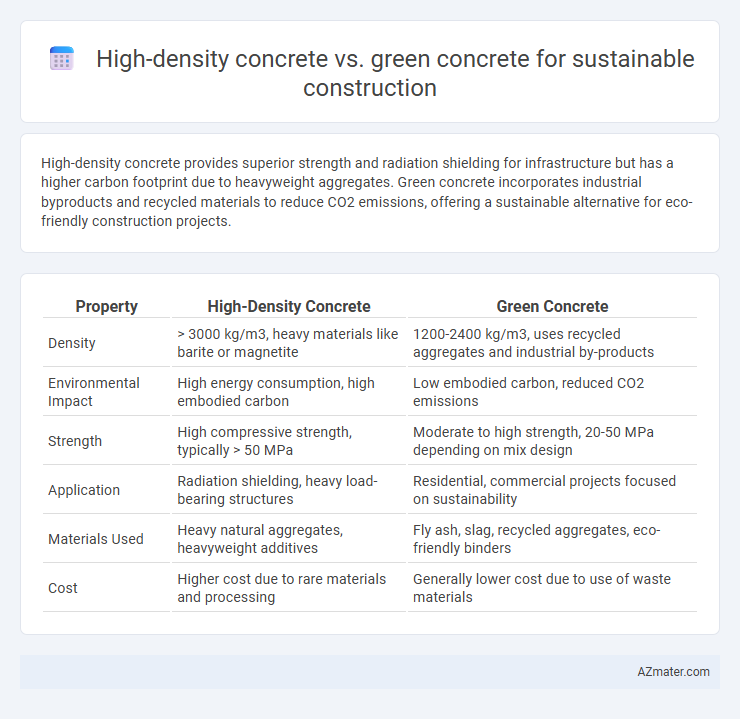
High-density concrete provides superior strength and radiation shielding for infrastructure but has a higher carbon footprint due to heavyweight aggregates. Green concrete incorporates industrial byproducts and recycled materials to reduce CO2 emissions, offering a sustainable alternative for eco-friendly construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete | Green Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | > 3000 kg/m3, heavy materials like barite or magnetite | 1200-2400 kg/m3, uses recycled aggregates and industrial by-products |
| Environmental Impact | High energy consumption, high embodied carbon | Low embodied carbon, reduced CO2 emissions |
| Strength | High compressive strength, typically > 50 MPa | Moderate to high strength, 20-50 MPa depending on mix design |
| Application | Radiation shielding, heavy load-bearing structures | Residential, commercial projects focused on sustainability |
| Materials Used | Heavy natural aggregates, heavyweight additives | Fly ash, slag, recycled aggregates, eco-friendly binders |
| Cost | Higher cost due to rare materials and processing | Generally lower cost due to use of waste materials |
Introduction to Sustainable Construction
High-density concrete enhances structural durability and radiation shielding, making it ideal for nuclear facilities and heavy-load structures, while green concrete prioritizes reduced carbon footprint and eco-friendly materials such as recycled aggregates and industrial byproducts. Sustainable construction integrates these innovative materials to minimize environmental impact, improve energy efficiency, and promote long-term resource conservation. Implementing high-density and green concrete supports the industry's shift towards resilience and sustainability in building practices worldwide.
Overview of High-Density Concrete
High-density concrete is characterized by its greater mass per unit volume, typically achieved by incorporating heavy aggregates such as barite, magnetite, or hematite, which enhances its density beyond conventional concrete. This type of concrete offers superior radiation shielding, making it ideal for applications in nuclear power plants, medical facilities, and specialized industrial environments. While it provides excellent durability and structural strength, its environmental impact is higher compared to green concrete due to the energy-intensive extraction and processing of heavy aggregates.
What is Green Concrete?
Green concrete is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional high-density concrete, designed to reduce environmental impact by incorporating industrial by-products like fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates. It minimizes carbon emissions through lower cement consumption and promotes energy efficiency in construction. Green concrete enhances sustainability by improving durability and reducing resource depletion compared to conventional high-density concrete used mainly for heavy radiation shielding and structural applications.
Material Composition: High-Density vs Green Concrete
High-density concrete contains heavyweight aggregates such as barite, magnetite, or hematite, resulting in increased density and enhanced radiation shielding properties. Green concrete incorporates sustainable materials like fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates to reduce environmental impact and carbon footprint. The material composition difference directly influences their performance; high-density concrete suits specialized applications requiring mass and durability, while green concrete focuses on eco-friendliness and resource efficiency for sustainable construction.
Environmental Impact Comparison
High-density concrete typically relies on heavy aggregates like barite or magnetite, resulting in increased embodied energy and greater carbon emissions during production compared to green concrete, which incorporates recycled materials and industrial by-products such as fly ash or slag to reduce environmental impact. Green concrete significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions and conserves natural resources by minimizing demand for virgin aggregates and reducing waste sent to landfills. Life cycle assessments reveal that green concrete offers superior sustainability performance, contributing to reduced ecological footprints and enhanced carbon sequestration in sustainable construction projects.
Strength and Durability Factors
High-density concrete offers superior strength and enhanced durability due to its dense matrix and use of heavy aggregates, making it ideal for structures requiring high load-bearing capacity and radiation shielding. Green concrete emphasizes sustainability by incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, achieving comparable durability through reduced permeability and improved resistance to chemical attacks. Both types support sustainable construction goals, with high-density concrete excelling in strength-critical applications and green concrete prioritizing environmental impact without compromising long-term performance.
Cost Considerations and Economic Viability
High-density concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to the use of heavyweight aggregates like barite or magnetite, making it less economically viable for large-scale sustainable projects. Green concrete, utilizing recycled materials or industrial by-products such as fly ash or slag, offers significant cost savings and improved economic feasibility by reducing material expenses and enhancing resource efficiency. Long-term benefits of green concrete include lower maintenance and environmental compliance costs, reinforcing its advantage in sustainable construction economics.
Applications in Modern Construction
High-density concrete is widely used in radiation shielding, underwater structures, and heavy-load foundations due to its superior density and strength properties. Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, is favored in eco-friendly building projects aiming to reduce carbon footprint and enhance sustainability. Modern construction leverages high-density concrete for durability and structural integrity in specialized environments, while green concrete supports sustainable urban development through energy-efficient and environmentally responsible practices.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Type
High-density concrete often faces challenges related to its increased weight, which complicates transportation and handling while demanding stronger structural support, raising overall construction costs. Green concrete's limitations include variability in material properties due to the use of industrial by-products and recycled materials, which can impact consistency and long-term durability. Both types require careful consideration of environmental impact versus performance, with high-density concrete offering superior radiation shielding at the expense of sustainability, whereas green concrete prioritizes eco-friendliness but may compromise on strength and lifespan.
Future Trends in Sustainable Concrete Technologies
High-density concrete, known for its enhanced strength and radiation shielding properties, is increasingly integrated with eco-friendly materials to reduce environmental impact in sustainable construction. Green concrete, leveraging industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, leads the future trend by decreasing carbon emissions and promoting resource efficiency. Emerging technologies focus on combining these approaches with nanomaterials and carbon capture to advance durability, reduce energy consumption, and meet stringent sustainability standards.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Green concrete for Sustainable construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com