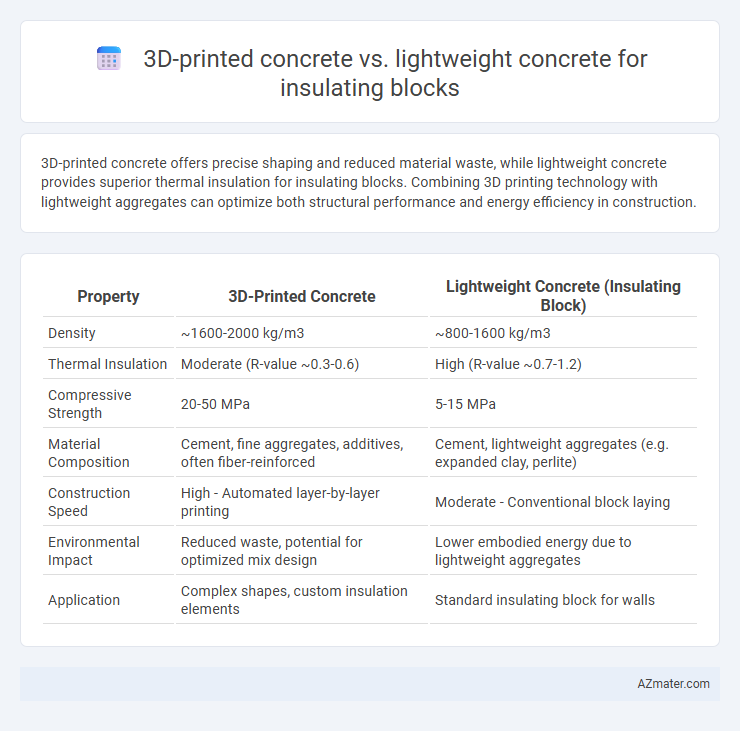
3D-printed concrete offers precise shaping and reduced material waste, while lightweight concrete provides superior thermal insulation for insulating blocks. Combining 3D printing technology with lightweight aggregates can optimize both structural performance and energy efficiency in construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | 3D-Printed Concrete | Lightweight Concrete (Insulating Block) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | ~1600-2000 kg/m3 | ~800-1600 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate (R-value ~0.3-0.6) | High (R-value ~0.7-1.2) |
| Compressive Strength | 20-50 MPa | 5-15 MPa |
| Material Composition | Cement, fine aggregates, additives, often fiber-reinforced | Cement, lightweight aggregates (e.g. expanded clay, perlite) |
| Construction Speed | High - Automated layer-by-layer printing | Moderate - Conventional block laying |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced waste, potential for optimized mix design | Lower embodied energy due to lightweight aggregates |
| Application | Complex shapes, custom insulation elements | Standard insulating block for walls |
Understanding 3D-Printed Concrete for Insulating Blocks
3D-printed concrete for insulating blocks offers precise control over material composition and internal geometry, enabling enhanced thermal insulation and structural performance compared to traditional lightweight concrete. This technology incorporates additives and voids to reduce density while maintaining strength, optimizing heat transfer characteristics crucial for energy-efficient building envelopes. Understanding the layer-by-layer deposition process allows for customization of insulation properties, making 3D-printed concrete a cutting-edge solution in sustainable construction materials.
What Is Lightweight Concrete? Key Properties for Insulation
Lightweight concrete is a type of concrete that incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, resulting in reduced density and enhanced thermal insulation properties. Its key properties for insulation include low thermal conductivity, high fire resistance, and improved sound absorption, making it an effective material for insulating blocks. Compared to 3D-printed concrete, lightweight concrete offers superior insulation performance due to its porous structure, which traps air and reduces heat transfer.
Thermal Performance: 3D-Printed vs. Lightweight Concrete Blocks
3D-printed concrete blocks exhibit enhanced thermal performance due to their precise layering and potential for customized internal geometries, enabling optimized insulation properties compared to traditional lightweight concrete blocks. Lightweight concrete blocks, typically composed of aggregates like expanded clay or perlite, offer lower thermal conductivity but lack the design flexibility of 3D printing to further reduce heat transfer. The ability of 3D-printed concrete to incorporate complex cavity structures can significantly improve thermal resistance, making it a superior choice for insulating block applications.
Structural Strength and Durability Comparison
3D-printed concrete insulating blocks exhibit superior structural strength due to their layered fabrication process, which allows for optimized reinforcement and reduced material wastage compared to traditional lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete blocks, while effective in thermal insulation due to their porous nature, typically have lower compressive strength and may experience higher susceptibility to cracking and degradation over time when exposed to environmental stresses. The durability of 3D-printed concrete insulating blocks benefits from precise control over mix design and curing conditions, resulting in enhanced resistance to moisture penetration and freeze-thaw cycles relative to lightweight concrete alternatives.
Material Composition and Environmental Impact
3D-printed concrete insulating blocks typically use a mix of cement, sand, and additives optimized for extrusion and rapid setting, often incorporating recycled aggregates or supplementary cementitious materials to enhance sustainability. Lightweight concrete insulating blocks are composed of traditional cement combined with lightweight fillers such as expanded clay, perlite, or foam beads, reducing density and improving thermal insulation properties with lower thermal conductivity values. In terms of environmental impact, 3D-printed concrete reduces material waste through precise layering and customization, while lightweight concrete relies on low-density aggregates that often have lower embodied energy but may involve more resource-intensive processing.
Speed and Efficiency in Construction Applications
3D-printed concrete significantly accelerates construction speed by enabling continuous, layer-by-layer deposition that reduces labor and formwork time compared to lightweight concrete insulating blocks, which require traditional casting and curing processes. The precision and automation of 3D printing improve efficiency by minimizing material waste and enabling complex geometries without additional assembly. Lightweight concrete blocks provide good thermal insulation but generally involve longer installation times and manual handling, making 3D-printed concrete more advantageous for rapid, efficient building projects.
Cost Analysis: 3D-Printed vs. Lightweight Concrete Blocks
3D-printed concrete blocks typically offer lower labor costs and reduced material waste compared to lightweight concrete blocks, resulting in overall cost savings despite higher initial equipment investment. Lightweight concrete blocks generally have higher material costs due to specialized aggregates and additives but provide advantages in thermal insulation and reduced structural load. When evaluating cost, 3D-printed blocks benefit from automation and design flexibility, while lightweight blocks incur recurring expenses related to material sourcing and traditional manufacturing processes.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
3D-printed concrete offers superior design flexibility and customization options compared to lightweight concrete for insulating blocks, enabling complex geometries and precise control over internal structures. The additive manufacturing process allows for tailored porosity and integrated channels to enhance thermal insulation and structural performance. Lightweight concrete, while easier to produce, typically limits design complexity and customization due to traditional casting methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
3D-printed concrete insulating blocks face challenges such as limited material variability, high initial equipment costs, and difficulties in achieving consistent thermal performance due to layer adhesion issues. Lightweight concrete blocks encounter limitations including lower compressive strength compared to traditional concrete, potential moisture absorption leading to reduced insulation efficiency, and longer curing times that can delay construction schedules. Both methods require advancements in material formulation and quality control to optimize thermal insulation and structural integrity in building applications.
Future Trends in Insulating Block Technologies
3D-printed concrete offers precise material placement and complex geometries, enhancing thermal insulation performance and reducing waste compared to traditional lightweight concrete blocks. Advances in additive manufacturing enable integration of advanced insulating materials, such as aerogels and phase-change materials, directly into 3D-printed blocks, pushing the boundaries of energy efficiency. Future trends indicate a shift towards customizable, smart insulating blocks with embedded sensors for real-time thermal monitoring and adaptive insulation capabilities in building envelopes.
Infographic: 3D-printed concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Insulating block
 azmater.com
azmater.com