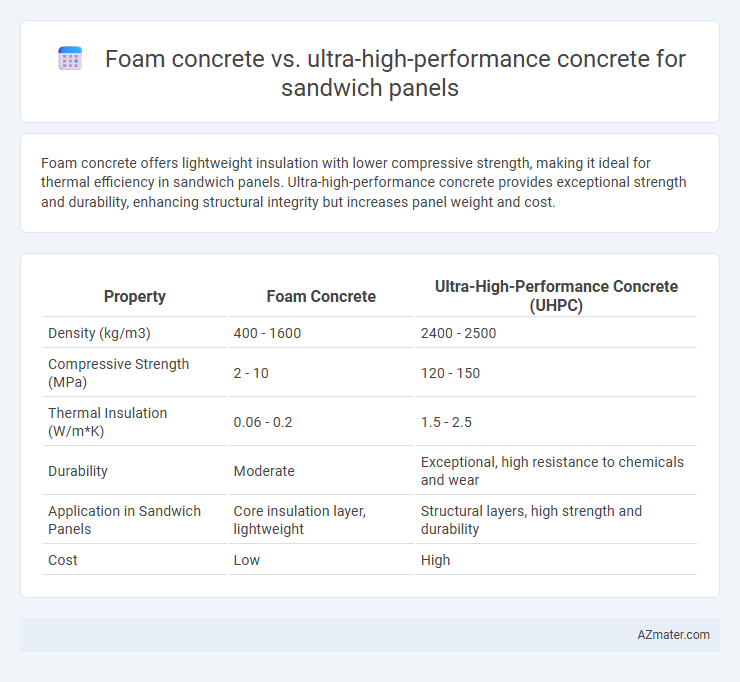
Foam concrete offers lightweight insulation with lower compressive strength, making it ideal for thermal efficiency in sandwich panels. Ultra-high-performance concrete provides exceptional strength and durability, enhancing structural integrity but increases panel weight and cost.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Foam Concrete | Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 400 - 1600 | 2400 - 2500 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 2 - 10 | 120 - 150 |
| Thermal Insulation (W/m*K) | 0.06 - 0.2 | 1.5 - 2.5 |
| Durability | Moderate | Exceptional, high resistance to chemicals and wear |
| Application in Sandwich Panels | Core insulation layer, lightweight | Structural layers, high strength and durability |
| Cost | Low | High |
Introduction to Sandwich Panels
Sandwich panels consist of two outer layers bonded to a lightweight core, offering superior thermal insulation and structural strength for building envelopes. Foam concrete serves as an effective core material due to its low density, excellent thermal properties, and ease of shaping. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) enhances sandwich panels by providing exceptional compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity and long service life.
Overview of Foam Concrete
Foam concrete is a lightweight, cellular material characterized by its low density and high thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for sandwich panel cores. Its porous structure results from air entrainment during mixing, providing enhanced fire resistance and soundproofing advantages. Foam concrete offers cost-effective production and ease of handling compared to ultra-high-performance concrete, though it has lower compressive strength and durability.
Overview of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC)
Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) is characterized by its exceptional compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa, superior durability, and enhanced tensile properties due to fine powders and fibers. In sandwich panels, UHPC provides remarkable load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental degradation, outperforming traditional foam concrete in terms of density and structural integrity. Its dense microstructure and low permeability significantly improve thermal insulation and fire resistance, making UHPC an optimal choice for high-performance building envelopes.
Material Composition Differences
Foam concrete features a lightweight composition primarily made from cement, water, and air bubbles introduced through foaming agents, which creates a porous structure ideal for thermal insulation in sandwich panels. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) incorporates a dense matrix of cement, fine powders such as silica fume, superplasticizers, and steel or organic fibers, resulting in superior mechanical strength and durability. The key material composition difference lies in foam concrete's focus on low density and insulation through air entrainment, whereas UHPC emphasizes high-performance characteristics via optimized particle packing and fiber reinforcement.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Foam concrete for sandwich panels offers low density and good thermal insulation but has lower compressive strength typically ranging from 3 to 10 MPa, making it suitable for non-load-bearing applications. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) exhibits superior mechanical properties with compressive strengths exceeding 150 MPa and exceptional tensile strength due to fiber reinforcement, making it ideal for load-bearing sandwich panel cores requiring high durability. The significant contrast in modulus of elasticity and fracture toughness between foam concrete and UHPC directly influences panel stiffness and impact resistance, with UHPC providing enhanced structural performance.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Foam concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its high porosity and low density, making it ideal for sandwich panels requiring energy efficiency. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), while denser and less effective in thermal insulation, excels in acoustic insulation by minimizing sound transmission through its compact microstructure. Sandwich panels combining foam concrete cores with UHPC layers optimize both thermal and acoustic performance for advanced building envelope solutions.
Durability and Lifespan Considerations
Foam concrete offers lightweight properties and good thermal insulation but generally has lower compressive strength and durability compared to Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) used in sandwich panels. UHPC exhibits superior durability due to its dense microstructure, enhanced resistance to environmental degradation, and longer lifespan exceeding 100 years in harsh conditions. Choosing UHPC for sandwich panels ensures superior structural integrity, reduced maintenance costs, and extended service life in demanding applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Foam concrete offers enhanced sustainability for sandwich panels due to its lightweight composition, which reduces raw material consumption and lowers transportation emissions, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) provides durability and longevity, minimizing maintenance and repair needs, thus extending the lifecycle and reducing environmental waste. Both materials support energy-efficient building designs, but foam concrete's superior thermal insulation capabilities further amplify its environmental benefits by decreasing heating and cooling demands.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Foam concrete offers significant cost savings in sandwich panel construction due to its lower material and production expenses compared to ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), which is substantially more expensive because of high cement content and specialized admixtures. The economic feasibility of foam concrete in large-scale projects is enhanced by reduced labor and energy costs, making it suitable for budget-sensitive applications. In contrast, UHPC's superior durability and strength justify higher initial investments in niche markets demanding long service life and minimal maintenance.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Sandwich Panels
Foam concrete offers lightweight insulation with excellent thermal properties, making it ideal for sandwich panels requiring energy efficiency and reduced structural load. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) provides superior strength, durability, and impact resistance, suited for sandwich panels demanding high structural integrity and longevity. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing thermal insulation needs with mechanical performance criteria specific to the sandwich panel application.
Infographic: Foam concrete vs Ultra-high-performance concrete for Sandwich panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com