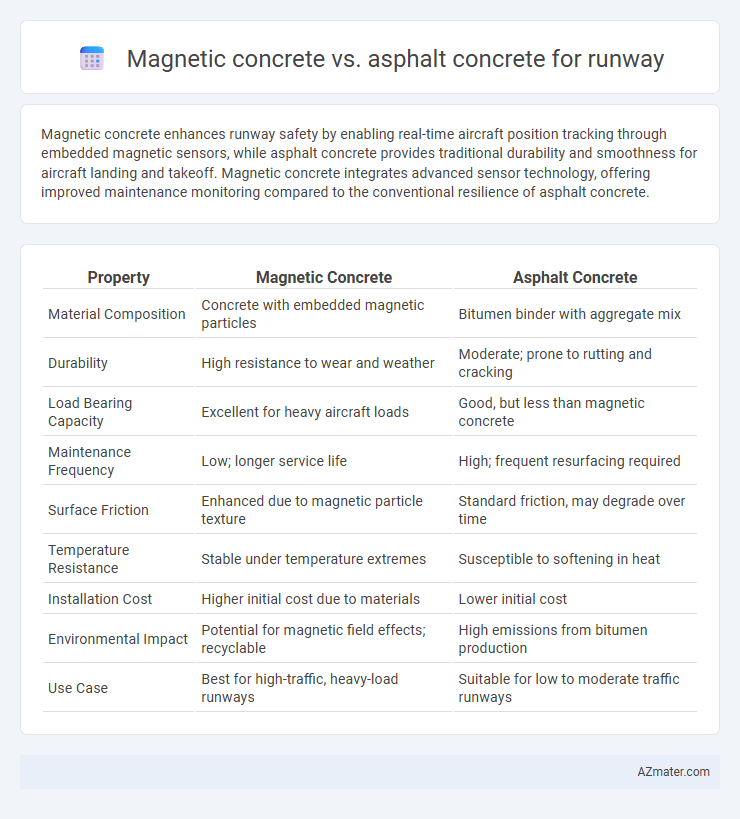
Magnetic concrete enhances runway safety by enabling real-time aircraft position tracking through embedded magnetic sensors, while asphalt concrete provides traditional durability and smoothness for aircraft landing and takeoff. Magnetic concrete integrates advanced sensor technology, offering improved maintenance monitoring compared to the conventional resilience of asphalt concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | Asphalt Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Concrete with embedded magnetic particles | Bitumen binder with aggregate mix |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and weather | Moderate; prone to rutting and cracking |
| Load Bearing Capacity | Excellent for heavy aircraft loads | Good, but less than magnetic concrete |
| Maintenance Frequency | Low; longer service life | High; frequent resurfacing required |
| Surface Friction | Enhanced due to magnetic particle texture | Standard friction, may degrade over time |
| Temperature Resistance | Stable under temperature extremes | Susceptible to softening in heat |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for magnetic field effects; recyclable | High emissions from bitumen production |
| Use Case | Best for high-traffic, heavy-load runways | Suitable for low to moderate traffic runways |
Introduction to Runway Surface Materials
Runway surface materials like magnetic concrete and asphalt concrete significantly impact airport operations and maintenance. Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles enhancing electromagnetic properties, while asphalt concrete offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness in construction. Selection depends on factors such as durability, weather resistance, and radar compatibility essential for runway performance.
Overview of Magnetic Concrete
Magnetic concrete integrates ferromagnetic materials such as iron oxide to enhance electromagnetic properties while maintaining structural strength, providing unique benefits for runway applications like improved de-icing and electromagnetic interference reduction. Its composition includes a mix of traditional cement, aggregates, and magnetic particles that can interact with external magnetic fields to facilitate snow and ice melting without chemical agents. Compared to conventional asphalt concrete, magnetic concrete offers potential for longer service life and reduced maintenance costs by leveraging its thermal and magnetic capabilities in harsh weather conditions.
Overview of Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt concrete is a widely used material for runway construction, known for its flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. It consists of aggregates bound together by bitumen, providing excellent resistance to heavy aircraft loads and varying weather conditions. The material also offers ease of maintenance and quicker repair times compared to alternatives like magnetic concrete, making it suitable for high-traffic airport runways.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles enhancing electromagnetic properties, which can improve runway surface sensing and heating systems, while asphalt concrete offers superior flexibility and water resistance, essential for maintaining smoothness and durability under varying weather conditions. The compressive strength of magnetic concrete typically ranges between 30-50 MPa, suitable for bearing heavy aircraft loads, whereas asphalt concrete's tensile strength averages around 1-5 MPa but excels in fatigue resistance. Thermal conductivity in magnetic concrete is higher due to metallic inclusions, potentially aiding snow and ice melting, whereas asphalt concrete's lower thermal conductivity contributes to heat retention and reduces surface deformation under high temperatures.
Installation and Construction Techniques
Magnetic concrete for runways requires embedding magnetic particles within the concrete mix, demanding precise placement and curing techniques to ensure uniform magnetic properties and structural integrity. Asphalt concrete installation involves hot-mix laying and compaction with rollers, offering faster construction times and easier maintenance compared to the more complex curing process of magnetic concrete. Both methods require specialized equipment, but magnetic concrete necessitates additional steps in mixing and quality control to achieve desired electromagnetic functionality alongside traditional strength standards.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Magnetic concrete offers enhanced durability for runways by providing superior crack resistance and thermal stability compared to traditional asphalt concrete, which is prone to rutting and surface degradation under heavy aircraft loads. Maintenance requirements for magnetic concrete are generally lower due to its long-lasting structural integrity and reduced susceptibility to weathering, whereas asphalt concrete demands frequent resurfacing and patching to address wear and damage. The extended lifespan and reduced maintenance frequency of magnetic concrete contribute to lower lifecycle costs and increased runway operational availability.
Performance in Diverse Weather Conditions
Magnetic concrete exhibits superior performance in diverse weather conditions due to its enhanced thermal conductivity and resistance to freezing, reducing ice formation and improving runway safety in cold climates. Asphalt concrete tends to soften in high temperatures, leading to rutting and deformation, whereas magnetic concrete maintains structural integrity under temperature extremes, ensuring consistent load-bearing capacity. These properties make magnetic concrete a more reliable choice for runways subject to significant temperature fluctuations and varying weather conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Magnetic concrete, embedded with ferromagnetic particles, offers enhanced durability and energy efficiency by enabling inductive heating for ice removal, reducing chemical de-icers that harm the environment. Asphalt concrete, while widely used, relies on petroleum products and contributes to urban heat islands due to its dark surface, increasing energy consumption and emissions. Sustainable runway designs prioritize magnetic concrete for its potential to lower carbon footprints and mitigate environmental impacts compared to traditional asphalt surfaces.
Cost Analysis: Magnetic vs Asphalt Concrete
Magnetic concrete for runways typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced materials and embedded electromagnetic systems, whereas asphalt concrete offers lower upfront expenses and widespread availability. Maintenance expenses for magnetic concrete tend to be reduced over time, benefiting from enhanced durability and self-heating properties that reduce snow and ice removal costs. Life-cycle cost analysis often favors magnetic concrete in colder climates despite its premium initial investment, while asphalt remains more cost-effective for regions with moderate weather and frequent resurfacing requirements.
Future Trends in Runway Surface Technology
Magnetic concrete for runways offers enhanced energy efficiency through electromagnetic braking and potential integration with electric aircraft systems, presenting a futuristic alternative to traditional asphalt concrete. Emerging runway surface technologies emphasize durability, self-healing properties, and smart sensor integration, where magnetic concrete can facilitate real-time monitoring and energy harvesting. As airport infrastructure evolves, combining magnetic concrete with advanced composites could revolutionize runway performance, reducing maintenance costs and improving safety compared to conventional asphalt surfaces.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Asphalt concrete for Runway
 azmater.com
azmater.com