Photocatalytic concrete enhances air purification and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for sustainable precast cladding. Lightweight concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced structural load, optimizing efficiency in precast cladding applications.
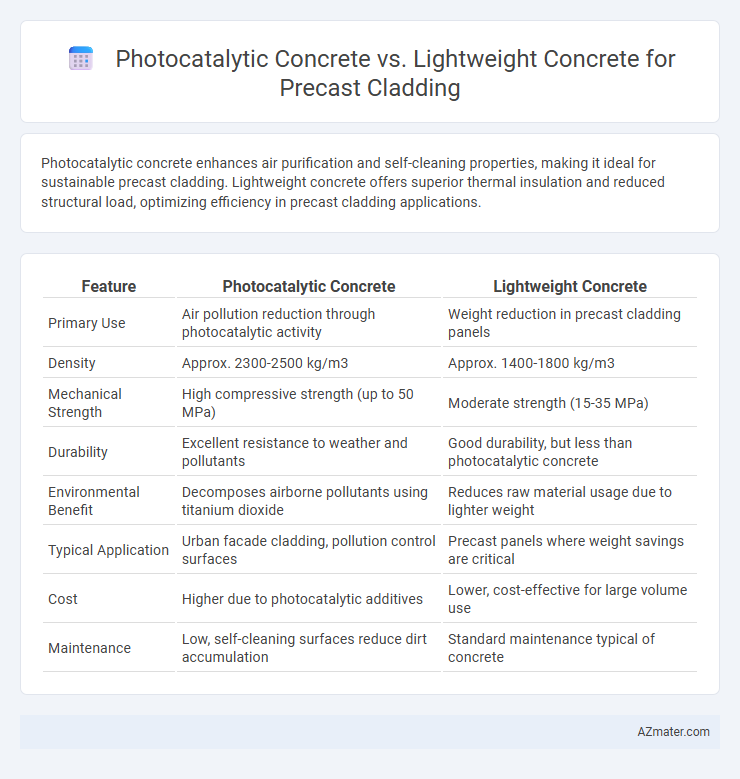
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photocatalytic Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Air pollution reduction through photocatalytic activity | Weight reduction in precast cladding panels |
| Density | Approx. 2300-2500 kg/m3 | Approx. 1400-1800 kg/m3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength (up to 50 MPa) | Moderate strength (15-35 MPa) |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to weather and pollutants | Good durability, but less than photocatalytic concrete |
| Environmental Benefit | Decomposes airborne pollutants using titanium dioxide | Reduces raw material usage due to lighter weight |
| Typical Application | Urban facade cladding, pollution control surfaces | Precast panels where weight savings are critical |
| Cost | Higher due to photocatalytic additives | Lower, cost-effective for large volume use |
| Maintenance | Low, self-cleaning surfaces reduce dirt accumulation | Standard maintenance typical of concrete |
Introduction to Precast Cladding Solutions
Precast cladding solutions benefit from diverse concrete types such as photocatalytic and lightweight concrete, each offering distinct advantages. Photocatalytic concrete enhances environmental performance by breaking down pollutants and improving air quality through titanium dioxide additives. Lightweight concrete reduces structural load and improves thermal insulation, making it ideal for energy-efficient and easy-to-install cladding panels in modern architecture.
Understanding Photocatalytic Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide nanoparticles that actively break down pollutants and organic matter on the surface, enhancing air quality and reducing maintenance for precast cladding. This innovative material leverages photocatalysis to achieve self-cleaning properties and long-term durability in urban environments. Compared to lightweight concrete, photocatalytic concrete offers functional benefits beyond structural performance, making it ideal for sustainable architectural facades.
Key Properties of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete used in precast cladding offers superior thermal insulation, reduced dead load, and enhanced ease of handling compared to photocatalytic concrete. Its low density, typically ranging from 800 to 1,600 kg/m3, results in improved structural efficiency and cost savings in foundation design. Despite lower compressive strength relative to traditional concrete, lightweight concrete provides sufficient durability and fire resistance needed for exterior cladding applications.
Photocatalytic vs Lightweight: Material Composition
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles that enable the material to break down pollutants through a chemical reaction triggered by sunlight, enhancing air purification capabilities. Lightweight concrete is typically composed of aggregates such as expanded clay, perlite, or vermiculite, reducing density while maintaining structural strength for easier handling and installation in precast cladding. The distinct material compositions of photocatalytic and lightweight concrete influence not only their environmental functions but also their mechanical performance and suitability for specific architectural applications.
Performance Comparison in Precast Cladding Applications
Photocatalytic concrete enhances precast cladding performance by actively breaking down pollutants, providing self-cleaning properties and improved air quality, while maintaining durability and weather resistance. Lightweight concrete offers reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation but may compromise strength and surface finish required for aesthetic cladding applications. Performance comparison highlights photocatalytic concrete's superior environmental benefits and maintenance reduction, whereas lightweight concrete excels in weight reduction and handling efficiency during installation.
Environmental Impact: Self-Cleaning and Sustainability
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide, enabling it to break down pollutants and maintain a self-cleaning surface, significantly reducing maintenance needs and enhancing urban air quality. Lightweight concrete offers reduced material usage and lower transportation emissions due to its lower density, contributing to overall sustainability by minimizing resource consumption. Combining photocatalytic properties with lightweight aggregates in precast cladding enhances environmental performance through improved durability, reduced carbon footprint, and active pollution mitigation.
Structural and Durability Considerations
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide, enhancing surface self-cleaning and pollution reduction, which significantly improves durability against environmental degradation in precast cladding applications. Lightweight concrete offers reduced dead load and improved thermal insulation but typically exhibits lower compressive strength and higher permeability, potentially compromising structural performance and long-term durability. Selecting the appropriate material depends on balancing the need for structural load capacity and enhanced durability, with photocatalytic concrete favored for high-exposure facades and lightweight concrete suited for weight-sensitive designs.
Aesthetic and Architectural Flexibility
Photocatalytic concrete offers high aesthetic value with self-cleaning surfaces that maintain a pristine appearance, ideal for sleek, modern precast cladding designs. Lightweight concrete provides enhanced architectural flexibility due to its reduced weight, enabling larger spans and more intricate shapes without compromising structural integrity. Both materials allow for diverse finishes and textures, but photocatalytic concrete excels in durability and low-maintenance facade applications.
Cost Implications and Long-Term Value
Photocatalytic concrete for precast cladding offers higher upfront costs due to advanced materials and enhanced self-cleaning properties, leading to reduced maintenance expenses and longer surface durability. Lightweight concrete provides cost savings in transportation and installation owing to its reduced weight but may incur higher maintenance costs over time due to lower durability in harsh environmental conditions. Evaluating total cost of ownership, photocatalytic concrete delivers greater long-term value through sustained aesthetics and lower lifecycle expenses despite its premium initial investment.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Precast Cladding
Photocatalytic concrete for precast cladding offers self-cleaning and pollution-reducing properties through the incorporation of titanium dioxide, making it ideal for urban environments with high air pollution. Lightweight concrete provides superior thermal insulation and reduced structural load, enhancing energy efficiency and ease of installation in building facades. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing environmental benefits, structural requirements, and long-term maintenance for optimal precast cladding performance.
Infographic: Photocatalytic concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Precast cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com