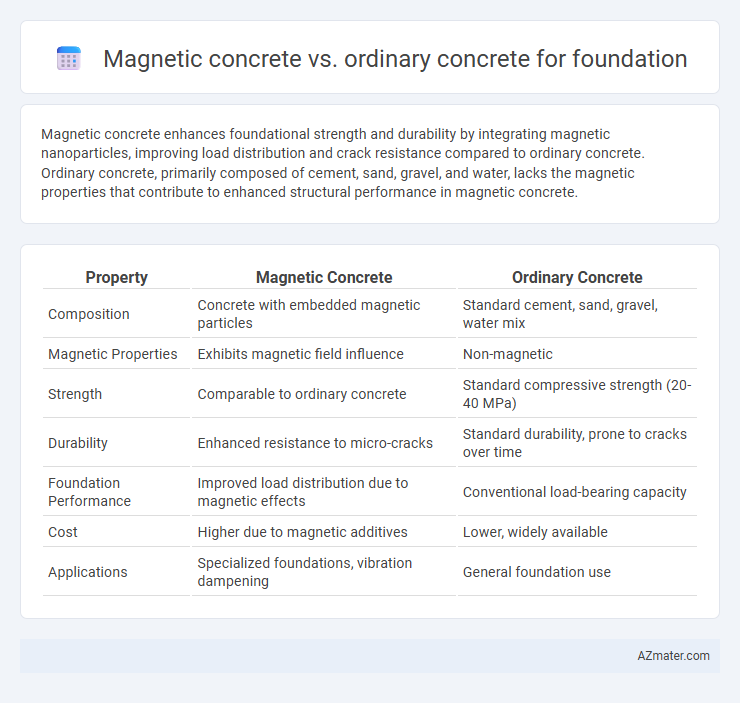
Magnetic concrete enhances foundational strength and durability by integrating magnetic nanoparticles, improving load distribution and crack resistance compared to ordinary concrete. Ordinary concrete, primarily composed of cement, sand, gravel, and water, lacks the magnetic properties that contribute to enhanced structural performance in magnetic concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | Ordinary Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete with embedded magnetic particles | Standard cement, sand, gravel, water mix |
| Magnetic Properties | Exhibits magnetic field influence | Non-magnetic |
| Strength | Comparable to ordinary concrete | Standard compressive strength (20-40 MPa) |
| Durability | Enhanced resistance to micro-cracks | Standard durability, prone to cracks over time |
| Foundation Performance | Improved load distribution due to magnetic effects | Conventional load-bearing capacity |
| Cost | Higher due to magnetic additives | Lower, widely available |
| Applications | Specialized foundations, vibration dampening | General foundation use |
Introduction to Magnetic Concrete and Ordinary Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates magnetically responsive materials such as iron filings or magnetic nanoparticles within its mixture, enhancing its durability and electromagnetic properties compared to Ordinary concrete, which is traditionally composed of cement, water, sand, and aggregates without magnetic additives. Ordinary concrete remains the standard choice for foundations due to its cost-effectiveness and proven compressive strength, while magnetic concrete offers potential advancements in structural health monitoring and electromagnetic interference resistance. Research into magnetic concrete's application in foundations highlights improved crack detection and energy dissipation capabilities, presenting a novel alternative to conventional concrete solutions.
Composition Differences Between Magnetic and Ordinary Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials such as iron ore or magnetite particles, enhancing its electromagnetic properties, whereas ordinary concrete primarily consists of cement, sand, gravel, and water without magnetic additives. The inclusion of magnetic minerals in magnetic concrete alters its microstructure and electromagnetic responsiveness, which can influence its mechanical strength and durability in foundation applications. These compositional differences are critical in determining the suitability and performance of concrete types for specialized foundation construction.
Physical Properties Comparison
Magnetic concrete exhibits enhanced density and compressive strength compared to ordinary concrete, resulting in superior load-bearing capacity for foundations. Its improved thermal conductivity and reduced porosity contribute to better durability and resistance to environmental degradation. Ordinary concrete, while widely used, typically has lower strength and higher permeability, making it less effective in harsh or magnetically influenced environments.
Magnetic Concrete: How It Works
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles such as iron or steel fibers into the concrete mix, creating a material that responds to magnetic fields while maintaining structural integrity. The embedded magnetic components enhance properties like crack resistance, self-sensing ability, and electromagnetic shielding, making it effective for advanced foundation applications. This functionality allows magnetic concrete to detect stress changes and structural faults in real-time, providing a smart foundation solution beyond the capabilities of ordinary concrete.
Structural Performance in Foundations
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles that enhance its structural performance by improving load-bearing capacity, reducing microcracks, and increasing durability compared to ordinary concrete. The magnetically influenced matrix exhibits superior resistance to tensile stress and dynamic loads, making it ideal for foundation applications requiring enhanced stability. Studies show that magnetic concrete foundations demonstrate higher compressive strength and better vibration damping, leading to prolonged structural integrity under varying environmental conditions.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Magnetic concrete exhibits enhanced durability due to its improved microstructural density, reducing porosity and resistance to environmental degradation compared to ordinary concrete. The incorporation of magnetic materials helps mitigate micro-cracking and enhances bonding strength, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance for foundations. Studies reveal magnetic concrete foundations maintain structural integrity under aggressive conditions better than conventional concrete, making them a superior choice for long-term durability and longevity.
Cost Implications and Resource Availability
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials, increasing initial costs by 20-30% compared to ordinary concrete due to specialized raw materials and manufacturing processes. Resource availability for magnetic concrete is limited, often requiring sourcing rare metals, which can delay project timelines and inflate expenses, while ordinary concrete uses widely available aggregates and cement, ensuring cost-effective material procurement. The long-term benefits of magnetic concrete, such as enhanced structural health monitoring, may offset upfront costs but require careful evaluation of project budgets and material supply chains.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferrous materials that enhance its structural integrity while reducing the need for traditional cement, significantly lowering CO2 emissions compared to ordinary concrete used in foundations. The reduced cement content in magnetic concrete decreases environmental degradation and promotes sustainability through lower energy consumption and resource extraction. This innovative material extends the lifespan of foundations, minimizing repair frequency and thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint associated with construction and maintenance.
Applications Best Suited for Each Concrete Type
Magnetic concrete is best suited for specialized foundations requiring electromagnetic shielding or enhanced structural health monitoring in industrial and research facilities. Ordinary concrete remains preferred for general construction projects due to its proven durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use in residential, commercial, and infrastructure foundations. Applications involving electromagnetic interference control or smart sensor integration benefit significantly from magnetic concrete's unique properties.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Foundation
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials that enhance its structural integrity and electromagnetic properties, offering superior durability and crack resistance compared to ordinary concrete. Choosing magnetic concrete for foundations can improve load-bearing capacity and reduce maintenance costs in critical infrastructure projects exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ordinary concrete remains a cost-effective option for standard residential foundations where electromagnetic properties are not required.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Ordinary concrete for Foundation
 azmater.com
azmater.com