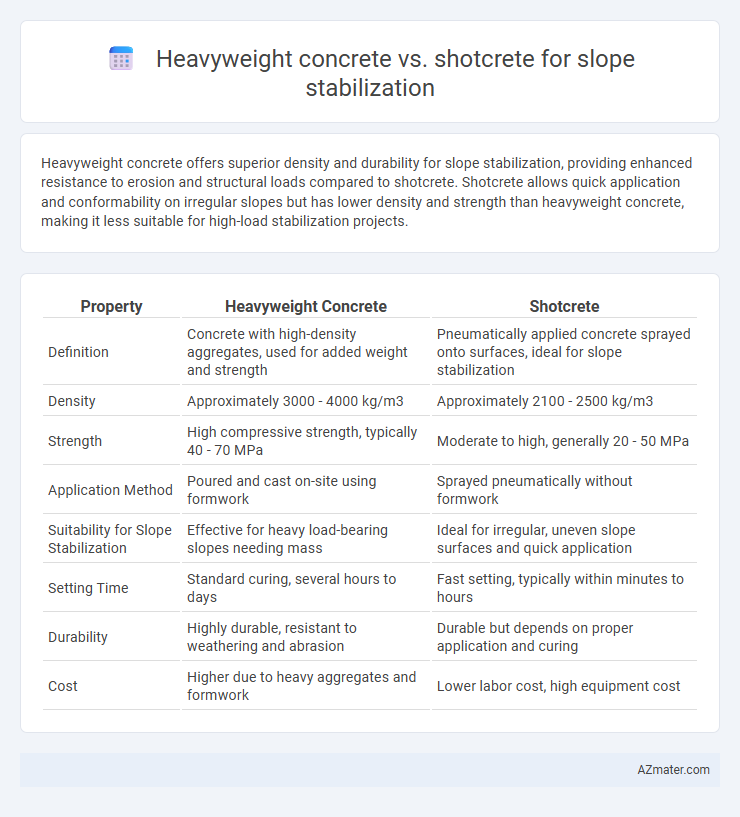
Heavyweight concrete offers superior density and durability for slope stabilization, providing enhanced resistance to erosion and structural loads compared to shotcrete. Shotcrete allows quick application and conformability on irregular slopes but has lower density and strength than heavyweight concrete, making it less suitable for high-load stabilization projects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Heavyweight Concrete | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete with high-density aggregates, used for added weight and strength | Pneumatically applied concrete sprayed onto surfaces, ideal for slope stabilization |
| Density | Approximately 3000 - 4000 kg/m3 | Approximately 2100 - 2500 kg/m3 |
| Strength | High compressive strength, typically 40 - 70 MPa | Moderate to high, generally 20 - 50 MPa |
| Application Method | Poured and cast on-site using formwork | Sprayed pneumatically without formwork |
| Suitability for Slope Stabilization | Effective for heavy load-bearing slopes needing mass | Ideal for irregular, uneven slope surfaces and quick application |
| Setting Time | Standard curing, several hours to days | Fast setting, typically within minutes to hours |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to weathering and abrasion | Durable but depends on proper application and curing |
| Cost | Higher due to heavy aggregates and formwork | Lower labor cost, high equipment cost |
Introduction to Slope Stabilization Techniques
Slope stabilization techniques are essential to prevent soil erosion, landslides, and structural failures, with Heavyweight concrete and shotcrete being prominent materials used for reinforcement. Heavyweight concrete offers exceptional compressive strength and density, making it ideal for counteracting large earth pressures in steep or high-risk slopes. Shotcrete provides versatile application with rapid setting times and excellent adhesion, allowing effective stabilization on irregular and hard-to-reach surfaces.
What is Heavyweight Concrete?
Heavyweight concrete is a specialized concrete mixture incorporating heavy aggregates such as magnetite, hematite, or barite to achieve densities typically above 3000 kg/m3, enhancing its mass and radiation shielding properties. It is widely used in slope stabilization to provide increased weight and structural support, counteracting soil movement on unstable slopes. Compared to shotcrete, heavyweight concrete offers greater durability and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for long-term retention and erosion control in challenging geotechnical environments.
Understanding Shotcrete for Slope Protection
Shotcrete, a high-strength sprayed concrete, is widely used for slope stabilization due to its ability to conform to irregular surfaces and provide immediate support, effectively preventing soil erosion and landslides. Its application involves pneumatically projecting a mixture of cement, sand, and aggregate directly onto the slope, enhancing bond strength and reducing voids compared to traditional heavyweight concrete. Shotcrete's rapid setting and adaptability to complex geometries make it a preferred choice for durability and long-term slope protection in civil engineering projects.
Material Properties: Heavyweight Concrete vs Shotcrete
Heavyweight concrete contains dense aggregates like barite or magnetite, providing high density and enhanced shielding properties ideal for slope stabilization in high-radiation areas or heavy load conditions. Shotcrete, composed of a cementitious mixture sprayed pneumatically onto surfaces, offers superior adhesion and quick setting, making it effective for immediate slope surface reinforcement and erosion control. Both materials deliver strong compressive strength, but heavyweight concrete excels in mass and durability, whereas shotcrete provides flexibility and rapid application on irregular slope geometries.
Installation Methods and Equipment Requirements
Heavyweight concrete requires conventional formwork and high-capacity concrete pumps or cranes for placement, making it suitable for large-scale, stable slope reinforcement projects. Shotcrete utilizes pneumatic or robotic spraying equipment that enables rapid application on uneven or complex surfaces without formwork, ideal for immediate slope stabilization and reduced labor costs. Both methods demand skilled operators, but shotcrete's flexibility in equipment and installation facilitates faster, more versatile slope protection in challenging terrain.
Structural Performance and Longevity
Heavyweight concrete offers superior structural performance for slope stabilization due to its high density and compressive strength, enhancing resistance to external forces such as landslides and erosion. Shotcrete, applied pneumatically, provides excellent adhesion and uniform coverage on irregular slope surfaces, promoting immediate stabilization and reducing rebound waste. While heavyweight concrete ensures long-term durability through its robust composition, shotcrete's longevity depends on proper application and curing, often requiring reinforcement for sustained performance in aggressive environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Heavyweight concrete generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized aggregates and mixing processes compared to shotcrete, which offers a faster application and reduced labor expenses. Long-term expenses for heavyweight concrete tend to be lower because of its superior density and durability, minimizing maintenance and repair needs on slopes. Shotcrete may require more frequent inspections and potential reapplications, impacting overall lifecycle costs despite its initial affordability.
Suitability for Various Slope Conditions
Heavyweight concrete offers superior compressive strength and radiation shielding properties, making it ideal for steep or heavily loaded slopes with complex structural requirements. Shotcrete provides excellent adaptability for irregular or curved surfaces, facilitating rapid application on varying slope geometries and preventing erosion or instability. Both materials suit differing slope stabilization needs, with heavyweight concrete preferred for high-load scenarios and shotcrete favored for flexible coverage on variable slope conditions.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Heavyweight concrete offers improved durability and radiation shielding but requires extensive quarrying and higher energy consumption, increasing its carbon footprint in slope stabilization projects. Shotcrete, applied pneumatically, reduces material waste and disturbance to surrounding vegetation, minimizing soil erosion and habitat disruption during slope reinforcement. Environmental Impact Assessment favors shotcrete for its rapid application and lower environmental degradation, despite heavyweight concrete's superior structural performance in critical conditions.
Selecting the Right Solution for Slope Stabilization
Heavyweight concrete offers superior density and strength, making it ideal for high-impact slope stabilization where significant load-bearing capacity is required. Shotcrete provides rapid application and excellent adhesion to irregular surfaces, allowing for efficient stabilization of slopes with complex geometries or difficult access. Selecting the right solution depends on specific project parameters such as load demands, environmental conditions, and application speed, ensuring optimal slope stability and durability.
Infographic: Heavyweight concrete vs Shotcrete for Slope stabilization
 azmater.com
azmater.com