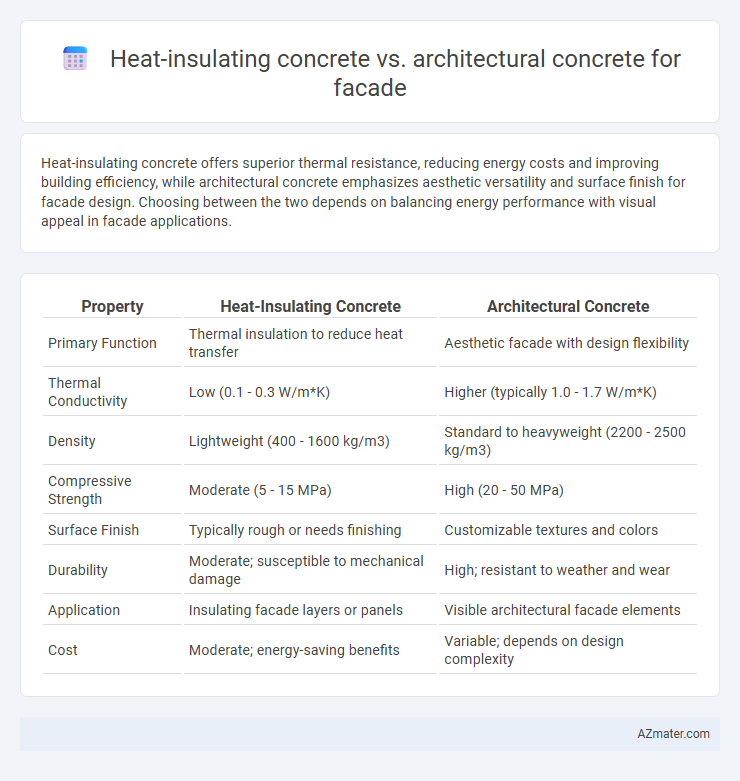
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance, reducing energy costs and improving building efficiency, while architectural concrete emphasizes aesthetic versatility and surface finish for facade design. Choosing between the two depends on balancing energy performance with visual appeal in facade applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Heat-Insulating Concrete | Architectural Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermal insulation to reduce heat transfer | Aesthetic facade with design flexibility |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.1 - 0.3 W/m*K) | Higher (typically 1.0 - 1.7 W/m*K) |
| Density | Lightweight (400 - 1600 kg/m3) | Standard to heavyweight (2200 - 2500 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (5 - 15 MPa) | High (20 - 50 MPa) |
| Surface Finish | Typically rough or needs finishing | Customizable textures and colors |
| Durability | Moderate; susceptible to mechanical damage | High; resistant to weather and wear |
| Application | Insulating facade layers or panels | Visible architectural facade elements |
| Cost | Moderate; energy-saving benefits | Variable; depends on design complexity |
Introduction to Facade Concrete Types
Heat-insulating concrete enhances building energy efficiency by integrating thermal insulation properties directly within the facade, reducing heat transfer and lowering cooling and heating demands. Architectural concrete prioritizes aesthetic appeal and surface finish, offering diverse textures, colors, and patterns that contribute to distinctive facade designs. Selecting between these concrete types depends on balancing thermal performance requirements with desired visual impact in facade applications.
What is Heat-Insulating Concrete?
Heat-insulating concrete is a specialized building material designed to enhance thermal resistance by incorporating insulating aggregates or additives that reduce heat transfer through facade structures. Unlike traditional architectural concrete, which primarily focuses on aesthetics and structural integrity, heat-insulating concrete improves energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and maintaining indoor temperature stability. This material is increasingly used in facade applications to meet stringent energy codes and reduce the need for additional insulation layers.
What is Architectural Concrete?
Architectural concrete is a type of concrete designed not only for structural integrity but also for aesthetic appeal, often featuring custom textures, colors, and finishes that enhance facade design. Unlike heat-insulating concrete, which primarily focuses on thermal performance and energy efficiency through specialized additives and foam ingredients, architectural concrete emphasizes visual impact and surface detail. This makes architectural concrete ideal for facades where appearance and durability are critical, combining functionality with artistic expression.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat-insulating concrete significantly outperforms architectural concrete in thermal performance due to its enhanced insulation properties, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in building facades. Its use of lightweight aggregates and insulating additives results in lower thermal conductivity values, typically ranging from 0.1 to 0.3 W/m*K, compared to 1.0 to 1.5 W/m*K in standard architectural concrete. This superior thermal resistance helps maintain stable indoor temperatures, lowering heating and cooling loads and contributing to sustainable building design.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Design Options
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal performance while allowing for a broad range of surface textures and finishes, enabling architects to create energy-efficient facades without compromising design versatility. Architectural concrete provides extensive aesthetic flexibility through customizable pigments, molds, and surface treatments, supporting intricate details and varied visual effects that enhance building identity. Both materials support diverse design options, but architectural concrete is preferred when emphasizing visual innovation, whereas heat-insulating concrete excels in balancing appearance with enhanced thermal insulation.
Structural Characteristics and Strength
Heat-insulating concrete for facades features a lightweight composition with integrated insulating materials that enhance thermal resistance while maintaining moderate compressive strength typically ranging from 15 to 30 MPa. Architectural concrete emphasizes surface aesthetics and durability, offering higher compressive strength levels from 30 to 50 MPa and superior structural integrity suitable for load-bearing facades. Both types require careful mix design to balance insulation properties and mechanical performance, but architectural concrete generally outperforms heat-insulating variants in structural strength.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Heat-insulating concrete enhances energy efficiency by significantly reducing thermal bridging and improving the building envelope's insulation performance, leading to lower heating and cooling demands. Architectural concrete prioritizes aesthetic versatility while offering moderate insulation benefits, but it generally requires supplementary thermal insulation systems to meet sustainability standards. Using heat-insulating concrete for facades supports sustainable design by decreasing energy consumption and carbon emissions over the building's lifecycle.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Heat-insulating concrete for facades offers superior thermal performance by integrating insulating materials that reduce energy loss, requiring careful installation to ensure continuous insulation without thermal bridges. Architectural concrete emphasizes aesthetic surface finishes and texture options, necessitating skilled application to maintain visual quality and durability over time. Maintenance for heat-insulating concrete involves monitoring insulation integrity and moisture control, while architectural concrete demands regular cleaning and protection against surface wear and environmental damage.
Cost Analysis: Heat-Insulating vs Architectural Concrete
Heat-insulating concrete typically incurs higher initial costs compared to architectural concrete due to advanced materials like insulating aggregates and additives that enhance thermal performance. Architectural concrete often offers cost advantages through standard mix designs, reduced material expenses, and less specialized installation requirements. Long-term savings on energy expenses with heat-insulating concrete can offset upfront costs, making it a cost-effective solution for facades focused on sustainability and thermal efficiency.
Choosing the Right Facade Concrete for Your Project
Heat-insulating concrete enhances energy efficiency by incorporating thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for facades in climates with extreme temperature variations. Architectural concrete offers superior aesthetic versatility with customizable textures and finishes, suitable for projects prioritizing design and visual impact. Selecting the right facade concrete depends on balancing thermal performance needs with architectural style requirements to achieve optimal durability and appearance.
Infographic: Heat-insulating concrete vs Architectural concrete for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com