkalis |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption |
| Applications | Ballistic armor, aerospace composites, industrial reinforcement | Medical textiles, tire cords, lightweight reinforcement |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced synthesis | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Textile Reinforcement Materials
Aramid fibers offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and high thermal resistance, making them ideal for demanding textile reinforcement applications such as aerospace and military gear. Rayon, derived from regenerated cellulose, provides excellent flexibility and moisture absorbency but lacks the tensile strength and durability exhibited by aramid fibers. Selecting between aramid and rayon depends on specific performance requirements like tensile strength, thermal stability, and environmental resistance within reinforcement composites.
What is Aramid Fiber?
Aramid fiber is a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers used extensively in textile reinforcement for aerospace, military, and industrial applications. Known for high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional thermal stability, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals, it outperforms traditional fibers like rayon in durability and performance under stress. Aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Twaron provide superior impact resistance, making them ideal for protective clothing, composites, and reinforced materials.
What is Rayon Fiber?
Rayon fiber is a semi-synthetic cellulose-based material derived from wood pulp, known for its silk-like feel, high moisture absorbency, and breathability, making it suitable for textile applications. Unlike aramid fibers, rayon offers less tensile strength and heat resistance but provides excellent drapability and dyeability. Its biodegradability distinguishes rayon from synthetic options, positioning it as an eco-friendly choice for reinforcement in textiles where flexibility and comfort are prioritized.
Comparative Physical Properties: Aramid vs Rayon
Aramid fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and excellent thermal resistance compared to rayon, making them ideal for high-performance textile reinforcement applications. Rayon offers good flexibility and moisture absorbency but lacks the durability and chemical stability of aramid, which limits its use in demanding environments. The physical properties of aramid, including high modulus and impact resistance, significantly outperform rayon's lower strength and abrasion resistance in reinforcement contexts.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Aramid fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and exceptional resistance to abrasion and heat compared to rayon, making them ideal for high-performance textile reinforcement applications. Rayon, while offering moderate strength and flexibility, lacks the durability and thermal stability required for demanding industrial uses. The molecular structure of aramid provides enhanced resilience under stress, ensuring long-term durability in reinforced composites.
Heat and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 500degC, while rayon fibers degrade rapidly above 150degC. Chemically, aramid resists acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, making it ideal for harsh environments, whereas rayon absorbs moisture and deteriorates when exposed to strong chemicals. These heat and chemical resistance properties position aramid as the preferred choice for durable textile reinforcement in high-performance applications.
Flexibility and Handling in Textile Applications
Aramid fibers exhibit superior flexibility and exceptional tensile strength compared to rayon, making them ideal for demanding textile reinforcement applications requiring durability and impact resistance. Rayon offers greater softness and ease of handling, enhancing fabric drape and comfort but lacks the high mechanical performance needed in technical textiles. Aramid's engineered fiber structure ensures consistent flexibility without compromising strength, while rayon's natural cellulose base favors versatility in less rigorous environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, known for their high strength and durability, have a significant environmental footprint due to their energy-intensive production and reliance on non-renewable petrochemicals. Rayon, derived from cellulose in wood pulp, offers better biodegradability and a renewable raw material base, but its manufacturing process involves toxic chemicals and water-intensive treatments that raise sustainability concerns. Incorporating advances like lyocell processing for rayon and recycling methods for aramid can improve the environmental profile of both materials in textile reinforcement applications.
Cost Considerations for Aramid and Rayon
Aramid fibers generally have higher manufacturing costs due to complex production processes and raw material expenses, making them more expensive compared to rayon. Rayon, derived from cellulose, benefits from lower raw material costs and simpler processing, resulting in a more economical option for textile reinforcement. When balancing performance and cost, rayon offers a budget-friendly alternative, while aramid's superior strength and durability justify its premium price in high-demand applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Textile Reinforcement
Aramid fibers offer exceptional tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for high-performance textile reinforcement in aerospace, automotive, and military applications. Rayon fibers provide cost-effective flexibility and good dye affinity but have lower mechanical strength and moisture sensitivity, limiting their reinforcement suitability to non-structural uses. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing performance requirements such as strength, thermal stability, and environmental exposure with budget constraints and specific end-use applications.
Infographic: Aramid vs Rayon for Textile Reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com