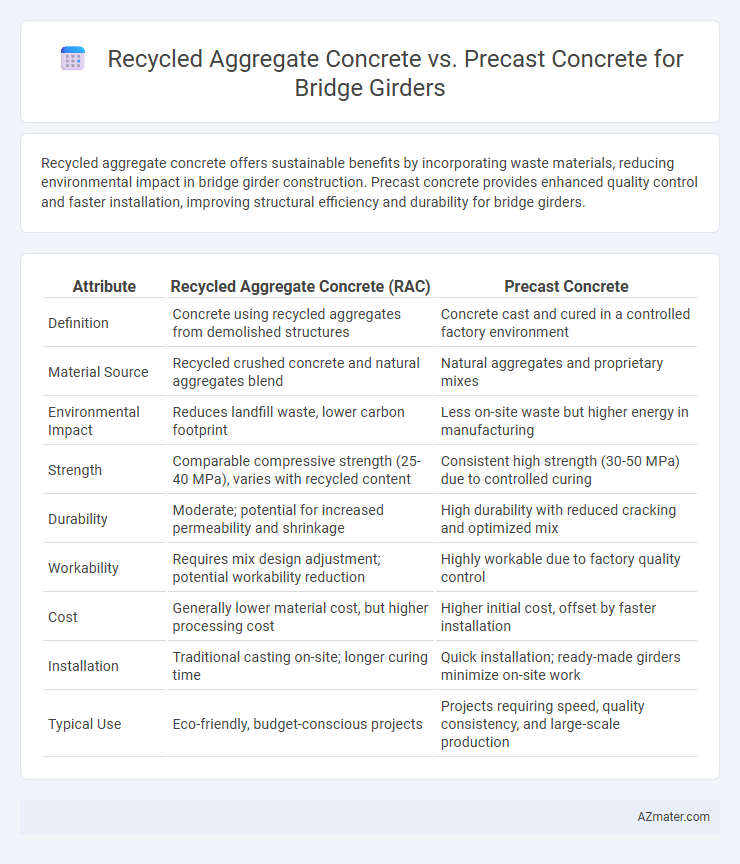
Recycled aggregate concrete offers sustainable benefits by incorporating waste materials, reducing environmental impact in bridge girder construction. Precast concrete provides enhanced quality control and faster installation, improving structural efficiency and durability for bridge girders.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete using recycled aggregates from demolished structures | Concrete cast and cured in a controlled factory environment |
| Material Source | Recycled crushed concrete and natural aggregates blend | Natural aggregates and proprietary mixes |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lower carbon footprint | Less on-site waste but higher energy in manufacturing |
| Strength | Comparable compressive strength (25-40 MPa), varies with recycled content | Consistent high strength (30-50 MPa) due to controlled curing |
| Durability | Moderate; potential for increased permeability and shrinkage | High durability with reduced cracking and optimized mix |
| Workability | Requires mix design adjustment; potential workability reduction | Highly workable due to factory quality control |
| Cost | Generally lower material cost, but higher processing cost | Higher initial cost, offset by faster installation |
| Installation | Traditional casting on-site; longer curing time | Quick installation; ready-made girders minimize on-site work |
| Typical Use | Eco-friendly, budget-conscious projects | Projects requiring speed, quality consistency, and large-scale production |
Introduction to Bridge Girders
Bridge girders serve as fundamental structural elements that support loads and transfer them to piers and abutments, ensuring stability and durability in bridge construction. Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) incorporates processed materials from demolished concrete, promoting sustainability while aiming to meet the mechanical strength and durability requirements of bridge girders. Precast concrete girders, manufactured in controlled factory settings, offer enhanced quality control, faster installation, and improved consistency compared to on-site casting methods, making them a reliable choice for critical bridge components.
Overview of Recycled Aggregate Concrete
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) incorporates crushed concrete debris as aggregate, significantly reducing natural resource consumption and construction waste in bridge girder production. This sustainable material exhibits comparable compressive strength and durability to conventional concrete when properly processed and mixed, making it a viable alternative for structural applications. RAC enhances environmental sustainability by lowering the carbon footprint and promoting circular economy principles in bridge construction.
Overview of Precast Concrete
Precast concrete for bridge girders offers high strength, durability, and consistent quality due to controlled manufacturing conditions. It allows rapid construction and reduces onsite labor, minimizing traffic disruptions and enhancing project timelines. Its adaptability to complex shapes and integration with prestressing techniques improves structural performance and longevity compared to recycled aggregate concrete options.
Material Properties Comparison
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) for bridge girders often exhibits lower compressive strength and higher water absorption compared to precast concrete due to the variability in recycled material quality. Precast concrete offers superior durability, uniformity, and high early strength, benefiting from controlled factory conditions and optimized mix designs. While RAC promotes sustainability by reusing construction waste, precast concrete's enhanced mechanical properties and consistency make it preferable for critical load-bearing bridge girder applications.
Structural Performance and Durability
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) for bridge girders offers enhanced sustainability by utilizing processed construction waste but may exhibit reduced compressive strength and increased permeability compared to traditional precast concrete, potentially impacting long-term durability. Precast concrete girders provide consistent structural performance with controlled curing conditions, resulting in higher strength, reduced shrinkage, and superior resistance to environmental deterioration such as freeze-thaw cycles and chloride ion penetration. Optimizing mix design and quality control in RAC can improve its mechanical properties and durability, but precast concrete remains the preferred choice for critical load-bearing bridge girders due to its proven reliability and longevity.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing crushed concrete waste, lowering natural resource depletion and decreasing landfill usage compared to conventional precast concrete. Life cycle assessments reveal that RAC bridges have substantially lower carbon footprints due to reduced energy consumption in raw material extraction and transportation. Precast concrete, while offering durability and quality control, typically involves higher environmental costs through cement production and aggregate mining, intensifying ecological footprint in bridge girder projects.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Recycled aggregate concrete reduces material costs by utilizing industrial waste, making it a sustainable and cost-effective option for bridge girders compared to conventional precast concrete. Precast concrete offers faster construction timelines and lower labor costs, but its initial production expenses and transportation costs can be higher than those associated with recycled aggregate concrete. Economic feasibility depends on local availability of recycled materials, transportation logistics, and project scale, with recycled aggregate concrete showing greater potential in regions prioritizing sustainability and cost reduction.
Construction Techniques and Timeline
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) requires meticulous handling to ensure consistent quality, often involving additional processing like washing and sorting before mixing, resulting in slightly extended curing times compared to conventional materials. Precast concrete girders are manufactured in controlled factory environments, allowing for rapid on-site installation and significantly reduced construction timelines due to simultaneous casting and site preparation. The choice between RAC and precast concrete affects overall project duration, with precast solutions enabling faster bridge girder erection, while RAC supports sustainable practices with potentially longer curing and quality control phases.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Considerations
Recycled aggregate concrete for bridge girders offers enhanced sustainability by reducing environmental impact through material reuse, though it may require more frequent maintenance due to potential variability in aggregate quality affecting durability. Precast concrete provides consistent quality and controlled manufacturing conditions, resulting in lower maintenance demands and a longer lifecycle under standard load and environmental conditions. Lifecycle cost analysis often favors precast concrete for its predictable performance and reduced repair frequency, while recycled aggregate concrete requires careful mix design and quality control to optimize maintenance intervals and lifespan.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) is best suited for non-structural or secondary elements of bridge girders due to its environmental benefits and satisfactory durability in less critical applications, while precast concrete offers superior quality control, higher strength, and faster installation ideal for primary load-bearing girders and high-performance bridge components. For optimal results, use precast concrete in projects requiring rapid construction and stringent load specifications, and implement recycled aggregate concrete in sustainable designs or rehabilitation works where cost reduction and resource conservation are priorities. Combining both materials in hybrid approaches can enhance sustainability without compromising structural integrity in bridge girder applications.
Infographic: Recycled aggregate concrete vs Precast concrete for Bridge Girder
 azmater.com
azmater.com