Rapid-setting concrete cures within hours, offering fast strength gain essential for urgent crack repair, while polymer-modified concrete incorporates polymers to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and durability for long-lasting crack resistance. Choosing between them depends on repair speed requirements versus performance demands in dynamic or load-bearing conditions.
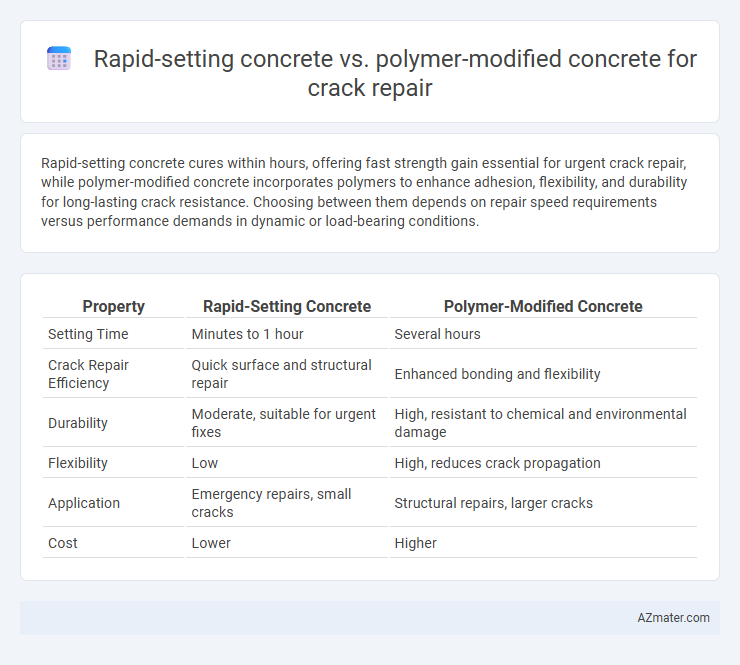
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rapid-Setting Concrete | Polymer-Modified Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Setting Time | Minutes to 1 hour | Several hours |
| Crack Repair Efficiency | Quick surface and structural repair | Enhanced bonding and flexibility |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for urgent fixes | High, resistant to chemical and environmental damage |
| Flexibility | Low | High, reduces crack propagation |
| Application | Emergency repairs, small cracks | Structural repairs, larger cracks |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Concrete Crack Repair Methods
Rapid-setting concrete offers fast strength gain and early load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for urgent crack repair in structural concrete. Polymer-modified concrete enhances adhesion, flexibility, and durability, effectively sealing cracks and preventing future deterioration in diverse environmental conditions. Both methods are essential in concrete crack repair, chosen based on the specific application requirements and repair timelines.
Understanding Rapid-Setting Concrete
Rapid-setting concrete is engineered for fast strength development, achieving initial set within minutes and significantly reducing downtime in crack repair projects. Its high early strength allows for quick load application and minimal curing periods, making it ideal for urgent structural fixes and emergency repairs. Unlike polymer-modified concrete, which enhances flexibility and adhesion through polymer additives, rapid-setting concrete relies on specialized chemical accelerators to speed up hydration and hardening processes.
What is Polymer-Modified Concrete?
Polymer-modified concrete is a composite material enhanced by the addition of polymers, which improve its adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to cracking compared to traditional rapid-setting concrete. It offers superior durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for repairing cracks in structures exposed to harsh environmental conditions. This type of concrete reduces water permeability and enhances bonding with existing substrates, resulting in longer-lasting repairs.
Key Differences Between Rapid-Setting and Polymer-Modified Concrete
Rapid-setting concrete achieves strength within hours due to its fast hydration process, making it ideal for urgent crack repairs requiring quick load-bearing capacity. Polymer-modified concrete incorporates synthetic polymers that enhance adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to shrinkage, providing superior durability for cracks subjected to movement or environmental stress. The key differences lie in rapid-setting concrete's speedy curing time versus the polymer-modified concrete's enhanced mechanical properties and long-term performance in crack durability.
Application Techniques for Crack Repair
Rapid-setting concrete cures within minutes, allowing for fast application in emergency crack repairs on concrete structures, with techniques involving pouring or injecting directly into cleaned and prepped cracks. Polymer-modified concrete enhances bonding and flexibility, requiring careful surface preparation and the use of primers or bonding agents before applying as a patch or injection to ensure durable crack sealing. Both materials demand proper moisture control and mixing to optimize adhesion and prevent further crack propagation.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Rapid-setting concrete offers quick strength gain within hours, making it ideal for urgent crack repairs, but typically exhibits lower long-term durability compared to polymer-modified concrete. Polymer-modified concrete incorporates resins that enhance adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to environmental stressors, resulting in superior crack bridging and improved durability over time. Performance metrics show polymer-modified concretes maintain crack sealing effectiveness under freeze-thaw cycles and chemical exposure better than rapid-setting variants, supporting prolonged structural integrity.
Setting Time and Strength Development
Rapid-setting concrete typically achieves initial set within 20 to 40 minutes and reaches significant strength, often above 3,000 psi, in 4 to 6 hours, making it ideal for emergency crack repairs requiring quick load-bearing capacity. Polymer-modified concrete demonstrates enhanced adhesion and flexibility due to its polymer content, with setting times ranging from 1 to 3 hours and strength development that can reach 4,000 psi within 24 hours, improving crack resistance and durability. Choosing between rapid-setting and polymer-modified concretes depends on balancing the need for fast setting versus long-term performance and crack resilience in repair applications.
Cost Effectiveness and Material Availability
Rapid-setting concrete offers cost advantages through faster curing times, reducing labor and downtime expenses, making it highly cost-effective for urgent crack repairs. Polymer-modified concrete, while typically more expensive due to additive costs, provides superior durability and enhanced bonding, potentially lowering long-term maintenance costs. Material availability favors rapid-setting concrete as its components are widely accessible, whereas polymer additives may have limited procurement options depending on the region.
Best Use Cases for Each Concrete Type
Rapid-setting concrete is ideal for emergency repairs where minimizing downtime is critical, such as highway patches, airport runways, and industrial floor repairs due to its fast strength gain within hours. Polymer-modified concrete excels in environments requiring enhanced durability and flexibility, including bridge decks, water reservoirs, and structures exposed to freeze-thaw cycles, as it offers superior adhesion, reduced permeability, and improved crack resistance. Selecting between the two depends on the urgency of repair and the environmental or mechanical stresses anticipated on the repaired surface.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Crack Repair
Rapid-setting concrete offers fast strength gain, making it ideal for urgent crack repairs requiring immediate load-bearing capacity. Polymer-modified concrete enhances adhesion, flexibility, and durability, providing superior long-term crack resistance in dynamic or moisture-prone environments. Selecting between these materials depends on repair urgency, environmental exposure, and structural requirements to ensure optimal crack rehabilitation performance.
Infographic: Rapid-setting concrete vs Polymer-modified concrete for Crack repair
 azmater.com
azmater.com