Geo-polymer concrete offers superior durability and environmental benefits due to its low carbon footprint, while lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and reduced structural load for wall construction. Choosing between them depends on project requirements for sustainability and insulation performance.
Table of Comparison
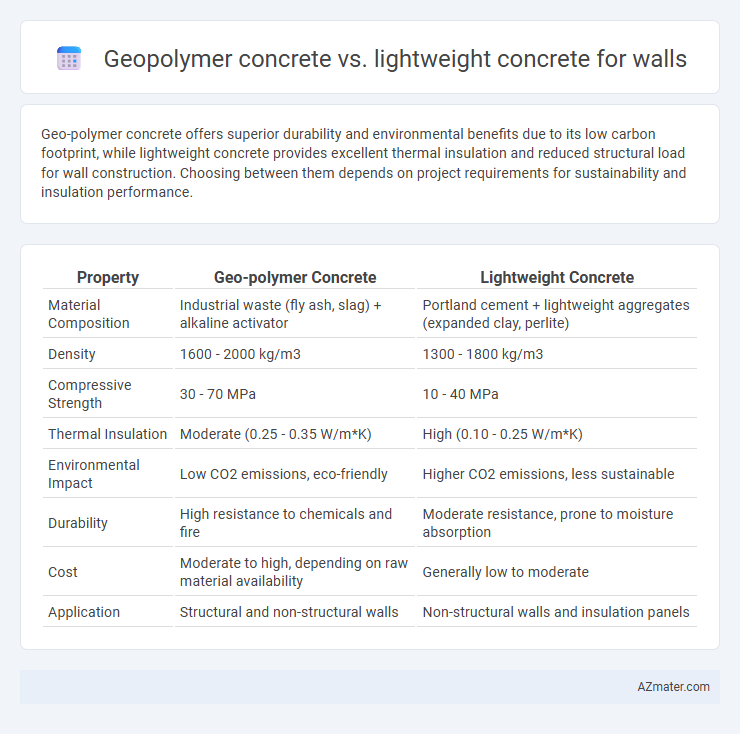
| Property | Geo-polymer Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Industrial waste (fly ash, slag) + alkaline activator | Portland cement + lightweight aggregates (expanded clay, perlite) |
| Density | 1600 - 2000 kg/m3 | 1300 - 1800 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 30 - 70 MPa | 10 - 40 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate (0.25 - 0.35 W/m*K) | High (0.10 - 0.25 W/m*K) |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 emissions, eco-friendly | Higher CO2 emissions, less sustainable |
| Durability | High resistance to chemicals and fire | Moderate resistance, prone to moisture absorption |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on raw material availability | Generally low to moderate |
| Application | Structural and non-structural walls | Non-structural walls and insulation panels |
Introduction to Geo-Polymer Concrete and Lightweight Concrete
Geo-polymer concrete is an innovative construction material composed of industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, offering high durability, low carbon footprint, and superior resistance to chemicals and heat. Lightweight concrete is formulated with lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, resulting in reduced density, improved thermal insulation, and ease of handling. Both materials present environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional concrete, with geo-polymer concrete emphasizing sustainability and mechanical strength, while lightweight concrete prioritizes weight reduction and energy efficiency in wall applications.
Composition and Material Differences
Geo-polymer concrete utilizes industrial by-products like fly ash or slag combined with alkaline activators, forming a cementitious binder without traditional Portland cement. Lightweight concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, significantly reducing density while maintaining structural integrity. The primary material difference lies in geo-polymer concrete's reliance on chemical activation of aluminosilicate materials versus lightweight concrete's physical reduction of weight through porous aggregates.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Geopolymer concrete exhibits higher compressive strength and superior durability compared to lightweight concrete, making it more suitable for load-bearing wall applications. The mechanical properties of geopolymer concrete, including enhanced tensile strength and resistance to chemical attack, surpass those of lightweight concrete, which typically offers lower density but reduced structural capacity. Lightweight concrete is advantageous for insulation and reducing dead load, but geopolymer concrete provides a stronger and more durable alternative for structural wall components.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior thermal insulation properties due to its dense matrix and reduced thermal conductivity, outperforming traditional lightweight concrete in minimizing heat transfer through walls. This enhanced insulation capacity contributes to significant energy savings by lowering the demand for heating and cooling systems in buildings. In contrast, lightweight concrete, while providing some insulation benefits due to its low density, typically falls short in energy efficiency compared to geo-polymer alternatives designed for optimal thermal performance.
Structural Performance in Wall Applications
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior structural performance in wall applications due to its enhanced compressive strength, durability, and resistance to chemical attacks compared to lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete offers advantages in reducing the overall weight of the structure and improving thermal insulation but typically has lower load-bearing capacity and strength. For load-bearing walls and infrastructure requiring high durability, geo-polymer concrete provides a more robust and longer-lasting solution.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geo-polymer concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional Portland cement-based lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete, while offering excellent thermal insulation and reduced material usage, often relies on aggregates that may not be environmentally friendly or recycled. The sustainable advantage of geo-polymer concrete lies in its lower embodied energy and ability to enhance wall durability, contributing to longer lifecycle performance and reduced environmental footprint.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Geopolymer concrete typically offers cost benefits by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash, reducing reliance on expensive Portland cement and lowering overall material expenses. Lightweight concrete has higher costs due to specialized aggregates and admixtures required for reduced density, often increasing production and transportation expenses. Economically, geopolymer concrete can achieve comparable strength and durability at a lower life-cycle cost, making it a more sustainable option for wall construction in budget-sensitive projects.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior durability compared to lightweight concrete, offering enhanced resistance to chemical attacks, high temperatures, and environmental degradation. Maintenance requirements for geo-polymer concrete walls are minimal due to their reduced permeability and increased resistance to cracking and corrosion. Lightweight concrete walls may require more frequent upkeep to address issues such as surface wear, moisture absorption, and potential structural weaknesses over time.
Installation and Construction Techniques
Geopolymer concrete offers faster installation due to its rapid setting time and excellent workability, reducing overall construction duration for wall applications. Lightweight concrete requires specialized formwork and handling techniques to accommodate its lower density and higher porosity, ensuring structural integrity and thermal efficiency in walls. Both materials demand precise mixing and curing protocols, but geopolymer concrete provides greater resistance to shrinkage and cracking during installation.
Suitability for Different Wall Types and Uses
Geo-polymer concrete offers superior fire resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for industrial and high-temperature wall applications, while its high compressive strength suits load-bearing walls. Lightweight concrete, characterized by excellent thermal insulation and reduced dead load, is preferred for partition walls and structures requiring enhanced energy efficiency. Both materials cater to specific demands: geo-polymer concrete excels in heavy-duty, sustainable construction, whereas lightweight concrete optimizes thermal performance and ease of handling in residential and commercial walls.
Infographic: Geo-polymer concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com