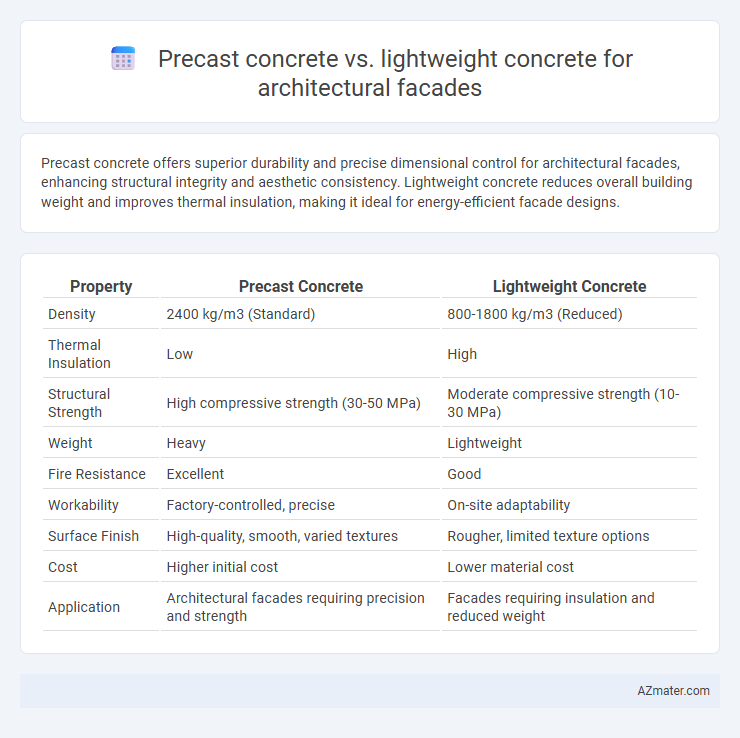
Precast concrete offers superior durability and precise dimensional control for architectural facades, enhancing structural integrity and aesthetic consistency. Lightweight concrete reduces overall building weight and improves thermal insulation, making it ideal for energy-efficient facade designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Precast Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2400 kg/m3 (Standard) | 800-1800 kg/m3 (Reduced) |
| Thermal Insulation | Low | High |
| Structural Strength | High compressive strength (30-50 MPa) | Moderate compressive strength (10-30 MPa) |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Workability | Factory-controlled, precise | On-site adaptability |
| Surface Finish | High-quality, smooth, varied textures | Rougher, limited texture options |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower material cost |
| Application | Architectural facades requiring precision and strength | Facades requiring insulation and reduced weight |
Introduction to Precast and Lightweight Concrete Facades
Precast concrete facades are fabricated in controlled factory environments, offering precise dimensions, enhanced durability, and rapid on-site installation, making them ideal for complex architectural designs. Lightweight concrete facades, composed of aggregates like expanded clay or shale, provide reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation, optimizing energy efficiency in building envelopes. Both materials support versatile aesthetic finishes but differ significantly in weight, structural performance, and insulation properties critical for facade engineering decisions.
Material Composition and Properties
Precast concrete for architectural facades typically consists of cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures, offering high compressive strength and durability with excellent dimensional control. Lightweight concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, resulting in reduced density, improved thermal insulation, and enhanced ease of handling without significantly compromising structural integrity. The choice between precast and lightweight concrete depends on balancing load-bearing requirements, thermal performance, and installation efficiency in facade applications.
Structural Performance and Durability
Precast concrete offers superior structural performance for architectural facades due to its high compressive strength and ability to be cast in controlled environments, ensuring consistent quality and reduced defects. Lightweight concrete provides enhanced thermal insulation and reduces overall facade weight, but it generally exhibits lower strength and durability compared to precast options, making it less suitable for high-load applications. Durability of precast concrete facades is significantly improved by minimized porosity and reinforced curing processes, whereas lightweight concrete requires additional protective coatings to withstand weathering and abrasion over time.
Aesthetic Versatility and Design Flexibility
Precast concrete offers exceptional aesthetic versatility with its ability to incorporate intricate textures, patterns, and colors during manufacturing, allowing for highly customized architectural facades. Lightweight concrete enhances design flexibility by reducing structural loads, enabling larger panel sizes and innovative shapes without compromising durability or thermal performance. Both materials support diverse architectural expressions, but precast concrete excels in detailed surface finishes while lightweight concrete prioritizes ease of installation and structural efficiency.
Installation Process and Construction Speed
Precast concrete panels offer faster installation for architectural facades due to factory-controlled conditions and precise manufacturing, enabling rapid on-site assembly and reducing construction time. Lightweight concrete requires on-site casting and longer curing periods, which can slow down the installation process compared to precast options. The use of precast concrete minimizes weather-related delays and labor costs, making it a preferred choice for projects with tight schedules.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Benefits
Precast concrete offers superior thermal mass, effectively regulating indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption in building facades. Lightweight concrete provides enhanced acoustic insulation due to its porous structure, minimizing sound transmission and improving occupant comfort. Combining both materials in architectural facades maximizes thermal efficiency and noise reduction, creating sustainable and comfortable building environments.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Precast concrete offers high durability and thermal mass, reducing energy consumption over a building's lifecycle, while lightweight concrete contributes to lower structural loads and decreased material usage, minimizing carbon emissions during construction. Both materials can incorporate recycled aggregates and supplementary cementitious materials to enhance sustainability. Choosing between them depends on project-specific environmental goals, with precast concrete excelling in longevity and lightweight concrete offering benefits in reduced embodied energy and transport efficiency.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Precast concrete offers higher initial costs due to factory production and transportation but provides long-term savings through durability and reduced maintenance for architectural facades. Lightweight concrete features lower material and handling expenses, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects, though it may require more frequent repairs over time. Evaluating total lifecycle expenditure, including installation speed and facade complexity, is essential for accurate budget considerations.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Precast concrete panels offer superior durability with minimal maintenance, often lasting over 50 years due to their dense composition and factory-controlled production, which reduces susceptibility to cracking and weathering. Lightweight concrete facades, while easier to handle and install, may require more frequent inspections and repairs due to lower density and increased permeability, potentially shortening their effective lifespan to around 30 years. Selecting precast concrete minimizes long-term maintenance costs and ensures sustained architectural integrity in exterior applications.
Choosing the Right Concrete Type for Architectural Facades
Precast concrete offers superior durability, precise dimensional control, and faster installation, making it ideal for complex architectural facades requiring consistent quality and detailed finishes. Lightweight concrete provides enhanced thermal insulation, reduced dead load, and improved fire resistance, which benefits energy-efficient buildings and designs with weight constraints. Selecting between precast and lightweight concrete hinges on balancing structural requirements, aesthetic goals, and performance criteria such as load capacity and insulation needs for the facade project.
Infographic: Precast concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Architectural facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com