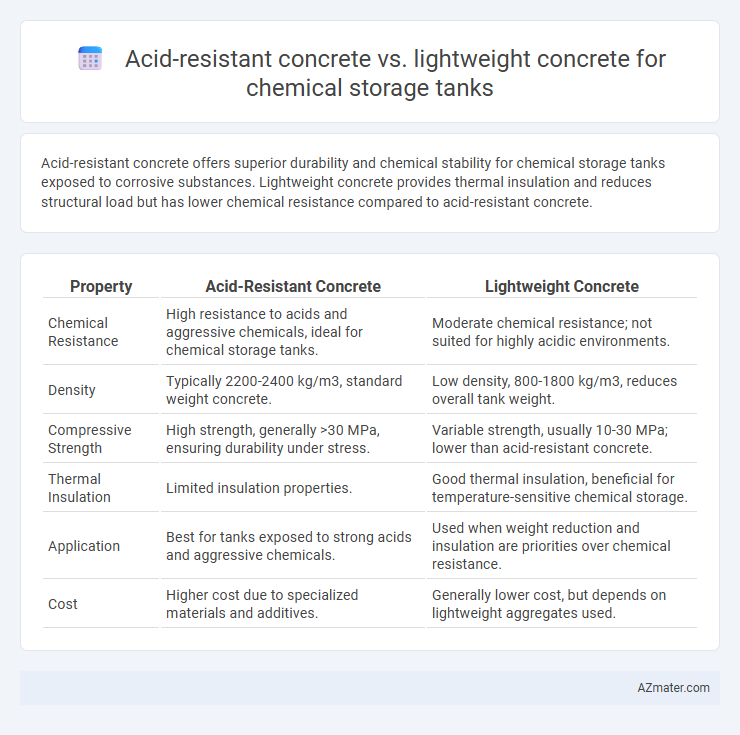
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability and chemical stability for chemical storage tanks exposed to corrosive substances. Lightweight concrete provides thermal insulation and reduces structural load but has lower chemical resistance compared to acid-resistant concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids and aggressive chemicals, ideal for chemical storage tanks. | Moderate chemical resistance; not suited for highly acidic environments. |
| Density | Typically 2200-2400 kg/m3, standard weight concrete. | Low density, 800-1800 kg/m3, reduces overall tank weight. |
| Compressive Strength | High strength, generally >30 MPa, ensuring durability under stress. | Variable strength, usually 10-30 MPa; lower than acid-resistant concrete. |
| Thermal Insulation | Limited insulation properties. | Good thermal insulation, beneficial for temperature-sensitive chemical storage. |
| Application | Best for tanks exposed to strong acids and aggressive chemicals. | Used when weight reduction and insulation are priorities over chemical resistance. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized materials and additives. | Generally lower cost, but depends on lightweight aggregates used. |
Understanding Acid-Resistant Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is specifically formulated with materials such as silica, quartz, and polymers to withstand highly corrosive chemical environments, making it ideal for chemical storage tanks exposed to acids. Its dense microstructure prevents acid penetration, significantly reducing chemical degradation and extending the lifespan of storage tanks. Lightweight concrete, while offering benefits like reduced structural load, lacks the specialized chemical resistance properties essential for protecting tanks against acid corrosion.
Key Properties of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete used in chemical storage tanks offers high thermal insulation, low density for ease of handling, and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion when properly formulated. Its porous structure reduces overall weight without compromising compressive strength, making it ideal for large-scale tank construction and minimizing structural load. Enhanced durability and resistance to acidic environments, achieved through specialized aggregates and additives, ensure long-term performance in chemical storage applications.
Chemical Storage Tank Requirements
Acid-resistant concrete for chemical storage tanks provides superior protection against aggressive chemical corrosion, ensuring long-term durability in highly acidic or corrosive environments. Lightweight concrete offers benefits such as reduced structural load and enhanced thermal insulation but typically lacks the chemical resistance necessary for storing aggressive chemicals. Selecting the appropriate concrete depends on the specific chemical storage tank requirements, including chemical compatibility, structural integrity, and environmental conditions.
Durability in Aggressive Chemical Environments
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in aggressive chemical environments due to its specialized cementitious materials and chemical-resistant additives that prevent corrosion and degradation. Lightweight concrete, while beneficial for structural weight reduction, typically lacks the chemical resistance required for harsh acidic conditions, making it more susceptible to deterioration and reduced lifespan in chemical storage tanks. Selecting acid-resistant concrete ensures enhanced longevity and reliability when exposed to strong acids and aggressive chemicals.
Structural Performance Comparison
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits superior chemical durability and enhanced structural integrity, making it ideal for chemical storage tanks exposed to corrosive substances. Lightweight concrete offers reduced density and improved thermal insulation but generally has lower compressive strength and chemical resistance compared to acid-resistant variants. For structural performance, acid-resistant concrete ensures higher durability and load-bearing capacity essential for maintaining long-term tank stability in aggressive environments.
Weight Considerations and Tank Design
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability against corrosive chemicals while maintaining a high density that increases tank weight, impacting foundation design and structural support requirements. Lightweight concrete reduces the overall tank load due to its lower density, facilitating easier handling and installation but may require additional protective coatings to resist chemical attack effectively. Selecting between acid-resistant and lightweight concrete for chemical storage tanks depends on balancing weight constraints with the necessity for chemical resistance to optimize tank design and performance.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Acid-resistant concrete for chemical storage tanks requires specialized installation techniques including the use of acid-proof aggregates and coatings to ensure durability against corrosive substances, which can increase initial labor costs and complexity. Lightweight concrete offers easier handling and faster installation due to its reduced weight, but may require additional protective measures or admixtures to withstand chemical exposure without degradation. Maintenance of acid-resistant concrete generally involves routine inspections for surface integrity and timely repair of any chemical damage, whereas lightweight concrete may demand more frequent upkeep to address potential porosity and structural vulnerability in harsh chemical environments.
Cost Analysis: Acid-Resistant vs Lightweight Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized raw materials like silica fume and chemical-resistant aggregates, which enhance durability against corrosive substances in chemical storage tanks. Lightweight concrete offers cost savings in transportation and handling because of reduced density, but may require additional protective coatings or liners to ensure chemical resistance, increasing overall maintenance expenses. Evaluating total life-cycle costs reveals acid-resistant concrete provides long-term economic benefits by minimizing repair frequency and extending tank lifespan in aggressive chemical environments.
Case Studies: Chemical Storage Applications
Case studies on chemical storage tanks highlight acid-resistant concrete's superior durability and resistance to aggressive chemicals compared to lightweight concrete, which often lacks sufficient chemical resistance. Projects in industrial plants demonstrate acid-resistant concrete preventing corrosion and structural damage in sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid storage tanks, extending service life beyond 20 years. Lightweight concrete is favored in applications prioritizing reduced dead load but typically requires protective coatings to withstand chemical exposure, increasing maintenance demands and lifecycle costs.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Chemical Storage Tanks
Selecting acid-resistant concrete for chemical storage tanks ensures superior protection against corrosive substances, preventing structural degradation and extending tank lifespan. Lightweight concrete offers advantages in reducing overall structural load and simplifying installation but may lack the chemical resistance required for aggressive storage environments. Prioritizing acid-resistant concrete balances durability and safety, making it the preferred choice for handling highly acidic or reactive chemicals in storage applications.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Chemical storage tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com