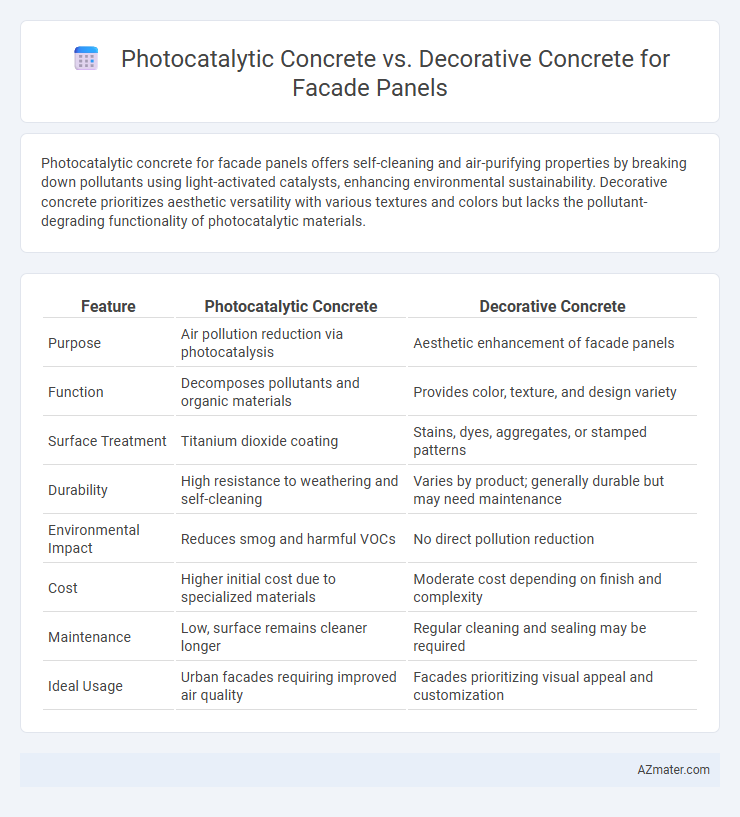
Photocatalytic concrete for facade panels offers self-cleaning and air-purifying properties by breaking down pollutants using light-activated catalysts, enhancing environmental sustainability. Decorative concrete prioritizes aesthetic versatility with various textures and colors but lacks the pollutant-degrading functionality of photocatalytic materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photocatalytic Concrete | Decorative Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Air pollution reduction via photocatalysis | Aesthetic enhancement of facade panels |
| Function | Decomposes pollutants and organic materials | Provides color, texture, and design variety |
| Surface Treatment | Titanium dioxide coating | Stains, dyes, aggregates, or stamped patterns |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and self-cleaning | Varies by product; generally durable but may need maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces smog and harmful VOCs | No direct pollution reduction |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to specialized materials | Moderate cost depending on finish and complexity |
| Maintenance | Low, surface remains cleaner longer | Regular cleaning and sealing may be required |
| Ideal Usage | Urban facades requiring improved air quality | Facades prioritizing visual appeal and customization |
Introduction to Photocatalytic and Decorative Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates photocatalysts such as titanium dioxide to break down pollutants and reduce air contaminants on facade panels, offering self-cleaning and environmental benefits. Decorative concrete enhances aesthetic appeal through various finishes, textures, and coloring techniques, focusing primarily on design and visual impact. Both types serve distinct purposes: photocatalytic concrete improves sustainability and maintenance efficiency, while decorative concrete prioritizes customization and architectural beauty.
Key Properties of Photocatalytic Concrete Façade Panels
Photocatalytic concrete facade panels utilize titanium dioxide to break down pollutants, providing self-cleaning and air-purifying properties that enhance urban environmental quality. These panels exhibit high durability, resistance to weathering, and reduced maintenance costs due to their ability to decompose organic matter and prevent surface staining. Compared to decorative concrete, photocatalytic concrete offers superior functional benefits for facades by actively improving air quality while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Aesthetic Features of Decorative Concrete Panels
Decorative concrete panels offer a wide range of aesthetic features including customizable textures, colors, and patterns that can mimic natural stone, wood, or intricate geometric designs. These panels enhance the visual appeal of facades by providing unique and artistic finishes that complement architectural styles. Unlike photocatalytic concrete, which primarily focuses on self-cleaning and pollution reduction, decorative concrete prioritizes creative expression and surface detailing for striking exterior appearances.
Environmental Benefits: Photocatalytic vs Decorative Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide, which actively breaks down pollutants and reduces nitrogen oxide levels, improving air quality around the facade. Decorative concrete primarily focuses on aesthetic appeal without contributing to environmental cleansing or pollution reduction. The photocatalytic properties offer a sustainable solution by promoting cleaner urban environments, whereas decorative concrete supports design versatility but lacks direct environmental benefits.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Photocatalytic concrete offers superior durability due to its self-cleaning and pollution-reducing properties, which minimize surface degradation and extend facade lifespan. Decorative concrete, while aesthetically versatile, often requires frequent maintenance such as sealing or recoating to preserve appearance and prevent weather-related damage. Maintenance for photocatalytic concrete is typically lower, reducing lifecycle costs by enhancing resistance to dirt, grime, and environmental pollutants on facade panels.
Architectural Design Flexibility
Photocatalytic concrete offers enhanced architectural design flexibility by integrating advanced self-cleaning and pollution-reducing properties without compromising aesthetic options. Decorative concrete provides a broader palette of textures, colors, and patterns, allowing architects to customize facade panels extensively. Combining photocatalytic additives with decorative finishes can optimize both environmental performance and design versatility in modern facades.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Photocatalytic concrete typically incurs higher upfront costs than decorative concrete due to advanced photocatalyst additives and specialized manufacturing processes, which enhance pollution reduction and self-cleaning properties. Decorative concrete offers a more budget-friendly option with versatile aesthetic finishes and lower material costs but lacks the environmental benefits and durability enhancements of photocatalytic variants. Project budgets must balance initial investment against long-term maintenance savings and environmental impact when choosing between photocatalytic and decorative facade panels.
Impact on Urban Air Quality
Photocatalytic concrete for facade panels significantly reduces urban air pollution by breaking down harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) through a light-activated chemical reaction, improving air quality around buildings. Decorative concrete lacks these self-cleaning and pollutant-degrading properties, offering primarily aesthetic benefits without contributing to air purification. Integrating photocatalytic technology in urban construction can actively mitigate smog and particulate matter, enhancing environmental health in densely populated areas.
Installation Techniques and Challenges
Photocatalytic concrete facade panels require precise installation techniques to ensure the surface remains exposed to air and light for optimal pollutant degradation, often necessitating specialized mounting systems and protective coatings to maintain photocatalytic efficiency. Decorative concrete panels prioritize aesthetic customization with diverse textures and pigments, allowing more flexibility during installation but requiring careful handling to avoid surface damage that can compromise visual appeal. Both types face challenges such as weight management and ensuring structural compatibility with buildings, but photocatalytic panels demand additional attention to maintaining surface activity over time.
Application Scenarios and Best Use Cases
Photocatalytic concrete is ideal for urban facades requiring pollution reduction and self-cleaning properties, making it suitable for high-traffic public buildings and commercial structures exposed to environmental pollutants. Decorative concrete excels in aesthetic customization for residential facades, retail spaces, and architectural projects prioritizing visual appeal with options like stamped patterns, colors, and textures. Selecting between the two depends on whether the primary goal is environmental functionality or enhanced design flexibility in facade panel applications.
Infographic: Photocatalytic concrete vs Decorative concrete for Façade panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com