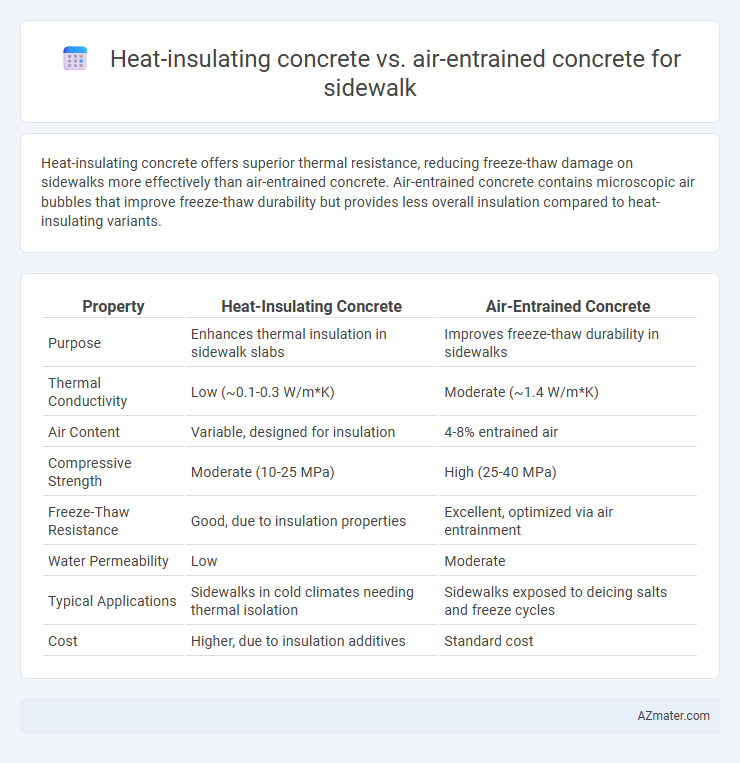
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance, reducing freeze-thaw damage on sidewalks more effectively than air-entrained concrete. Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw durability but provides less overall insulation compared to heat-insulating variants.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Heat-Insulating Concrete | Air-Entrained Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances thermal insulation in sidewalk slabs | Improves freeze-thaw durability in sidewalks |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (~0.1-0.3 W/m*K) | Moderate (~1.4 W/m*K) |
| Air Content | Variable, designed for insulation | 4-8% entrained air |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (10-25 MPa) | High (25-40 MPa) |
| Freeze-Thaw Resistance | Good, due to insulation properties | Excellent, optimized via air entrainment |
| Water Permeability | Low | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | Sidewalks in cold climates needing thermal isolation | Sidewalks exposed to deicing salts and freeze cycles |
| Cost | Higher, due to insulation additives | Standard cost |
Introduction to Sidewalk Concrete Technologies
Heat-insulating concrete incorporates materials like expanded polystyrene beads or aerogel to significantly reduce thermal conductivity, enhancing sidewalk durability in freeze-thaw conditions. Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles created by entraining agents, improving resistance to freeze-thaw cycles and reducing surface scaling. Both technologies optimize concrete performance for sidewalks by increasing longevity and minimizing damage caused by temperature fluctuations and moisture intrusion.
What is Heat-Insulating Concrete?
Heat-insulating concrete is a specialized composite material designed to reduce thermal conductivity and maintain surface temperature stability in sidewalks, enhancing energy efficiency and freeze-thaw resistance. This concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates, insulating additives, or air pockets to limit heat transfer, providing superior thermal insulation compared to standard air-entrained concrete. While air-entrained concrete improves durability by entrapping microscopic air bubbles to resist freeze-thaw damage, heat-insulating concrete specifically optimizes thermal performance, making it ideal for climates with extreme temperature variations.
Understanding Air-Entrained Concrete
Air-entrained concrete incorporates microscopic air bubbles that enhance durability and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, making it ideal for sidewalks in cold climates. These air pockets reduce internal stress caused by water expansion when freezing, significantly decreasing cracking and surface damage. In contrast, heat-insulating concrete focuses primarily on thermal resistance but may lack the freeze-thaw protection essential for long-lasting sidewalk performance.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat-insulating concrete exhibits lower thermal conductivity, enhancing energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through sidewalks, which helps maintain surface temperature stability. Air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, but its thermal resistance is generally less effective compared to heat-insulating concrete. For thermal performance, heat-insulating concrete provides superior insulation properties, making it ideal for sidewalks in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations.
Durability in Freeze-Thaw Cycles
Heat-insulating concrete enhances freeze-thaw durability by reducing thermal conductivity, which minimizes internal temperature fluctuations and stress damage during seasonal changes. Air-entrained concrete introduces microscopic air bubbles that act as pressure relief zones, significantly improving resistance to freeze-thaw cycling by preventing microcracking. Both concretes improve sidewalk longevity in cold climates, with air-entrained concrete offering superior freeze-thaw resistance due to its deliberate entrained air structure.
Impact on Sidewalk Longevity
Heat-insulating concrete enhances sidewalk longevity by reducing thermal stress and minimizing freeze-thaw damage through its superior insulation properties. Air-entrained concrete improves durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that alleviate internal pressure from freezing water, thereby preventing cracking and scaling. Both types contribute to extended sidewalk lifespan, but heat-insulating concrete offers added benefits in extreme temperature fluctuations due to its thermal regulation capabilities.
Installation and Workability Factors
Heat-insulating concrete features lightweight aggregates and high porosity, enhancing thermal resistance but requiring careful moisture control during installation to prevent cracking. Air-entrained concrete incorporates microscopic air bubbles, improving freeze-thaw durability and workability, making it easier to place and finish under cold weather conditions. Both types demand specialized mixing techniques and curing processes to optimize performance on sidewalks subject to temperature fluctuations.
Cost Implications for Urban Projects
Heat-insulating concrete typically incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes but offers long-term energy savings by reducing surface heat absorption in urban sidewalks. Air-entrained concrete is more cost-effective initially and improves durability by enhancing freeze-thaw resistance, thereby lowering maintenance expenses over time. Urban projects must balance the immediate budget constraints with potential lifecycle savings, where heat-insulating concrete suits thermal management priorities and air-entrained concrete optimizes structural longevity in colder climates.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Heat-insulating concrete for sidewalks reduces energy consumption by providing superior thermal resistance, lowering urban heat island effects and enhancing pedestrian comfort. Air-entrained concrete improves durability by increasing freeze-thaw resistance, minimizing maintenance needs and extending sidewalk lifespan, which reduces material consumption over time. Both options contribute to sustainability by optimizing resource efficiency and long-term environmental impact, with heat-insulating concrete prioritizing energy savings and air-entrained concrete focusing on structural longevity.
Recommendations for Sidewalk Applications
Heat-insulating concrete is recommended for sidewalks in regions with extreme temperature variations due to its superior thermal resistance, reducing freeze-thaw damage and energy transfer to underlying soil. Air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that relieve internal pressure but may have lower thermal insulation compared to heat-insulating concrete. For sidewalks exposed to harsh climates, combining air entrainment with heat-insulating additives offers enhanced durability and comfort, optimizing performance in cold environments.
Infographic: Heat-insulating concrete vs Air-entrained concrete for Sidewalk
 azmater.com
azmater.com