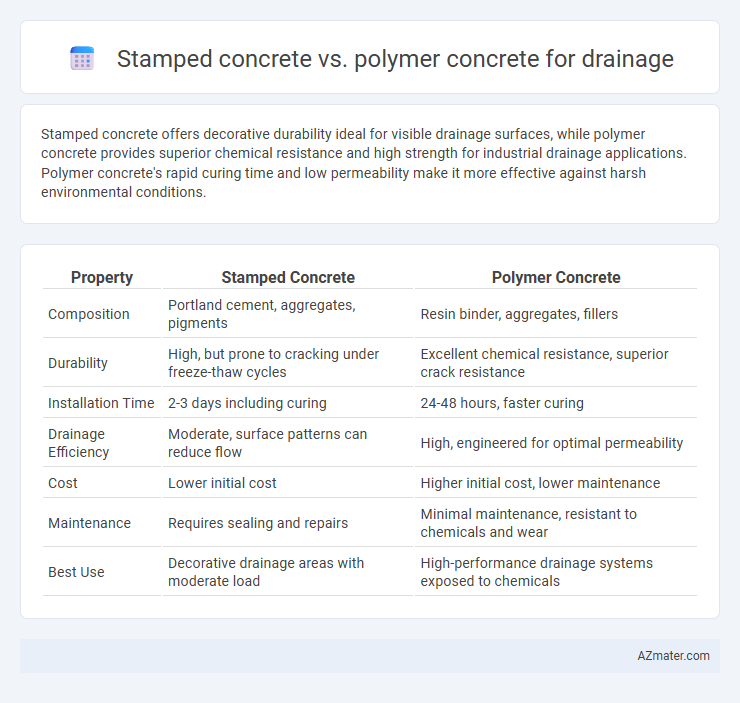
Stamped concrete offers decorative durability ideal for visible drainage surfaces, while polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and high strength for industrial drainage applications. Polymer concrete's rapid curing time and low permeability make it more effective against harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stamped Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Portland cement, aggregates, pigments | Resin binder, aggregates, fillers |
| Durability | High, but prone to cracking under freeze-thaw cycles | Excellent chemical resistance, superior crack resistance |
| Installation Time | 2-3 days including curing | 24-48 hours, faster curing |
| Drainage Efficiency | Moderate, surface patterns can reduce flow | High, engineered for optimal permeability |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing and repairs | Minimal maintenance, resistant to chemicals and wear |
| Best Use | Decorative drainage areas with moderate load | High-performance drainage systems exposed to chemicals |
Introduction to Stamped Concrete and Polymer Concrete
Stamped concrete mimics natural stone, brick, or wood patterns with durable, decorative finishes ideal for drainage areas requiring aesthetic appeal and slip resistance. Polymer concrete combines resin binders with aggregates, offering exceptional chemical resistance and strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty drainage infrastructure. Both materials provide effective solutions, with stamped concrete prioritizing design versatility and polymer concrete emphasizing performance in harsh environments.
Composition and Material Differences
Stamped concrete is primarily composed of a mixture of Portland cement, aggregates, water, and color pigments, allowing it to mimic natural stone or brick patterns through surface stamping techniques. Polymer concrete incorporates resin binders, such as epoxy or polyester, combined with aggregates, resulting in enhanced chemical resistance, faster curing times, and superior tensile strength compared to traditional cement-based mixtures. The material differences affect durability and performance, with polymer concrete offering greater resistance to corrosion and environmental stress, making it more suitable for demanding drainage systems.
Installation Process Comparison
Stamped concrete installation requires creating molds or stamps to imprint patterns onto a freshly poured concrete surface, followed by adding color hardeners and sealers for durability and aesthetics. Polymer concrete installation involves mixing resin with aggregates, then pouring and curing the mixture, which sets faster and offers superior chemical resistance compared to traditional concrete. For drainage applications, polymer concrete's rapid curing and corrosion resistance can reduce downtime and maintenance, while stamped concrete provides customizable surface textures but demands longer curing times.
Durability and Longevity
Stamped concrete and polymer concrete both offer strong solutions for drainage systems, but polymer concrete excels in durability due to its superior chemical and abrasion resistance. Polymer concrete's enhanced longevity withstands harsh environmental conditions and heavy traffic better than stamped concrete, which may suffer surface wear and cracking over time. Choosing polymer concrete ensures extended service life and reduced maintenance costs in drainage applications exposed to corrosive substances and mechanical stress.
Performance in Drainage Applications
Stamped concrete offers robust durability and aesthetic appeal but may be prone to surface wear and cracking under heavy water flow in drainage systems. Polymer concrete demonstrates superior chemical resistance, higher compressive strength, and enhanced impermeability, making it ideal for high-performance drainage applications exposed to aggressive chemicals and constant moisture. The choice between stamped and polymer concrete depends on balancing visual requirements with the need for long-term structural integrity and resistance to erosion in drainage environments.
Maintenance Requirements
Stamped concrete requires regular sealing every 2-3 years to prevent staining and wear, while polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and minimal upkeep due to its dense, non-porous surface. Polymer concrete's high durability reduces the need for repairs caused by freeze-thaw cycles and heavy traffic common in drainage systems. Maintenance for stamped concrete involves more frequent cleaning and resealing to maintain aesthetic appeal and structural integrity in drainage applications.
Cost Analysis
Stamped concrete typically incurs lower initial installation costs compared to polymer concrete, making it a budget-friendly option for decorative drainage surfaces. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and durability, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses despite its higher upfront price. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals that polymer concrete may provide better value for drainage systems exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Aesthetic Options and Customization
Stamped concrete offers extensive aesthetic options with customizable patterns, colors, and textures that mimic natural stone, brick, or wood, making it ideal for decorative drainage features. Polymer concrete provides a smooth, uniform finish with limited design variety but excels in durability and chemical resistance for functional drainage systems. Selecting between these materials depends on prioritizing either visual customization or enhanced performance in drainage applications.
Environmental Impact
Stamped concrete often involves cementitious materials with higher CO2 emissions during production, contributing more to environmental degradation compared to polymer concrete. Polymer concrete uses resin binders derived from industrial byproducts, offering lower permeability and increased resistance to chemical exposure, which reduces maintenance-related environmental impacts. Choosing polymer concrete for drainage systems supports sustainability goals by minimizing carbon footprint and enhancing durability against harsh environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Drainage Solutions
Stamped concrete offers aesthetic appeal with customizable patterns and colors but may lack the durability required for high-traffic or heavy-load drainage systems. Polymer concrete, composed of resin binders and aggregates, provides superior chemical resistance, rapid curing times, and enhanced mechanical strength, making it ideal for harsh drainage environments. Selecting polymer concrete for drainage solutions ensures long-term performance and reduced maintenance in infrastructure exposed to aggressive chemicals and heavy water flow.
Infographic: Stamped concrete vs Polymer concrete for Drainage
 azmater.com
azmater.com