Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide to actively degrade pollutants and improve air quality, making it ideal for sustainable facades. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior strength, durability, and aesthetic versatility, ensuring long-lasting and resilient facade applications.
Table of Comparison
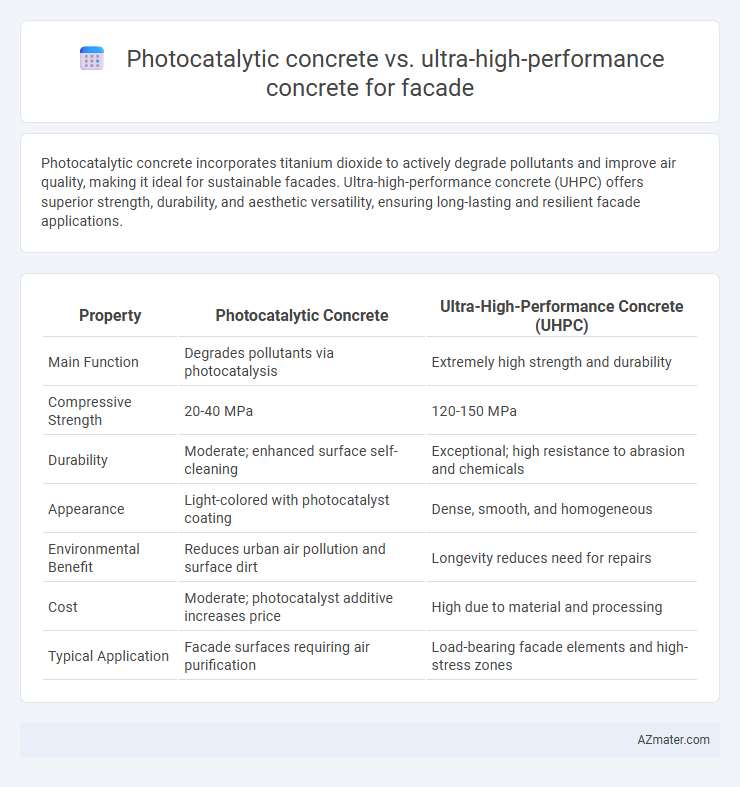
| Property | Photocatalytic Concrete | Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Degrades pollutants via photocatalysis | Extremely high strength and durability |
| Compressive Strength | 20-40 MPa | 120-150 MPa |
| Durability | Moderate; enhanced surface self-cleaning | Exceptional; high resistance to abrasion and chemicals |
| Appearance | Light-colored with photocatalyst coating | Dense, smooth, and homogeneous |
| Environmental Benefit | Reduces urban air pollution and surface dirt | Longevity reduces need for repairs |
| Cost | Moderate; photocatalyst additive increases price | High due to material and processing |
| Typical Application | Facade surfaces requiring air purification | Load-bearing facade elements and high-stress zones |
Introduction to Photocatalytic and Ultra-High-Performance Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete utilizes titanium dioxide additives to break down airborne pollutants and organic materials when exposed to sunlight, promoting self-cleaning and air-purifying facades. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) is characterized by its exceptional strength, durability, and low permeability due to a dense microstructure achieved through optimized particle packing and fiber reinforcement. Both materials offer innovative solutions for facade design, with photocatalytic concrete enhancing environmental quality and UHPC providing superior structural performance.
Defining Facade Requirements: Durability and Aesthetics
Photocatalytic concrete offers enhanced self-cleaning properties and pollution reduction, making it ideal for maintaining facade aesthetics over time in urban environments. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) provides superior durability, resistance to environmental stressors, and structural strength, ensuring long-term facade integrity under harsh conditions. Selecting between these materials depends on balancing aesthetic maintenance through photocatalysis and the mechanical resilience provided by UHPC to meet specific facade performance requirements.
Photocatalytic Concrete: Principles and Advantages
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles that activate under UV light to break down pollutants, leading to self-cleaning and air-purifying facades. This innovative material reduces airborne nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), improving urban air quality while maintaining durability and aesthetic appeal. In contrast to ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), photocatalytic concrete offers environmental benefits by mitigating pollution and reducing maintenance costs for building exteriors.
Ultra-High-Performance Concrete: Features and Benefits
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) features a dense microstructure and exceptional strength, achieving compressive strengths exceeding 150 MPa, making it ideal for durable facade applications. Its superior durability and low permeability enhance resistance to environmental degradation and reduce maintenance costs over time. UHPC also offers design flexibility with slender profiles and improved aesthetic options, supporting innovative architectural expressions while ensuring longevity.
Environmental Impact: Air Purification vs Resource Efficiency
Photocatalytic concrete enhances urban air quality by breaking down pollutants through its titanium dioxide coating, offering significant air purification benefits on building facades. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) focuses on resource efficiency by utilizing optimized material compositions that reduce cement content and increase durability, leading to lower lifecycle carbon emissions. While photocatalytic concrete actively mitigates atmospheric pollution, UHPC minimizes environmental impact through extended service life and reduced material consumption.
Mechanical Strength Comparison for Facade Use
Photocatalytic concrete exhibits good compressive strength typically ranging from 30 to 50 MPa, making it suitable for facade applications requiring moderate mechanical durability with added self-cleaning and air-purification functions. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers exceptional mechanical strength, often exceeding 150 MPa in compressive strength and superior tensile strength due to its dense microstructure and fiber reinforcement, ideal for load-bearing facade elements subjected to high stresses. For facade use, UHPC provides significantly enhanced mechanical performance compared to photocatalytic concrete, enabling slimmer profiles and longer spans, while photocatalytic concrete contributes environmental benefits without compromising standard structural requirements.
Maintenance and Longevity in Urban Environments
Photocatalytic concrete offers self-cleaning properties by breaking down pollutants, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and preserving facade aesthetics in urban environments. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) prioritizes exceptional strength and durability, offering enhanced resistance to weathering and mechanical stress, thus extending facade longevity. While photocatalytic concrete reduces cleaning costs, UHPC minimizes structural repairs, making them complementary solutions depending on maintenance strategies and environmental challenges.
Cost Analysis and Implementation Challenges
Photocatalytic concrete, incorporating titanium dioxide for pollution reduction, generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials and maintenance requirements compared to ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), known for its superior strength and durability but often at a premium price. Implementation challenges for photocatalytic concrete include ensuring long-term photocatalytic activity and environmental conditions influence effectiveness, whereas UHPC demands advanced mixing, placement techniques, and skilled labor to manage shrinkage and curing. Cost analysis reveals photocatalytic concrete may offer environmental value offsetting maintenance expenses, while UHPC's upfront investment is balanced by extended lifespan and reduced structural thickness, requiring a detailed life-cycle cost evaluation for facade applications.
Architectural and Design Flexibility
Photocatalytic concrete offers superior surface self-cleaning and pollution reduction, making it ideal for visually dynamic facades with sustainable design goals. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) provides exceptional strength and durability, allowing for slender, intricate architectural forms and large-span elements without bulky supports. The combination of aesthetic versatility and functional innovation in UHPC supports complex geometries, while photocatalytic concrete enhances facade longevity through environmental resilience.
Choosing the Right Concrete Technology for Facades
Photocatalytic concrete enhances facade durability by actively reducing air pollutants and maintaining surface cleanliness through titanium dioxide additives, making it ideal for urban environments with high pollution levels. Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers exceptional strength, durability, and design flexibility, suitable for facades requiring minimal maintenance and superior structural performance under extreme weather conditions. Selecting the right concrete technology depends on environmental considerations, structural demands, and aesthetic goals, with photocatalytic concrete prioritizing self-cleaning and air purification while UHPC emphasizes mechanical properties and longevity.
Infographic: Photocatalytic concrete vs Ultra-high-performance concrete for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com