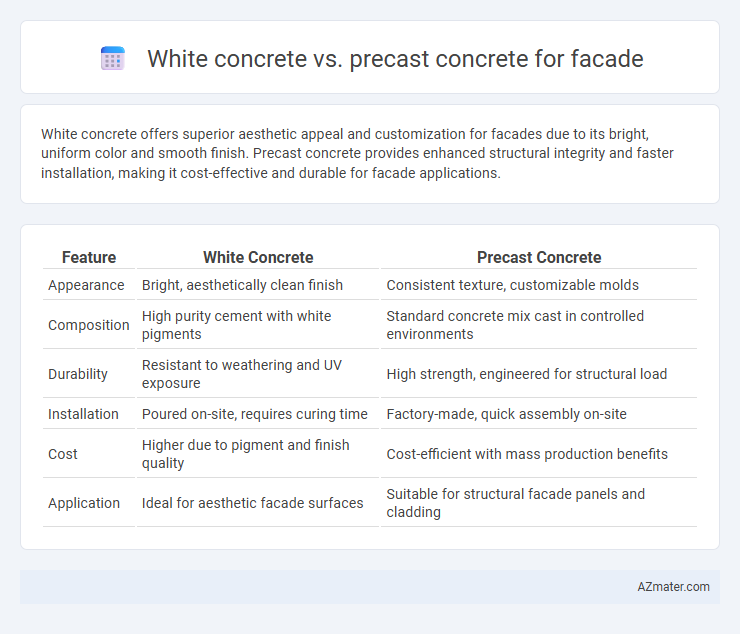
White concrete offers superior aesthetic appeal and customization for facades due to its bright, uniform color and smooth finish. Precast concrete provides enhanced structural integrity and faster installation, making it cost-effective and durable for facade applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | White Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Bright, aesthetically clean finish | Consistent texture, customizable molds |
| Composition | High purity cement with white pigments | Standard concrete mix cast in controlled environments |
| Durability | Resistant to weathering and UV exposure | High strength, engineered for structural load |
| Installation | Poured on-site, requires curing time | Factory-made, quick assembly on-site |
| Cost | Higher due to pigment and finish quality | Cost-efficient with mass production benefits |
| Application | Ideal for aesthetic facade surfaces | Suitable for structural facade panels and cladding |
Understanding White Concrete and Precast Concrete
White concrete, characterized by its refined white Portland cement and absence of iron oxide, offers a bright, clean appearance ideal for modern facades requiring aesthetic appeal and durability. Precast concrete involves manufacturing concrete elements in controlled factory settings, allowing for precise dimensions and enhanced quality control, with options including white concrete mixes to combine visual appeal with structural efficiency. Understanding the material composition and production methods is crucial for selecting between white concrete's aesthetic properties and precast concrete's versatility in facade applications.
Key Differences Between White Concrete and Precast Concrete
White concrete is a specialized mix using white cement and light-colored aggregates, primarily chosen for aesthetic purposes in facades, offering a smooth, bright finish that enhances architectural designs. Precast concrete refers to factory-made concrete elements molded and cured off-site, ensuring uniform quality, faster installation, and reduced on-site labor, commonly used for structural and decorative facade panels. The key differences lie in their production methods, with white concrete emphasizing color and texture for visual appeal, while precast concrete prioritizes modular construction, durability, and speed of assembly.
Aesthetic Appeal: White Concrete vs Precast Options
White concrete offers a smooth, uniform surface that enhances facade brightness and allows for seamless integration with modern architectural designs. Precast concrete features customizable textures and patterns that add depth and character, enabling more intricate facade aesthetics. Selecting between white concrete and precast concrete depends on the desired visual effect and the level of design complexity for the building exterior.
Structural Performance and Durability Comparison
White concrete offers superior aesthetic appeal with its uniform color and smooth finish, making it ideal for visually striking facades, while precast concrete provides enhanced structural performance through controlled manufacturing conditions that ensure higher strength and dimensional accuracy. In terms of durability, precast concrete panels typically exhibit better resistance to environmental stresses such as freeze-thaw cycles and chemical exposure due to factory-controlled curing processes and dense mix designs. White concrete can be more susceptible to surface wear and discoloration over time unless treated with protective sealants, whereas precast panels maintain long-term durability with minimal maintenance, contributing to extended facade lifespan.
Cost Implications of Facade Choices
White concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials and pigmentation processes required for its bright, uniform finish. Precast concrete offers cost savings through mass production and reduced on-site labor, enabling efficient installation and minimized construction time. Long-term maintenance expenses tend to be lower for precast facades because of their controlled manufacturing environment, which enhances durability and consistency.
Installation and Construction Timeframes
White concrete offers on-site casting flexibility but requires longer curing times, extending installation and overall construction schedules. Precast concrete facade panels are manufactured off-site under controlled conditions, enabling faster installation and reduced on-site labor, significantly shortening construction timeframes. Choosing precast concrete improves project timelines by allowing parallel site preparation and panel fabrication.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
White concrete facades require routine cleaning to prevent discoloration and surface staining, maintaining their bright appearance over time. Precast concrete panels offer enhanced durability with factory-controlled conditions, resulting in consistent quality and reduced maintenance needs. Both materials provide long-lasting facade solutions, but precast concrete typically outperforms white concrete in resistance to environmental wear and structural integrity.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
White concrete offers high albedo properties, reflecting more sunlight and reducing urban heat island effects, which enhances sustainability in building facades. Precast concrete reduces construction waste through factory-controlled production and allows for efficient insulation integration, lowering energy consumption over the building's lifecycle. Both materials contribute to sustainable architecture, but precast concrete's offsite manufacturing process typically results in lower carbon emissions compared to traditional white concrete mixing onsite.
Applications and Best Use Cases for Facades
White concrete offers superior aesthetic appeal and is ideal for architectural facades requiring a clean, smooth finish and high reflectivity, making it perfect for modern commercial buildings and iconic structures. Precast concrete excels in durability and rapid installation, suited for large-scale projects like high-rise apartments and office buildings where uniformity, strength, and speed are critical. Combining white concrete with precast technology allows for prefabricated facade panels that deliver both elegance and efficiency in urban developments and landmark construction.
Choosing the Right Facade Material for Your Project
White concrete offers a smooth, customizable finish with high reflectivity, making it ideal for modern, aesthetic facades requiring durability and UV resistance. Precast concrete provides enhanced quality control, faster installation, and superior thermal insulation due to factory production, making it suitable for large-scale projects with tight deadlines. Selecting the right facade material depends on project priorities such as architectural design, budget constraints, and construction timelines.
Infographic: White concrete vs Precast concrete for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com