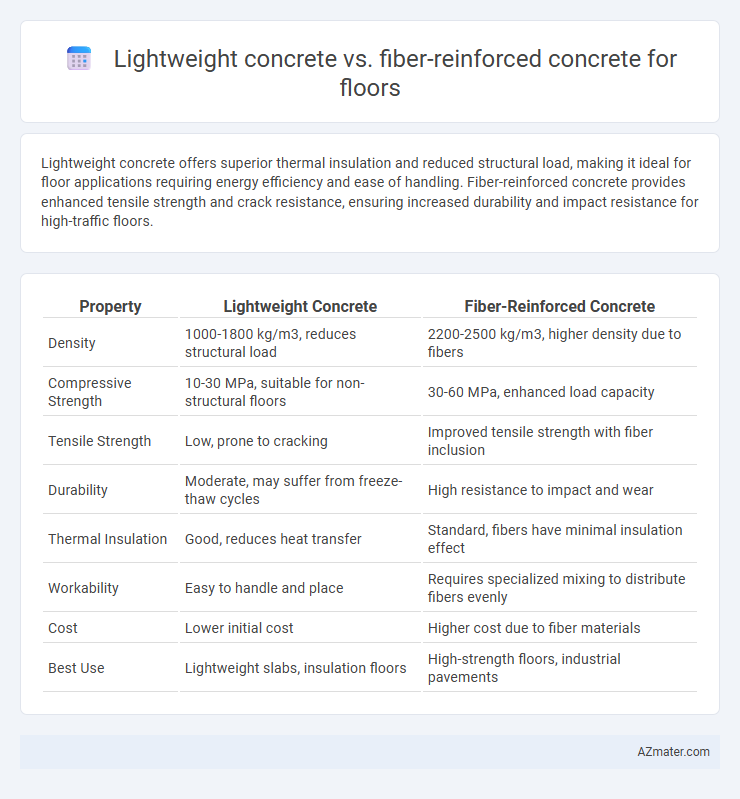
Lightweight concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced structural load, making it ideal for floor applications requiring energy efficiency and ease of handling. Fiber-reinforced concrete provides enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, ensuring increased durability and impact resistance for high-traffic floors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lightweight Concrete | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1000-1800 kg/m3, reduces structural load | 2200-2500 kg/m3, higher density due to fibers |
| Compressive Strength | 10-30 MPa, suitable for non-structural floors | 30-60 MPa, enhanced load capacity |
| Tensile Strength | Low, prone to cracking | Improved tensile strength with fiber inclusion |
| Durability | Moderate, may suffer from freeze-thaw cycles | High resistance to impact and wear |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, reduces heat transfer | Standard, fibers have minimal insulation effect |
| Workability | Easy to handle and place | Requires specialized mixing to distribute fibers evenly |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to fiber materials |
| Best Use | Lightweight slabs, insulation floors | High-strength floors, industrial pavements |
Introduction to Lightweight Concrete and Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Lightweight concrete, characterized by its reduced density due to the use of lightweight aggregates, offers enhanced thermal insulation and ease of handling for flooring applications. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates various fibers such as steel, glass, or synthetic materials to improve tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability of floors under dynamic or heavy loading. Choosing between lightweight and fiber-reinforced concrete depends on specific structural requirements, including load-bearing capacity and environmental conditions.
Composition and Materials Used
Lightweight concrete for floors is primarily composed of lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, pumice, or perlite, which reduce the overall density while maintaining adequate strength for load-bearing applications. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates various fibers like steel, glass, polypropylene, or synthetic fibers within a traditional concrete matrix to enhance tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability. The composition of fiber-reinforced concrete is engineered to optimize mechanical performance, whereas lightweight concrete focuses on reducing weight and thermal conductivity through the selection of porous aggregates.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Lightweight concrete offers reduced density and improved thermal insulation but generally exhibits lower compressive strength and brittleness compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, which benefits from enhanced tensile strength, toughness, and crack resistance due to the integration of fibers such as steel, glass, or synthetic materials. Fiber-reinforced concrete demonstrates superior flexural strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for floor applications subjected to dynamic loads and heavy traffic. Mechanical properties like modulus of elasticity and durability are significantly improved in fiber-reinforced mixtures, whereas lightweight concrete prioritizes weight reduction over mechanical performance.
Weight and Load-Bearing Capacity
Lightweight concrete offers reduced weight, making it ideal for floor applications where minimizing dead load is critical while still providing adequate compressive strength. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances load-bearing capacity by improving tensile strength and crack resistance, which increases durability under dynamic and heavy loads. For floors requiring both low weight and superior toughness, a hybrid approach combining lightweight aggregate with fiber reinforcement can optimize structural performance.
Flexural and Tensile Strength Differences
Lightweight concrete typically exhibits lower flexural and tensile strength compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, making it less suitable for applications demanding high structural performance on floors. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength by incorporating synthetic or steel fibers, which improve crack resistance and overall durability under bending stresses. The improved flexural capacity of fiber-reinforced concrete contributes to longer service life and reduced maintenance in floor systems subjected to dynamic or heavy loads.
Installation Techniques and Workability
Lightweight concrete offers easier handling and reduced labor costs during floor installation due to its lower density and improved slump, facilitating faster placement and finishing. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances workability by reducing segregation and bleeding, allowing for more uniform distribution across the slab, which improves durability and crack resistance without the need for additional reinforcement. Installation of fiber-reinforced concrete floors often requires less mechanical compaction, accelerating the curing process and minimizing labor intensity compared to traditional mixes.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Lightweight concrete provides superior thermal insulation due to its low density and entrapped air pockets, reducing heat transfer in flooring applications. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances acoustic insulation by damping vibrations and improving impact resistance, which decreases sound transmission through floors. Combining lightweight aggregates with fiber reinforcement offers an optimal balance of thermal and acoustic performance, making it ideal for energy-efficient and noise-sensitive floor constructions.
Durability and Crack Resistance
Lightweight concrete offers improved thermal insulation and reduced structural load but generally exhibits lower durability and higher susceptibility to cracking under stress compared to fiber-reinforced concrete. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates synthetic or steel fibers that significantly enhance crack resistance and overall durability, making it ideal for high-traffic floors requiring long-term performance. Studies indicate fiber-reinforced concrete can reduce crack width by up to 70%, extending floor lifespan and minimizing maintenance costs in industrial and commercial applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Lightweight concrete reduces structural load, lowering foundation costs and providing better insulation, which can decrease energy expenses over time. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances durability and crack resistance, potentially reducing maintenance and repair costs, but typically requires higher initial material investment. Economic considerations favor lightweight concrete for budget-sensitive projects, while fiber-reinforced concrete offers long-term cost savings in high-stress floor applications.
Best Applications for Floors
Lightweight concrete is ideal for floor applications requiring reduced structural load and enhanced thermal insulation, such as multi-story buildings and parking decks. Fiber-reinforced concrete excels in floors subjected to heavy impact, abrasion, and shrinkage cracking, including industrial warehouses and sports facilities. Selecting between the two depends on balancing load requirements, durability needs, and specific floor performance criteria.
Infographic: Lightweight concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Floor
 azmater.com
azmater.com