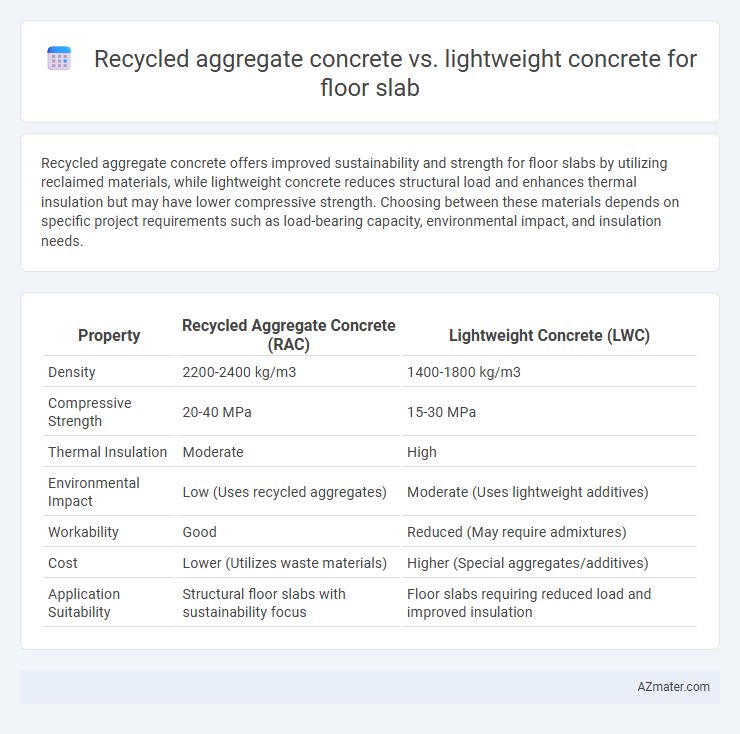
Recycled aggregate concrete offers improved sustainability and strength for floor slabs by utilizing reclaimed materials, while lightweight concrete reduces structural load and enhances thermal insulation but may have lower compressive strength. Choosing between these materials depends on specific project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental impact, and insulation needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) | Lightweight Concrete (LWC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2200-2400 kg/m3 | 1400-1800 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 20-40 MPa | 15-30 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Environmental Impact | Low (Uses recycled aggregates) | Moderate (Uses lightweight additives) |
| Workability | Good | Reduced (May require admixtures) |
| Cost | Lower (Utilizes waste materials) | Higher (Special aggregates/additives) |
| Application Suitability | Structural floor slabs with sustainability focus | Floor slabs requiring reduced load and improved insulation |
Introduction to Floor Slab Construction Materials
Recycled aggregate concrete utilizes crushed concrete and masonry waste, offering sustainable benefits and reduced environmental impact in floor slab construction. Lightweight concrete incorporates materials such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, significantly reducing the slab's weight and improving thermal insulation. Both materials influence structural performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness, requiring careful selection based on project-specific load-bearing and thermal requirements.
What is Recycled Aggregate Concrete?
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) is a sustainable building material made by replacing natural aggregates with crushed concrete debris from demolished structures, reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. It offers comparable compressive strength and durability to traditional concrete, making it suitable for floor slabs that require moderate load-bearing capacity. RAC provides cost-effective solutions for construction projects by utilizing recycled materials while maintaining structural performance.
What is Lightweight Concrete?
Lightweight concrete is a type of concrete composed of lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, resulting in a lower density compared to conventional concrete. It provides excellent thermal insulation, reduced dead load, and improved fire resistance, making it ideal for floor slabs in multi-story buildings or structures requiring weight reduction. Its lower density also enhances ease of handling and reduces structural demands, distinguishing it from recycled aggregate concrete, which primarily focuses on sustainability through reusing demolished concrete materials.
Material Properties Comparison
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) exhibits higher density and compressive strength compared to lightweight concrete, making it more suitable for load-bearing floor slabs requiring durability and mechanical performance. Lightweight concrete, incorporating materials such as expanded clay or pumice, offers superior thermal insulation and reduced dead load but presents lower strength and higher shrinkage tendencies. Material selection for floor slabs should balance strength requirements against thermal and weight considerations, with RAC preferred for structural robustness and lightweight concrete favored for energy efficiency.
Structural Performance Differences
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) typically exhibits higher density and compressive strength compared to lightweight concrete, contributing to enhanced load-bearing capacity for floor slabs. Lightweight concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced dead load but generally has lower modulus of elasticity and tensile strength, impacting slab deflection and crack resistance. Structural performance differences highlight RAC's suitability for high-strength requirements, while lightweight concrete is preferred for applications prioritizing weight reduction and energy efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) significantly reduces environmental impact by repurposing construction waste, decreasing landfill use, and lowering natural resource extraction compared to traditional aggregates. Lightweight concrete offers energy savings by improving thermal insulation, leading to reduced building energy consumption and associated carbon emissions over the slab's lifecycle. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction, with RAC emphasizing circular economy benefits and lightweight concrete enhancing building energy efficiency.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Recycled aggregate concrete typically offers cost savings due to lower material prices and reduced disposal fees, making it economically favorable for sustainable floor slab construction. Lightweight concrete, while more expensive upfront, can reduce structural loads and foundation costs, leading to long-term financial benefits in certain projects. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including material, labor, and lifecycle impacts, is crucial for determining the most cost-effective option for floor slabs.
Workability and Construction Techniques
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) for floor slabs offers improved sustainability by using crushed concrete waste but may present challenges in workability due to angular and porous aggregates, requiring adjustments in mix design such as increased water content or admixtures for proper flow. Lightweight concrete, often incorporating expanded clay or shale, enhances workability with reduced density and improved thermal insulation, facilitating easier handling and faster placement using conventional construction techniques like pumping or screeding. Construction methods for RAC demand careful quality control to manage moisture absorption and consistency, whereas lightweight concrete benefits from its reduced weight to minimize formwork pressure and accelerate curing time.
Durability and Maintenance Factors
Recycled aggregate concrete offers enhanced durability for floor slabs by utilizing crushed concrete waste that improves resistance to freeze-thaw cycles and reduces permeability, leading to lower maintenance requirements. Lightweight concrete, composed of expanded aggregates such as perlite or vermiculite, provides superior thermal insulation and reduced structural load but may require more frequent surface repairs due to lower abrasion resistance. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing durability needs with long-term maintenance costs, where recycled aggregate concrete generally outperforms in mechanical strength and longevity.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Concrete
Recycled aggregate concrete offers enhanced sustainability and strength, making it suitable for floor slabs in commercial and industrial buildings where load-bearing capacity is critical. Lightweight concrete provides superior thermal insulation and reduced self-weight, ideal for residential structures requiring energy efficiency and easier handling. Selecting the right concrete depends on project-specific demands such as structural load, thermal performance, and environmental impact.
Infographic: Recycled aggregate concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com