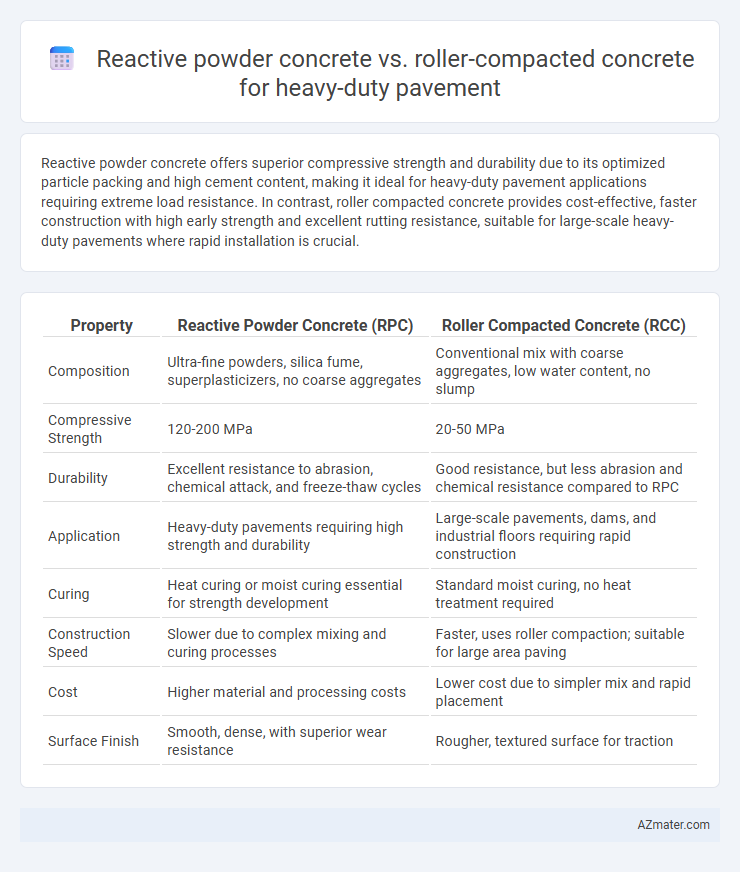
Reactive powder concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability due to its optimized particle packing and high cement content, making it ideal for heavy-duty pavement applications requiring extreme load resistance. In contrast, roller compacted concrete provides cost-effective, faster construction with high early strength and excellent rutting resistance, suitable for large-scale heavy-duty pavements where rapid installation is crucial.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) | Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Ultra-fine powders, silica fume, superplasticizers, no coarse aggregates | Conventional mix with coarse aggregates, low water content, no slump |
| Compressive Strength | 120-200 MPa | 20-50 MPa |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to abrasion, chemical attack, and freeze-thaw cycles | Good resistance, but less abrasion and chemical resistance compared to RPC |
| Application | Heavy-duty pavements requiring high strength and durability | Large-scale pavements, dams, and industrial floors requiring rapid construction |
| Curing | Heat curing or moist curing essential for strength development | Standard moist curing, no heat treatment required |
| Construction Speed | Slower due to complex mixing and curing processes | Faster, uses roller compaction; suitable for large area paving |
| Cost | Higher material and processing costs | Lower cost due to simpler mix and rapid placement |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, dense, with superior wear resistance | Rougher, textured surface for traction |
Introduction to Heavy Duty Pavement Materials
Heavy duty pavement materials require superior strength, durability, and resistance to heavy traffic loads and environmental stressors. Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits ultra-high strength and enhanced durability through optimized particle packing and micro-reinforcement, making it suitable for demanding pavement applications. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) offers rapid construction with reduced costs while maintaining high compressive strength, ideal for large-scale heavy duty pavement projects such as industrial yards and highways.
Overview of Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC)
Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) is an advanced cementitious material characterized by ultra-high strength and exceptional durability due to the optimized particle packing, fine powders, and low water-to-cement ratio. Its microstructure is densely packed with reactive silica fume and quartz sand, significantly enhancing mechanical properties and resistance to chemical attacks, making it suitable for heavy-duty pavement applications where strength and longevity are critical. Compared to traditional concrete types like Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC), RPC offers superior flexural strength and reduced permeability, contributing to extended pavement life under intense traffic loads.
Overview of Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC)
Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC) is a dense, zero-slump concrete characterized by its granular structure and high compressive strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty pavement applications such as highways and industrial floors. It is placed using asphalt laydown equipment and compacted with vibratory rollers, offering rapid construction, reduced formwork, and lower costs compared to traditional concrete. RCC's durability under heavy traffic loads and resistance to abrasion and freeze-thaw cycles ensure long service life in demanding pavement environments.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) utilizes ultra-fine powders such as silica fume, quartz flour, and a low water-to-cement ratio with steel fibers, resulting in ultra-high strength and exceptional durability for heavy-duty pavement applications. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) combines conventional concrete materials with lower cement content and zero-slump consistency, compacted using rollers to achieve high density and rapid construction, offering excellent load-bearing capacity and abrasion resistance. RPC provides superior mechanical properties and durability due to its optimized particle packing and minimized porosity, while RCC excels in cost-effectiveness and ease of placement for large-scale heavy-duty pavement projects.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits superior mechanical strength with compressive strengths often exceeding 200 MPa, making it highly suitable for heavy-duty pavement requiring exceptional load-bearing capacity. Its dense microstructure enhances durability by minimizing permeability and increasing resistance to abrasion, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical attacks. Roller compacted concrete (RCC), while possessing lower compressive strengths typically around 30-70 MPa, offers faster construction and cost efficiency but may require additional surface treatments to improve durability under heavy traffic conditions.
Construction Techniques and Ease of Placement
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) employs high-energy mixing and precise casting techniques, requiring skilled labor and specialized equipment for optimal densification and placement, which can limit ease of use on large-scale heavy duty pavements. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes conventional asphalt paving and compaction machinery, allowing rapid placement with lower labor intensity and straightforward construction workflows suited for extensive pavement surfaces. The high flowability and curing precision of RPC enhance structural performance but complicate on-site handling, whereas RCC's simpler, more robust placement methods provide cost-effective and efficient solutions for heavy duty pavement construction.
Performance in Heavy Traffic Conditions
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits superior performance in heavy traffic conditions due to its high compressive strength, low permeability, and enhanced durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty pavement subjected to intense loads. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) provides rapid construction and good load-bearing capacity but may experience higher susceptibility to cracking and lower tensile strength compared to RPC under continuous heavy traffic. The dense microstructure and refined aggregate packing of RPC result in better resistance to fatigue, abrasion, and environmental degradation, ensuring longer service life in demanding pavement applications.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior durability and high compressive strength, resulting in significantly lower maintenance requirements and extended lifecycle performance for heavy-duty pavements. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) provides cost-effective initial construction but often incurs higher maintenance costs due to lower tensile strength and susceptibility to cracking under heavy loads. Overall, RPC's enhanced mechanical properties contribute to reduced repair frequency and lifecycle costs, making it a preferred choice for heavy-duty pavement applications with long-term cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior durability and strength with reduced material usage, leading to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional concrete types. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes less cement and requires minimal water, reducing overall environmental impact and enabling faster construction with lower energy consumption. Both materials support sustainable heavy-duty pavement by enhancing service life and minimizing maintenance, yet RPC's dense microstructure provides greater resistance to chemical attack and wear, extending pavement longevity.
Recommended Applications and Conclusion
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) is highly recommended for heavy-duty pavements requiring superior compressive strength, durability, and resistance to chemical attacks, making it ideal for airport runways, industrial floors, and heavy-load highway surfaces. Roller compacted concrete (RCC), with its moderate strength and rapid construction benefits, suits applications such as dam embankments, pavements with lower traffic stresses, and large-scale industrial platforms. For heavy-duty pavement, RPC offers enhanced longevity and load-bearing capacity, while RCC provides cost-effective, fast placement for projects prioritizing speed and economy.
Infographic: Reactive powder concrete vs Roller compacted concrete for Heavy duty pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com