Mass concrete offers high compressive strength and durability for industrial flooring, while polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and faster curing times. Choosing between them depends on specific load requirements and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
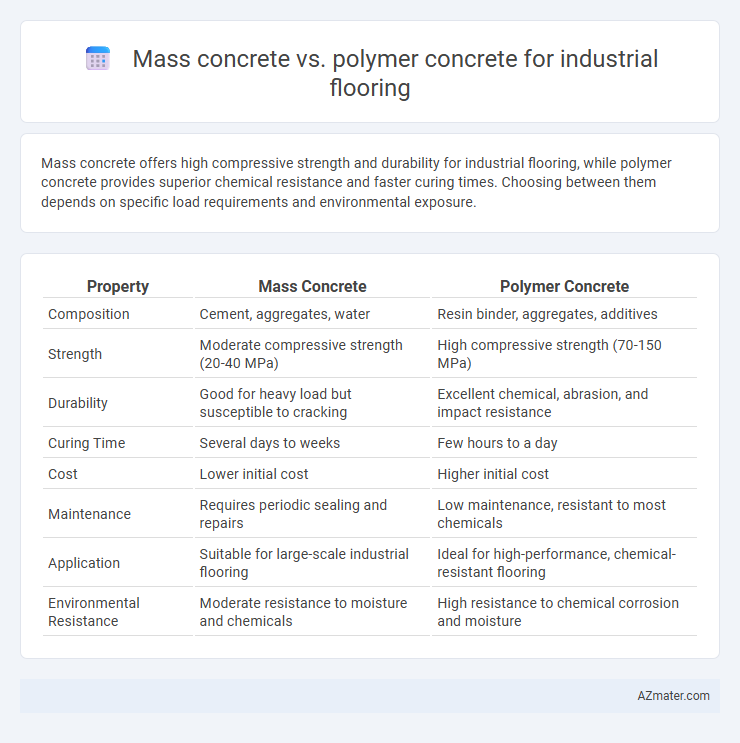
| Property | Mass Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cement, aggregates, water | Resin binder, aggregates, additives |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength (20-40 MPa) | High compressive strength (70-150 MPa) |
| Durability | Good for heavy load but susceptible to cracking | Excellent chemical, abrasion, and impact resistance |
| Curing Time | Several days to weeks | Few hours to a day |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic sealing and repairs | Low maintenance, resistant to most chemicals |
| Application | Suitable for large-scale industrial flooring | Ideal for high-performance, chemical-resistant flooring |
| Environmental Resistance | Moderate resistance to moisture and chemicals | High resistance to chemical corrosion and moisture |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Solutions
Industrial flooring solutions demand materials that offer high durability and resistance to heavy loads. Mass concrete provides a cost-effective foundation with excellent compressive strength, while polymer concrete enhances chemical resistance and rapid curing times, making it suitable for aggressive industrial environments. Selecting between mass concrete and polymer concrete depends on specific operational requirements such as load intensity, chemical exposure, and installation speed.
Overview of Mass Concrete
Mass concrete, characterized by its large volume and minimal reinforcement, offers high compressive strength and durability ideal for industrial flooring exposed to heavy loads and mechanical stress. Its thermal management capabilities reduce the risk of cracking during curing, ensuring long-term stability and structural integrity in demanding industrial environments. Compared to polymer concrete, mass concrete typically provides a more cost-effective solution for large-scale flooring projects requiring robust performance and resistance to abrasion.
Overview of Polymer Concrete
Polymer concrete consists of a composite material where polymer resins replace traditional cement binders, offering superior chemical resistance and rapid curing times compared to mass concrete. Its enhanced mechanical strength and durability make it ideal for industrial flooring exposed to heavy loads, chemicals, and abrasive conditions. The increased adhesion properties and reduced permeability of polymer concrete contribute to extended service life and low maintenance requirements in demanding industrial environments.
Composition and Material Differences
Mass concrete for industrial flooring primarily consists of cement, aggregates like sand and gravel, and water, forming a dense, durable base suitable for heavy loads and large areas. Polymer concrete incorporates synthetic resins such as epoxy or polyester polymers combined with aggregates, offering superior chemical resistance, faster curing times, and enhanced adhesion. The fundamental difference lies in polymer concrete's use of resin binders instead of traditional cement, resulting in improved mechanical properties and resistance to industrial chemicals.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Mass concrete exhibits high compressive strength and excellent durability, making it suitable for heavy-load industrial flooring but prone to cracking due to low tensile strength and limited flexibility. Polymer concrete offers superior tensile and flexural strength, enhanced chemical resistance, and better adhesion properties, which reduce cracking and increase lifespan under dynamic loading conditions. For industrial flooring, polymer concrete provides improved mechanical performance in environments requiring resistance to mechanical stresses, abrasion, and chemicals compared to traditional mass concrete.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Polymer concrete offers superior chemical and corrosion resistance compared to mass concrete, making it ideal for industrial flooring exposed to harsh chemicals and aggressive environments. Its resin-based composition prevents penetration and degradation by acids, alkalis, oils, and solvents, ensuring long-term durability. Mass concrete, while strong, is more porous and susceptible to chemical attack and corrosion, requiring additional protective coatings to enhance its resistance.
Installation Process and Timeframe
Mass concrete industrial flooring involves pouring large volumes of traditional concrete, requiring extensive curing periods of 28 days for full strength, which extends installation time significantly. Polymer concrete floors utilize resin binders that cure chemically, allowing installation to be completed within 24 to 48 hours, drastically reducing downtime in industrial settings. The quicker curing time and simplified installation process of polymer concrete make it ideal for facilities requiring fast floor turnaround without compromising durability.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Mass concrete offers high compressive strength and excellent durability against heavy loads and abrasion, making it suitable for industrial flooring with minimal maintenance needs. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and faster curing times, which reduces downtime and decreases susceptibility to cracking or deterioration in harsh chemical environments. Both materials require periodic inspections, but polymer concrete generally demands less frequent maintenance due to its enhanced bonding properties and resistance to environmental wear.
Cost Analysis: Mass Concrete vs Polymer Concrete
Mass concrete offers a lower initial material cost compared to polymer concrete, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale industrial flooring. Polymer concrete, while more expensive upfront due to synthetic resin binders and specialized aggregates, provides superior durability and chemical resistance, reducing long-term maintenance and repair expenses. Evaluating life-cycle cost analysis often favors polymer concrete for facilities exposed to heavy chemical or mechanical stress, despite higher initial investment.
Best Applications and Industry Recommendations
Mass concrete offers excellent load-bearing capacity and durability, making it ideal for heavy industrial flooring subjected to high compressive forces such as warehouses and manufacturing plants. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and faster curing times, recommended for industries dealing with corrosive materials and requiring quick turnaround, like chemical processing facilities and food production areas. Selecting between mass and polymer concrete depends on specific operational demands, with industry experts advising mass concrete for structural strength and polymer concrete for environments needing enhanced chemical resilience and minimal downtime.
Infographic: Mass concrete vs Polymer concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com